Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2012; 18(45): 6690-6692
Published online Dec 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i45.6690
Published online Dec 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i45.6690
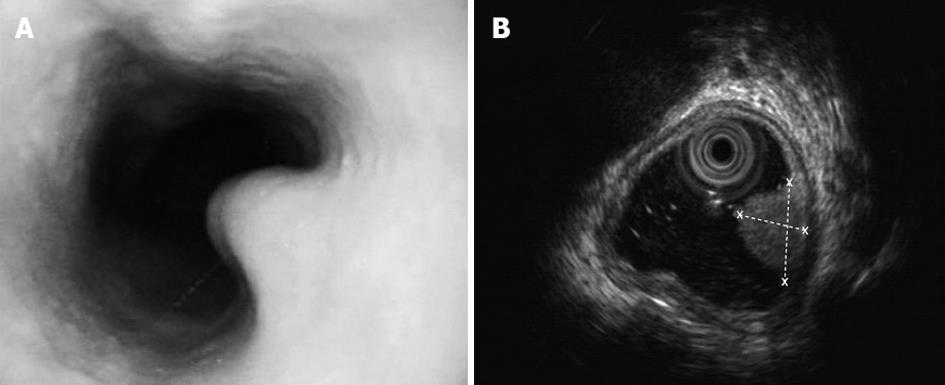
Figure 1 Soft yellow nodules protruding into the esophageal cavity.
A: Gastroscopy presentation: soft yellow nodules protruding into the esophageal cavity; B: Endoscopic ultrasonography: a space-occupying lesion (8.1 mm × 5.1 mm) in the substratum sized 8.1 mm × 5.1 mm (dotted lines).
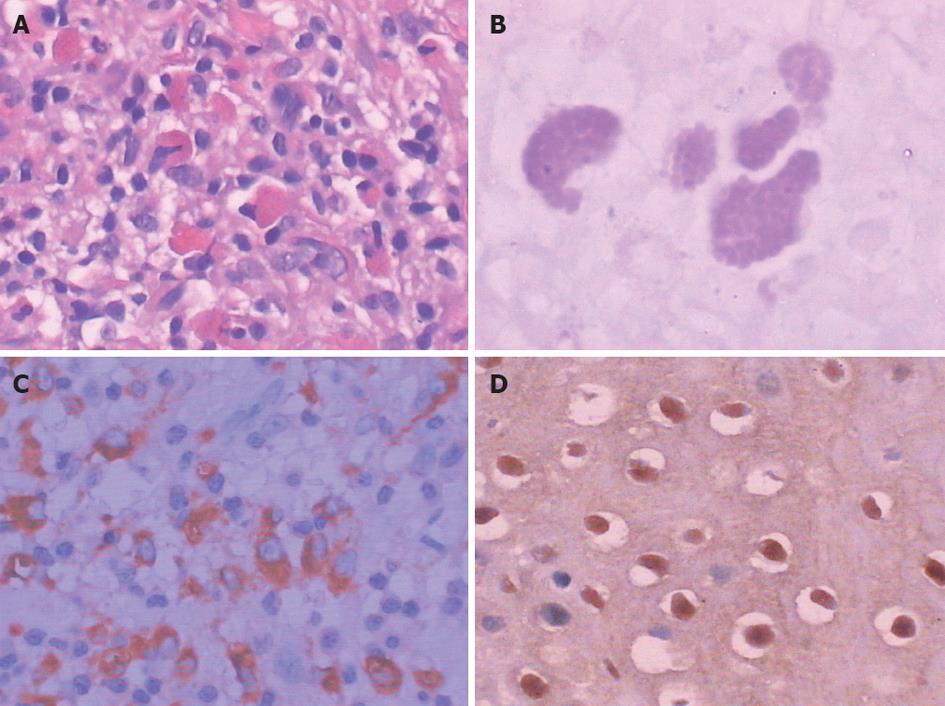
Figure 2 Michaelis-Gutmann bodies.
A: Basophilic laminated inclusions in the cytoplasm (hematoxylin and eosin, ×200); B: Periodic acid-Schiff: targetoid appearance with a dense central core (×400); C: CD68 positivity by immunohistochemistry (×400); D: Esophageal squamous epithelium positive for human papillomavirus by immunohistochemistry, halo-shaped cells (×200).
- Citation: Yang YL, Xie YC, Li XL, Guo J, Sun T, Tang J. Malakoplakia of the esophagus caused by human papillomavirus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(45): 6690-6692
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i45/6690.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i45.6690