Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2012; 18(42): 6018-6026
Published online Nov 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6018
Published online Nov 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6018
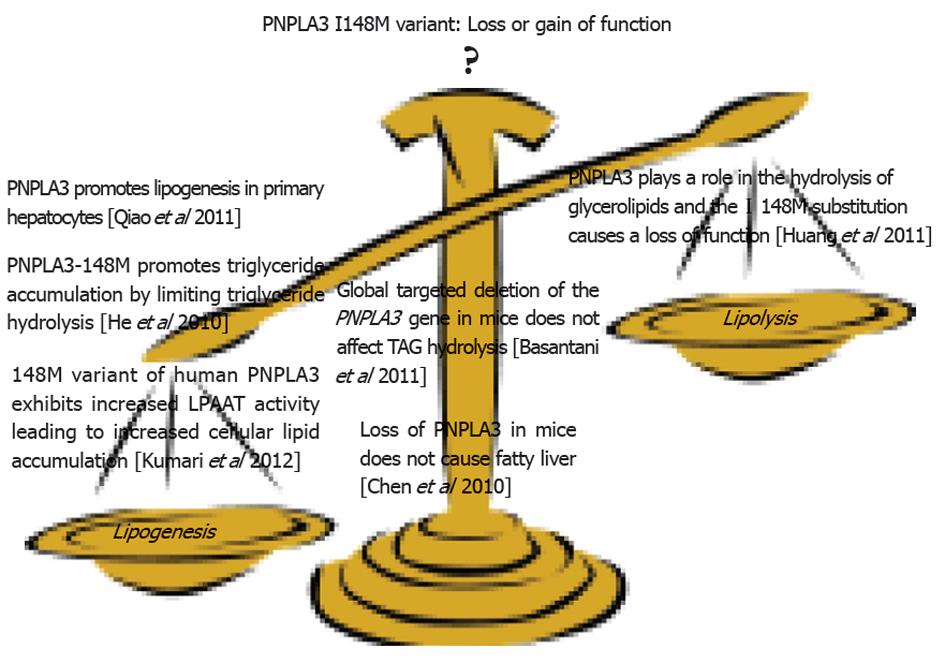
Figure 1 Patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 rs738409 and its role in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Summary of the evidence from human and rodent studies. PNPLA3: Patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3.
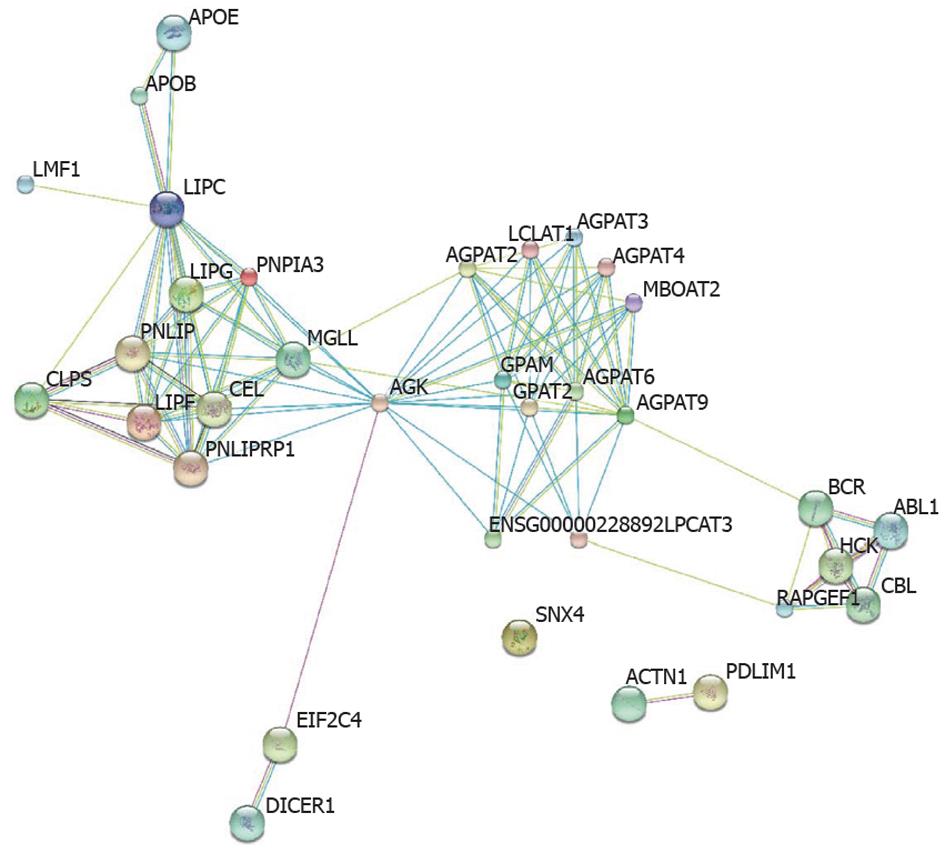
Figure 2 Protein network around patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 by the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins resource (http://string-db.org/). The interactions include direct (physical) and indirect (functional) associations; they are derived from four sources: Genomic Context, High-throughput Experiments, Conserved-Coexpression