Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2012; 18(38): 5479-5484
Published online Oct 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5479
Published online Oct 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5479
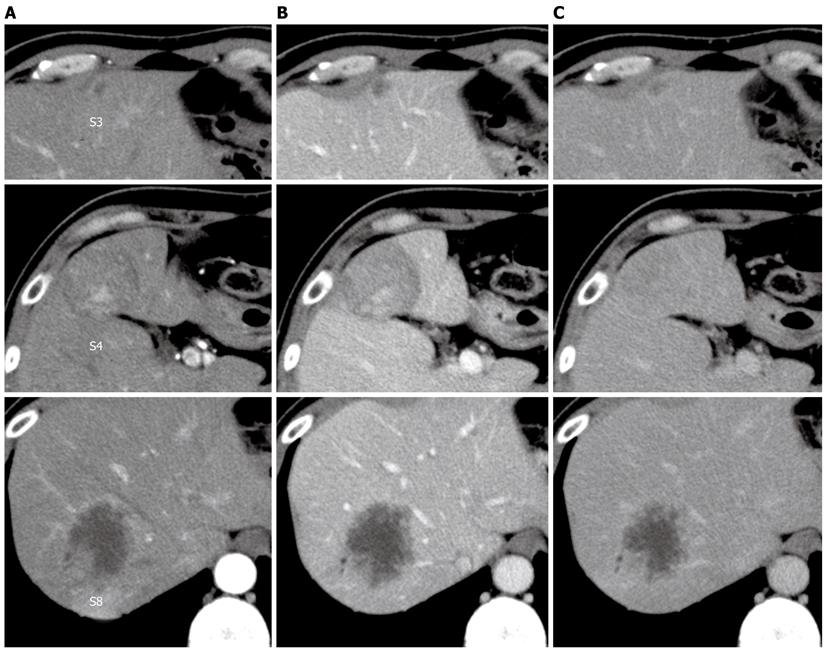
Figure 1 Dynamic computed tomography of the liver.
A: Arterial phase; B: Portal phase; C: Venous phase. A hypo- or iso-dense tumor with heterogeneous enhancement in segment 4, a hypodense tumor with peripheral enhancement in segment 8, and a small hypodense tumor in segment 3.
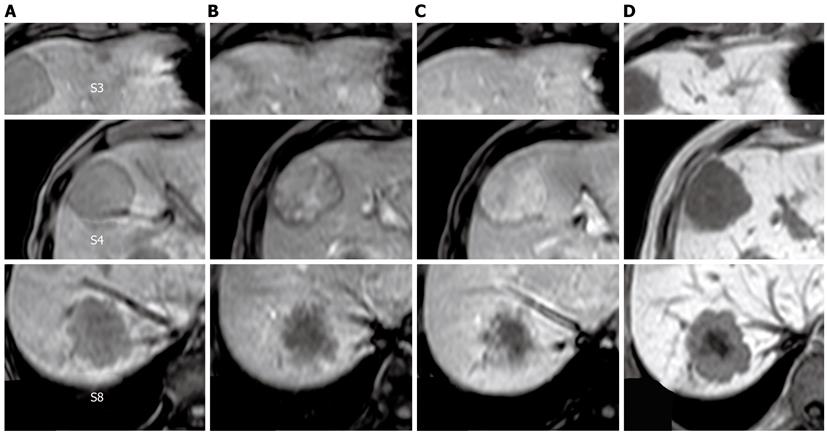
Figure 2 T1-weighted gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging.
A: Pre-enhancement; B: 30 s; C: 120 s; D: Hepatocellular phase. The tumor in segment 4 showed heterogeneous enhancement in the dynamic phase. The tumors in segments 3 and 8 showed gradual peripheral enhancement.
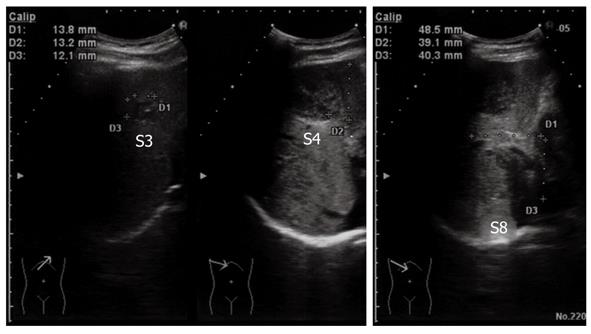
Figure 3 Ultrasonography of the abdomen.
All of the tumors showed hypo- or isoechoic heterogeneous masses without halos.
