Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2012; 18(27): 3617-3622
Published online Jul 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i27.3617
Published online Jul 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i27.3617
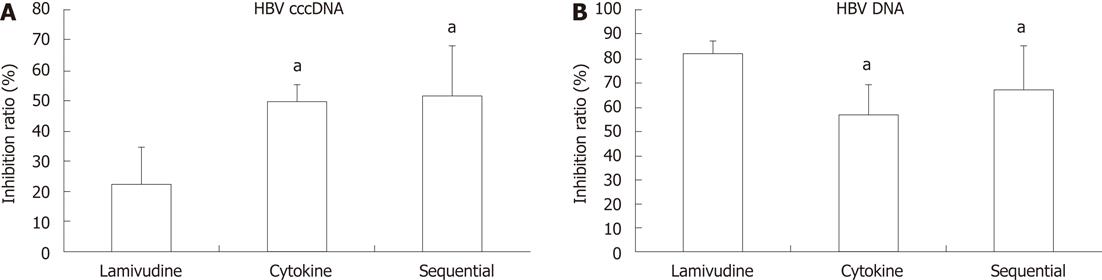
Figure 1 Inhibition ratio of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA (A) and DNA (B) following different treatments of HepG2.
2.15 cells. A: Hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA (HBV cccDNA) was quantified with real-time polymerase chain reaction; B: Hepatitis B virus DNA (HBV DNA) was quantified with real-time polymerase chain reaction. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD from three individual experiments. aP < 0.05 vs lamivudine group.
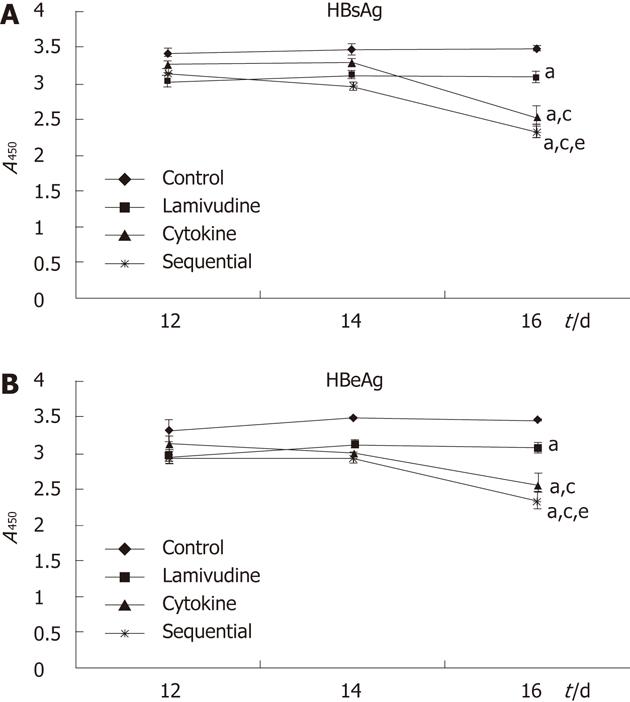
Figure 2 Levels of hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen following different treatments of HepG2.
2.15 cells. