Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2012; 18(42): 6096-6105
Published online Nov 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6096
Published online Nov 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6096
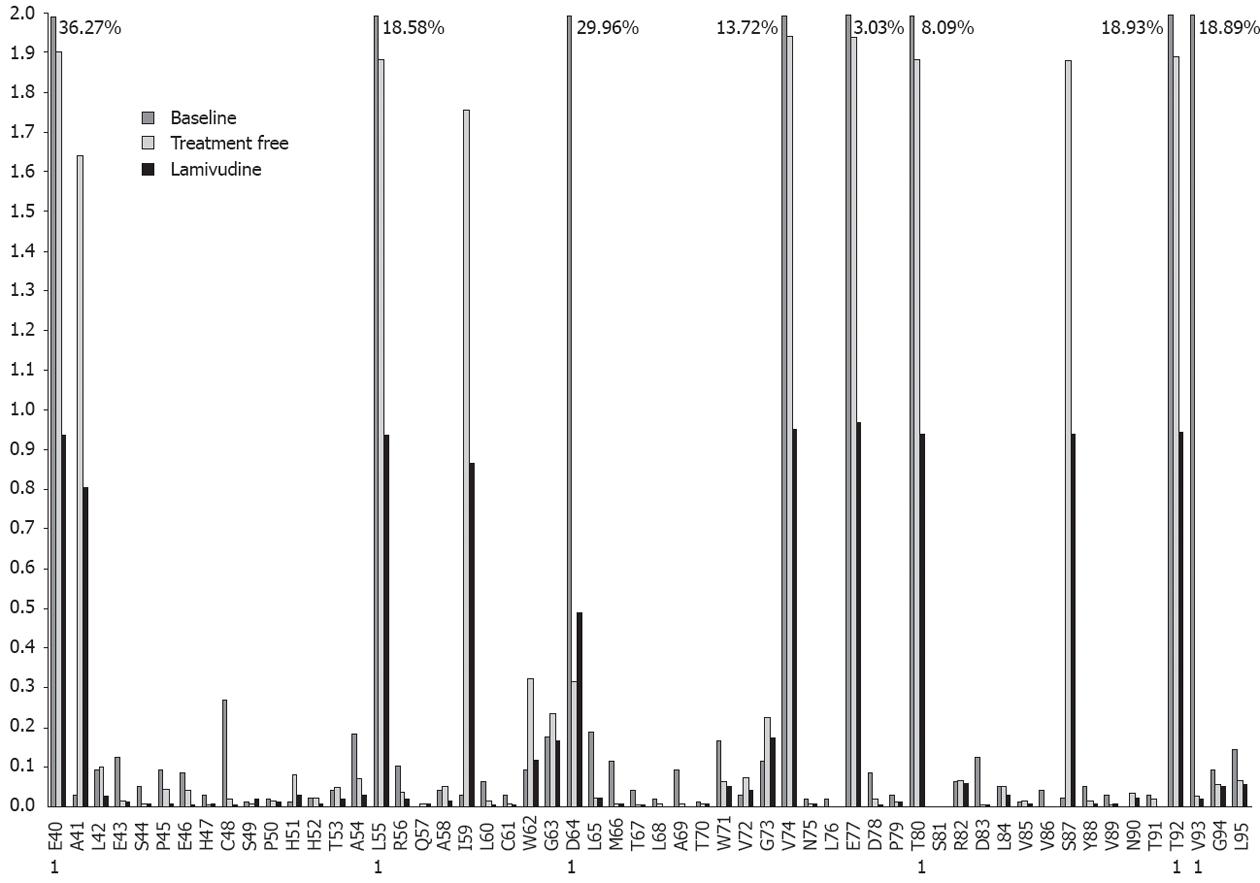
Figure 1 Variability of all codons analyzed from the 3 sequentially studied samples, corresponding to patient 4.
Percentages higher than 2% are indicated at the top of the bars. 1: Master aminoacid different between treatment free and lamivudine samples.