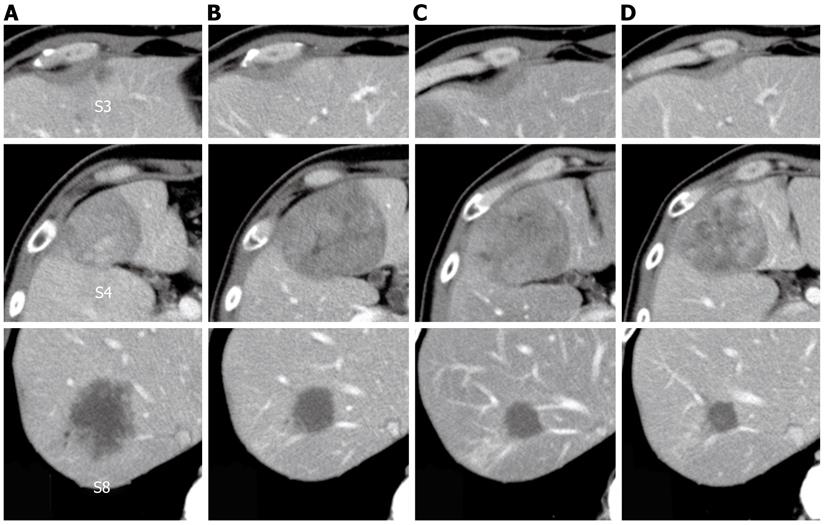
Figure 4 Change in tumor size observed using computed tomography during the clinical course.
A: Before treatment; B: After six courses of modified FOLFOX6 plus bevacizumab; C: After seven courses of FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab; D: After one course of irinotecan plus cetuximab.
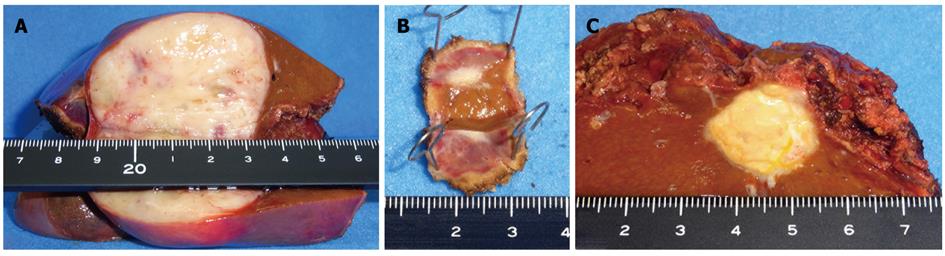
Figure 5 A macroscopic view of the cut-end surfaces of the resected specimens.
A: Segment 3; B: Segment 8; C: Segment 4.
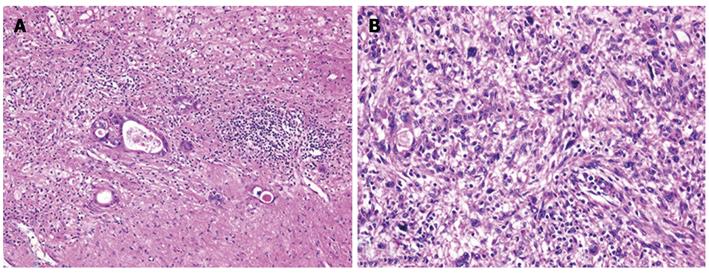
Figure 6 Histological findings of the tumors and hematoxylin and eosin staining.
A: The tumor in segment 8 demonstrated fibrosis and calcification, with a few degenerated residual adenocarcinoma cells; B: The tumor in segment 4 had irregular fascicles of spindle-shaped cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and nuclear atypia.
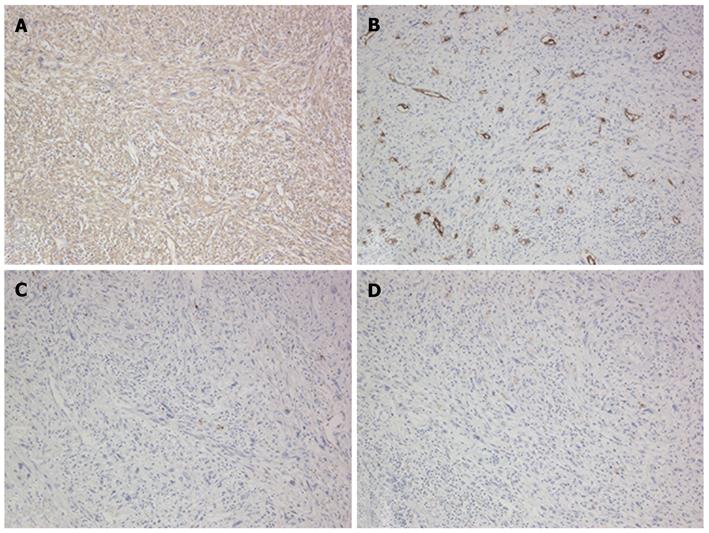
Figure 7 Immunohistochemical features of the tumor in segment 4.
A: Positive for α-smooth muscle actin; B: Negative for CD34; C: Negative for S-10; D: Negative for c-kit.
- Citation: Takehara K, Aoki H, Takehara Y, Yamasaki R, Tanakaya K, Takeuchi H. Primary hepatic leiomyosarcoma with liver metastasis of rectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(38): 5479-5484
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i38/5479.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i38.5479