and Previous Knowledge. PNPLA3: Patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3; LIPF: Lipase, gastric; SNX4: Sorting nexin 4; AGPAT9: 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 9; MGLL: Monoglyceride lipase; GPAM: Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase, mitochondrial; AGPAT3: 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 3; LIPC: Lipase, hepatic; MBOAT2: Membrane-bound O-acyltransferase domain containing 2; LCLAT1: Lysocardiolipin acyltransferase 1; AGPAT4: 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 4; LPCAT3: Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; AGK: Acylglycerol kinase; PNLIPRP1: Pancreatic lipase-related protein 1, GPAT2: Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 2, mitochondrial; PNLIP: Pancreatic lipase; PDLIM1: PDZ and LIM domain 1; AGPAT2: 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 2; CEL: Carboxyl ester lipase; EIF2C4: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2C, 4; HCK: Hemopoietic cell kinase; AGPAT6: 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 6; ENSG00000228892: 1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase.
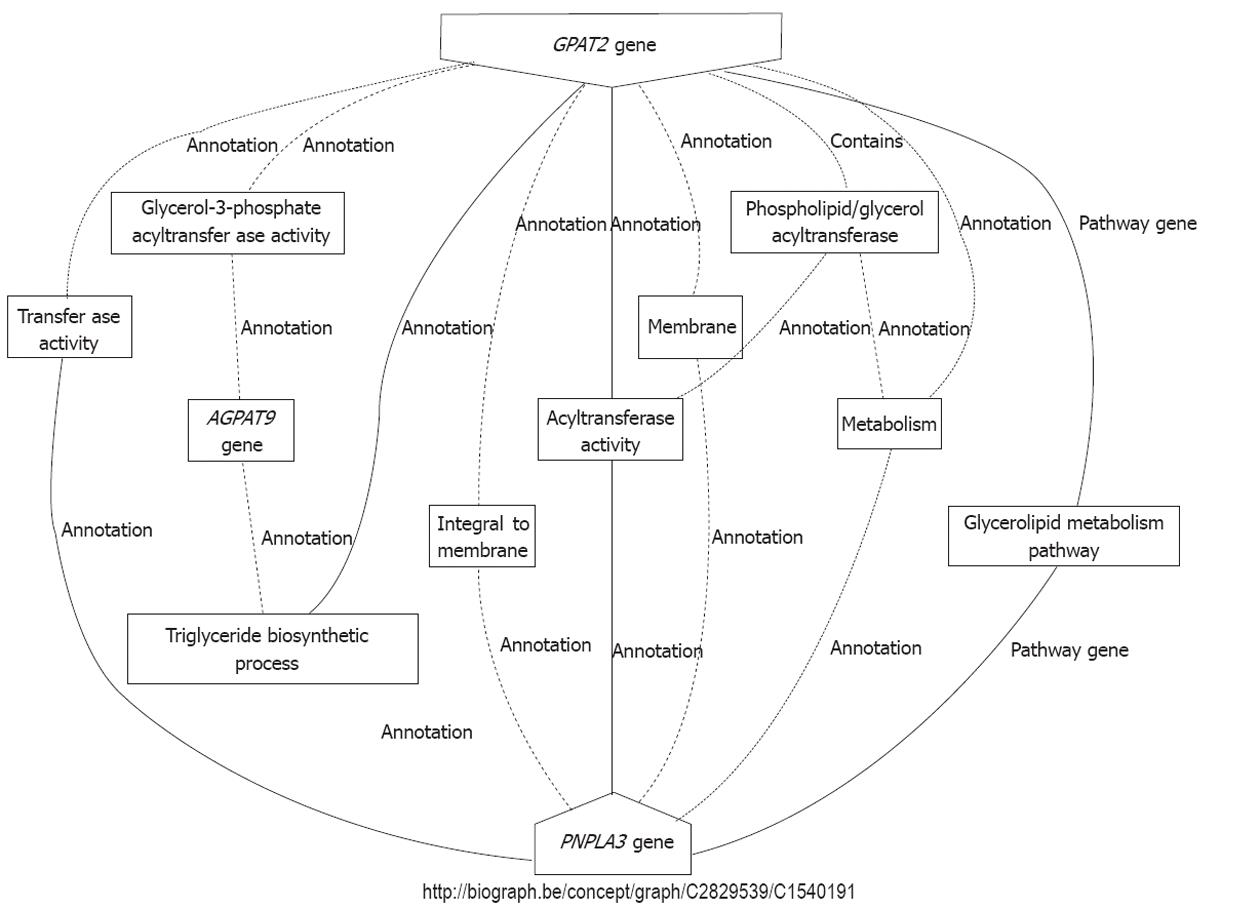
Figure 3 Interaction between patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 and glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 2.
Prediction was performed by the tool BioGraph (http://biograph.be/about/welcome), a data mining framework that allows for the automated formulation of comprehensible functional hypotheses relating a context to targets. PNPLA3: Patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3; GAPT2: Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 2; AGAPT9: Acylglycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase isoform.
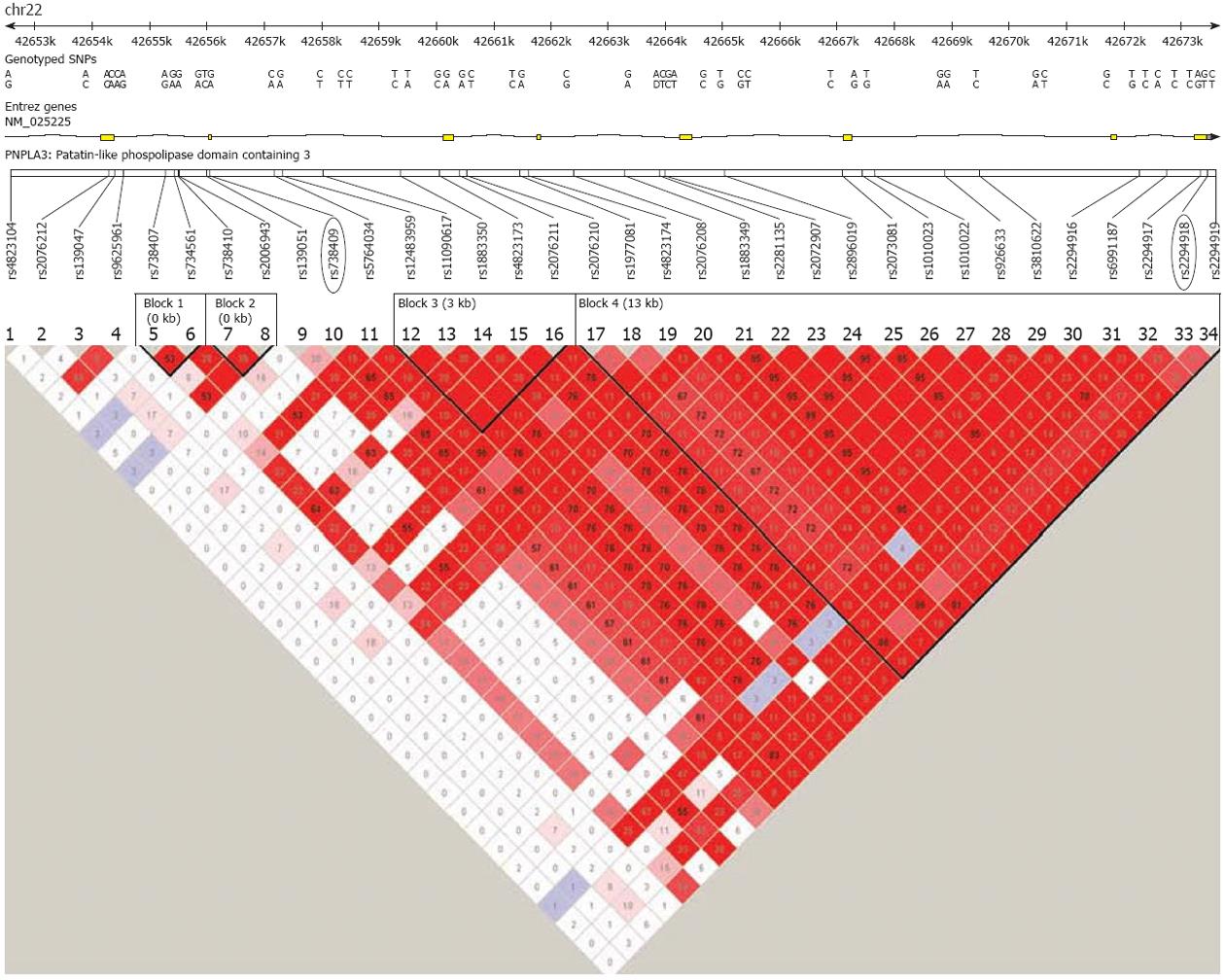
Figure 4 Linkage disequilibrium plot across the patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 gene.
The horizontal white line depicts the DNA segment of chromosome 22q13.31. The rs738409 location is highlighted in a black ellipse. An LD plot is depicted in the bottom part of the figure: each diamond represents the magnitude of LD for a single pair of markers, with colors indicating strong LD (red r2 = 1.0) and no LD (white, rr = 0) as the extremes (different red tones indicate intermediate LD). Numbers inside the diamonds stand for r2 values. Haplotype analysis of PNPLA3 shows that the rs738409 is in moderate LD (no more than r2: 0.65) with other variants. Plot was obtained by the software Haploview 2.0 freely available at http://www.broad.mit.edu/mpg/haploview/. LD: Linkage disequilibrium; PNPLA3: Patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3.
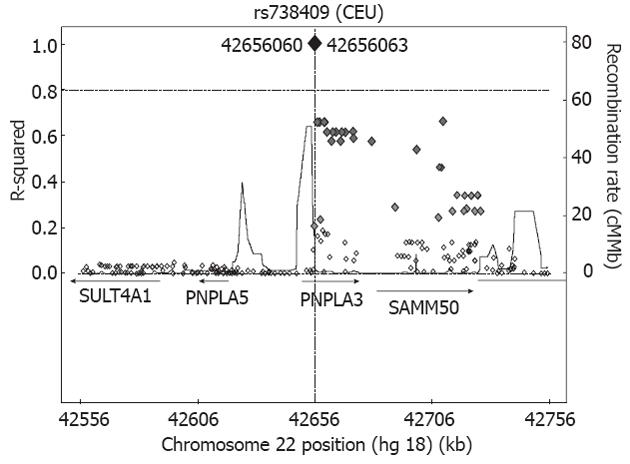
Figure 5 Regional Linkage disequilibrium plot for the rs738409 at chromosome 22 (22q13.
31). The single nucleotide polymorphisms are plotted with their proxies (showed as diamonds) (based on HapMap data for CEU) as a function of genomic location, annotated by the recombination rate across the locus and nearby genes. The regional association plot was performed by the SNAP server, available at http://www.broad.mit.edu/mpg/snap/. SULT4A1: Sulfotransferase-4A1; PNPLA5: Patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 5; PNPLA3: Patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3; SAMM50: Sorting and assembly machinery component 50 homolog.
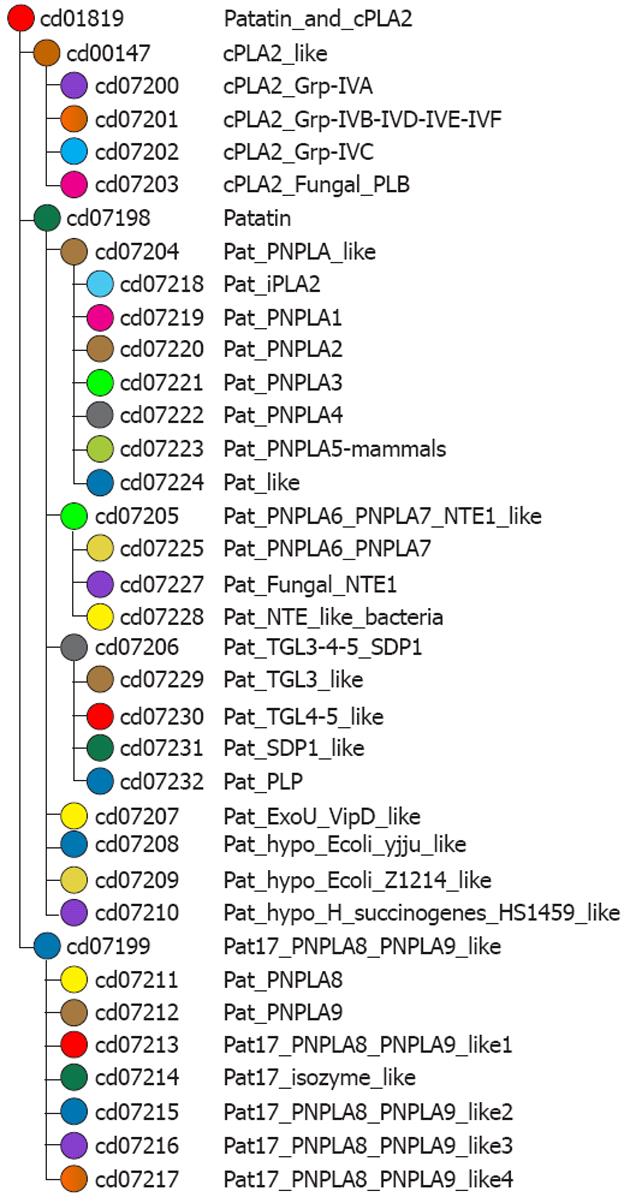
Figure 6 Domain family hierarchy of patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 protein.
Data extracted from NCBI-curated domains at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cdd.shtml. This picture provides data about how patterns of residue conservation and divergence in a family relate to functional properties. In this particular case, picture shows the patatin-like phospholipase family. Patatin is a storage protein, but it also has the enzymatic activity of a lipid acyl hydrolase, catalyzing the cleavage of fatty acids from membrane lipids. Members of this family have also been found in vertebrates. This family also includes the catalytic domain of cytosolic phospholipase A2 (PLA2; EC 3.1.1.4) hydrolyzes the sn-2-acyl ester bond of phospholipids to release arachidonic acid. At the active site, cPLA2 contains a serine nucleophile through which the catalytic mechanism is initiated. PNPLA3: Patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3; TGL: Triglyceride lipase; PLP: Pyridoxal phosphate.
Figure 7 Prediction of patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 gene structure extracted from The University of California-Santa Cruz (UCSC) Genome Browser.
http://www.genome.ucsc.edu/.
- Citation: Sookoian S, Pirola CJ. PNPLA3, the triacylglycerol synthesis/hydrolysis/storage dilemma, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(42): 6018-6026
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i42/6018.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i42.6018