Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2012; 18(41): 5905-5911
Published online Nov 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i41.5905
Published online Nov 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i41.5905
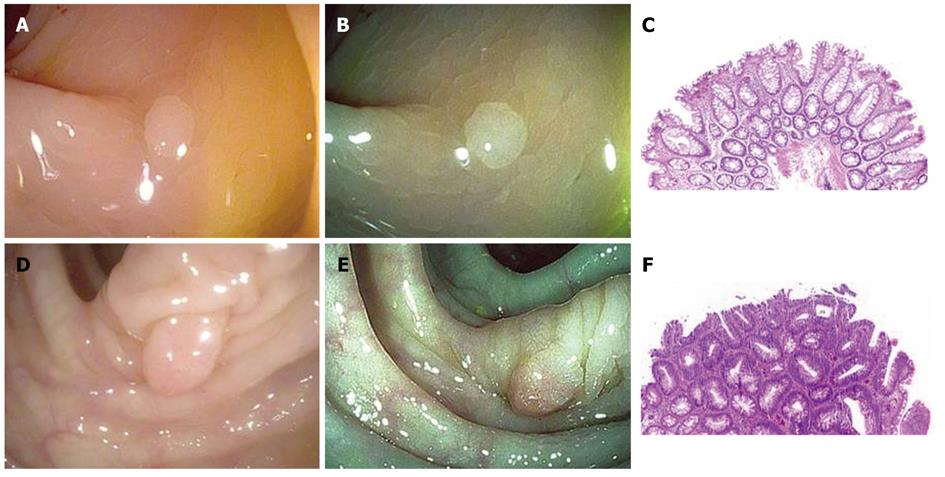
Figure 1 Correct prediction of small colonic polyps.
A: Correctly predicted as hyperplastic, visualized under high-definition white light; B: Correctly predicted as hyperplastic, visualized under i-SCAN; C: Pathology demonstrating colonic mucosa with serrated architecture extending midway down the glands and non-dysplastic cytology, consistent with a hyperplastic polyp [hematoxylin and eosin (HE); 4 ×]; D: Correctly predicted as adenoma, visualized under high-definition white light; E: Correctly predicted as adenoma, visualized under i-SCAN; F: Pathology demonstrating colonic mucosa with hyperchromatic, elongated, and pseudostratified nuclei, consistent with a tubular adenoma (HE; 4 ×).
-
Citation: Chan JL, Lin L, Feiler M, Wolf AI, Cardona DM, Gellad ZF. Comparative effectiveness of
i -SCAN™ and high-definition white light characterizing small colonic polyps. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(41): 5905-5911 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i41/5905.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i41.5905