Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2012; 18(32): 4323-4334
Published online Aug 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i32.4323
Published online Aug 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i32.4323
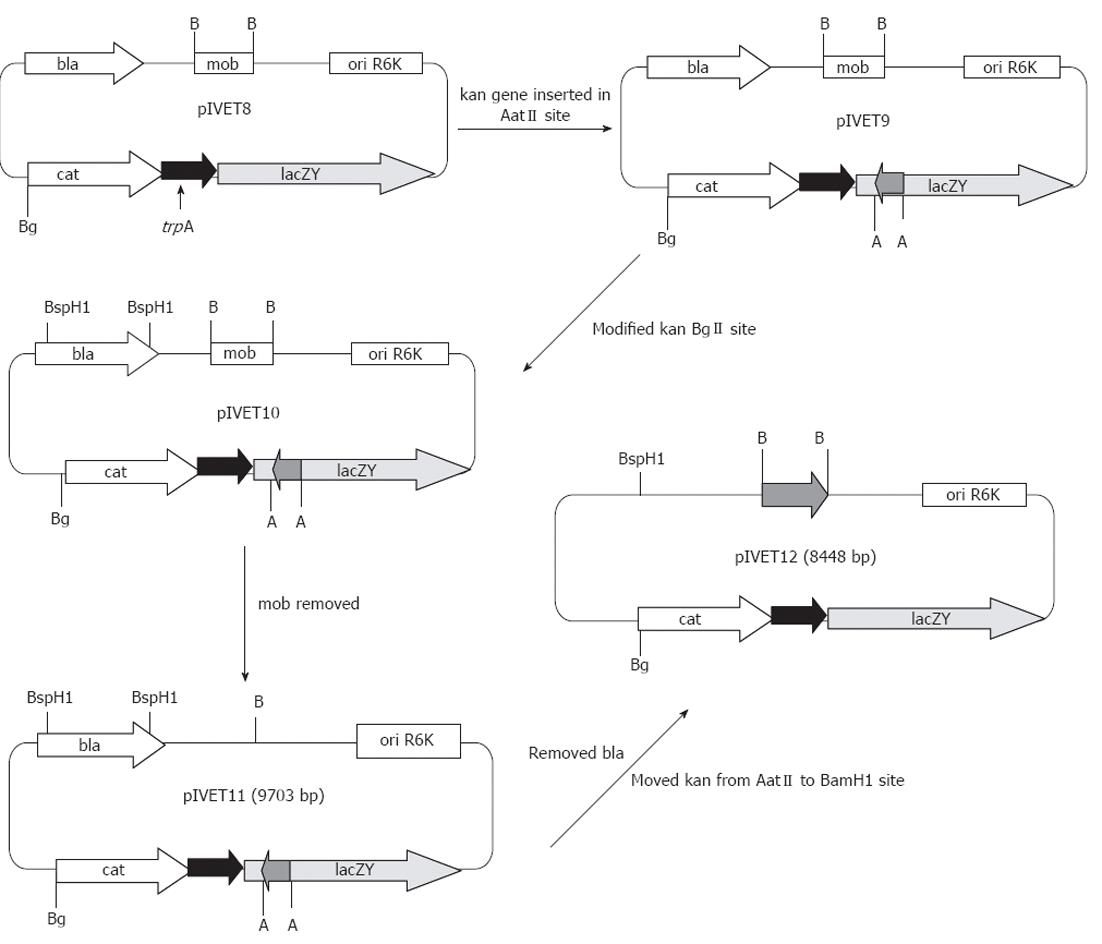
Figure 1 Construction of Helicobacter pylori specific antibiotic-based in vivo expression technology plasmids, pIVET11 and pIVET12.
These plasmids are derivatives of plasmid pIVET8[10]. A: AatII; B: BamHI; Bg: BglII; bla: β-lactamase; kan: Kanamycin gene; mob: Plasmid mobilization; trpA: Tryptophan synthase α-subunit.
