Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2012; 18(43): 6189-6196
Published online Nov 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i43.6189
Published online Nov 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i43.6189
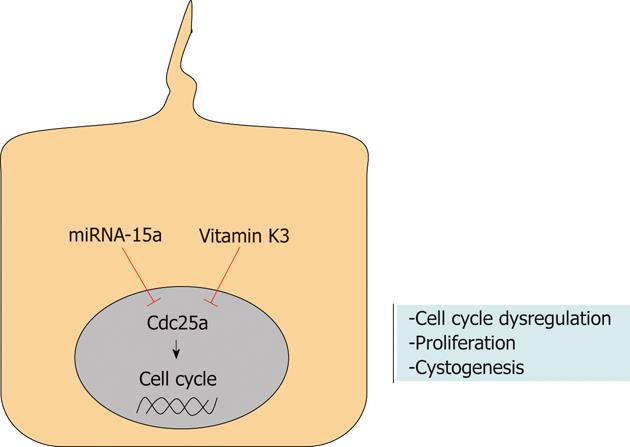
Figure 1 miRNA-15a/Cdc25a interplay participates in hepatic cystogenesis of polycystic liver diseases.
miRNA-15a directly targets the cell cycle regulator Cdc25a. In polycystic rat and human cholangiocytes, miR15a is downregulated, thus resulting in Cdc25a upregulation, cell proliferation and cystogenesis. The Cdc25a inhibitor vitamin K3 was demonstrated to target Cdc25a, blocking the hepatorenal cystogenesis of several rodent models of polycystic kidney and liver disease. This suggests the therapeutic potential of vitamin K3 for polycystic kidney and liver diseases.
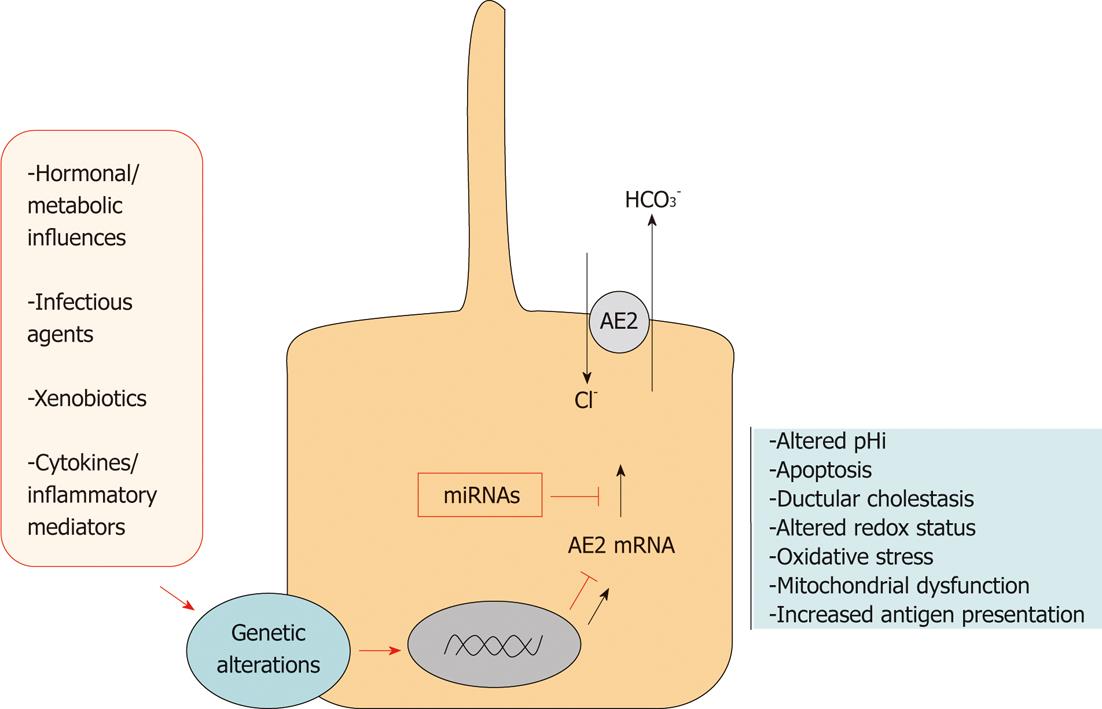
Figure 2 Role of miRNA-506 in the etiopathogenesis of primary biliary cirrhosis.
Different risk factors could induce genetic alterations leading to anion exchange 2 (AE2) downregulation in primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) cholangiocytes. miRNA-506 is overexpressed in PBC cholangiocytes, thus resulting in the inhibition of both AE2 protein translation and subsequent Cl-/HCO3- activity, and impairing the biliary secretory functions.
- Citation: Munoz-Garrido P, Fernandez-Barrena MG, Hijona E, Carracedo M, Marín JJG, Bujanda L, Banales JM. MicroRNAs in biliary diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(43): 6189-6196
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i43/6189.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i43.6189