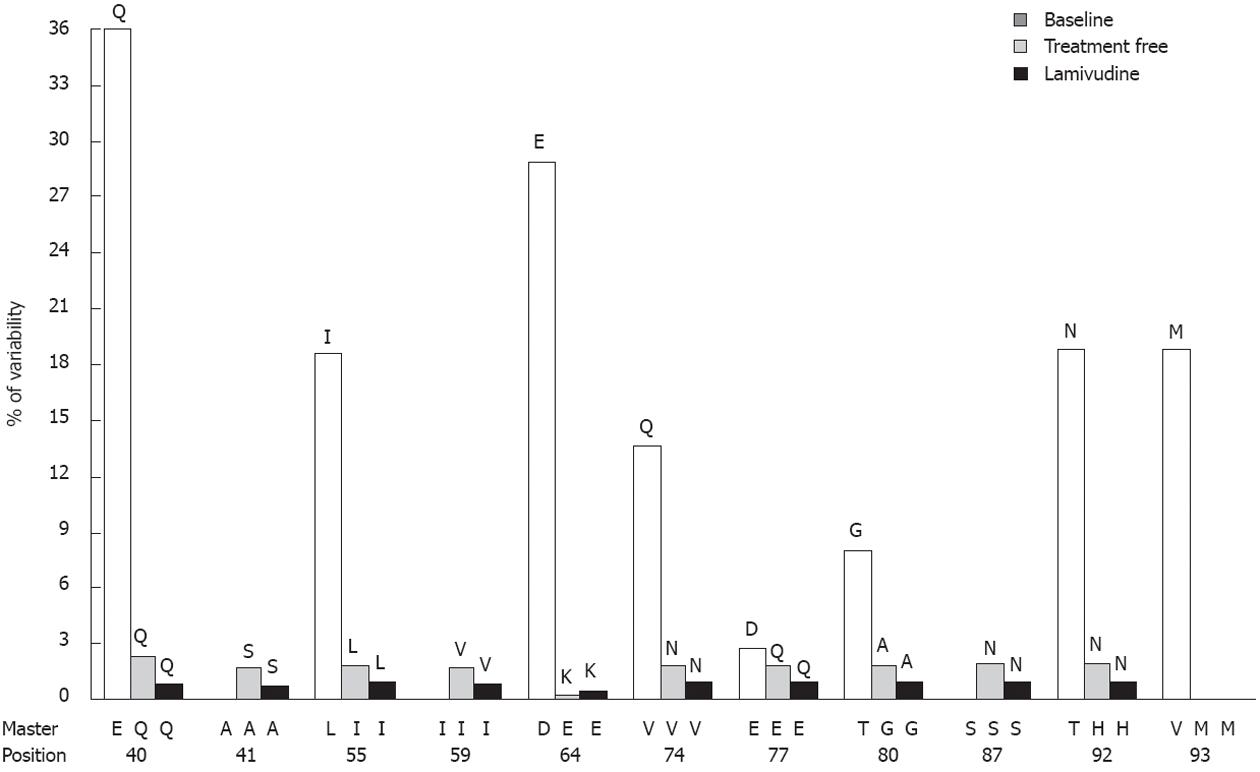
Figure 2 Evolution of the most variable codons of the core region analyzed in the sequentially studied patient.
The variable position and its corresponding master amino acid are shown on the X-axis. The main mutated amino acids are indicated at the top of the bars.
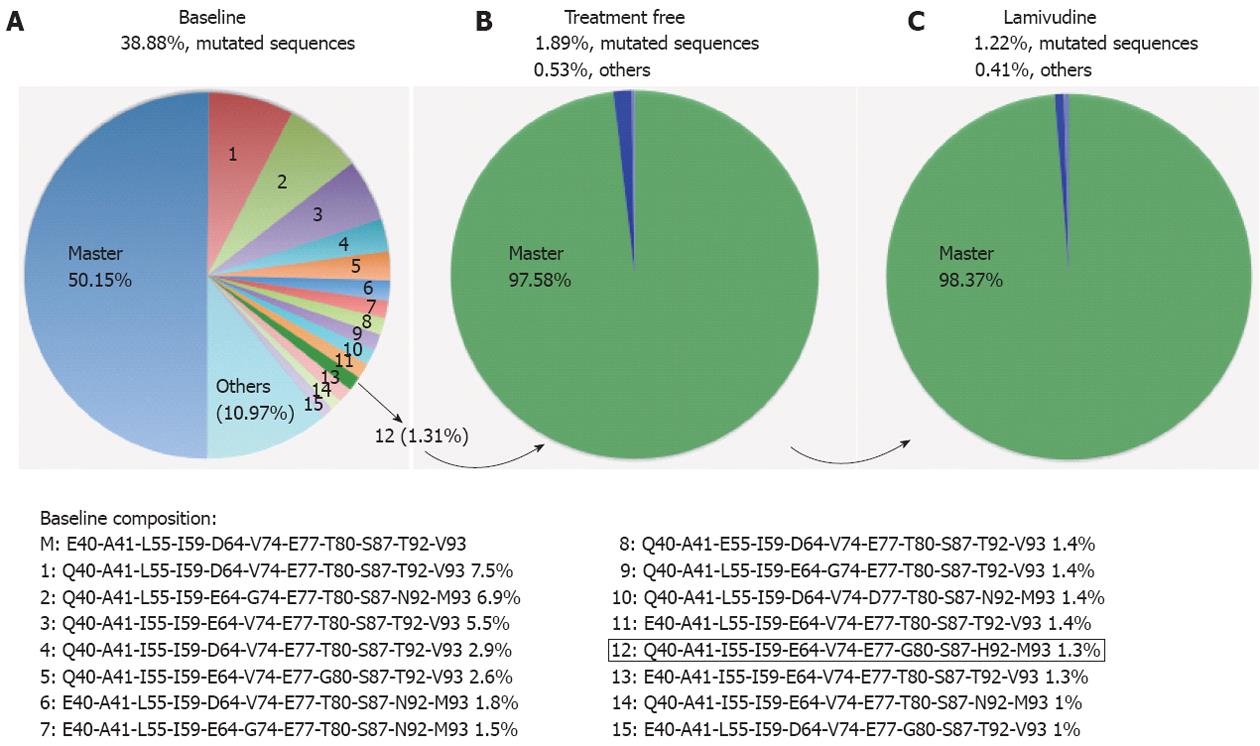
Figure 3 Quasispecies composition of the hepatitis B virus core region in the 3 sequentially analyzed samples.
A: Baseline variants (1-15) in percentages ≥ 1%; B: Treatment-free variability; C: Lamivudine sample variability of the most frequent amino acid substitutions defined in Figure 2. Linkage analysis was also performed attending these most variable codons.
- Citation: Homs M, Buti M, Tabernero D, Quer J, Sanchez A, Corral N, Esteban R, Rodriguez-Frias F. Quasispecies dynamics in main core epitopes of hepatitis B virus by ultra-deep-pyrosequencing. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(42): 6096-6105
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i42/6096.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6096