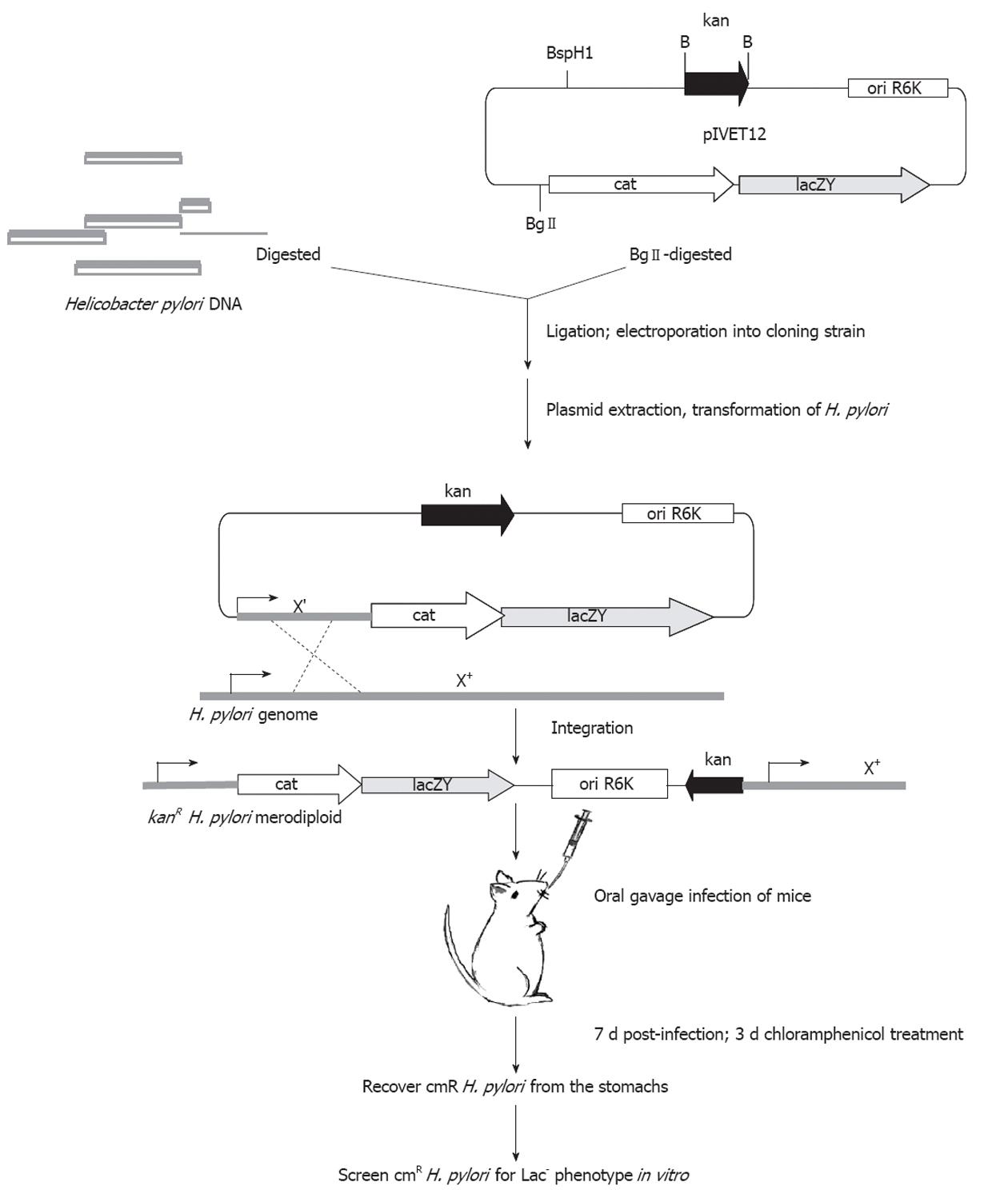
Figure 2 Helicobacter pylori specific in vivo expression technology strategy.
H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; B: BamHI; Bg: BglII; kan: Kanamycin gene.
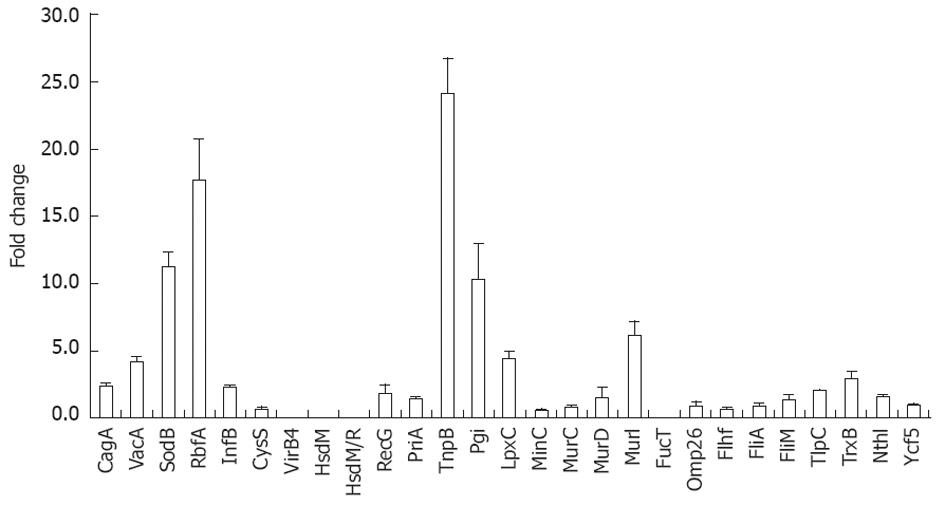
Figure 3 Gene expression of Helicobacter pylori induced by phagocytosis.
Up-regulation and down-regulation of Helicobacter pylori in vivo induced genes expressed by macrophage engulfed bacteria.
-
Citation: Singh A, Hodgson N, Yan M, Joo J, Gu L, Sang H, Gregory-Bryson E, Wood WG, Ni Y, Smith K, Jackson SH, Coleman WG. Screening
Helicobacter pylori genes induced during infection of mouse stomachs. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(32): 4323-4334 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i32/4323.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i32.4323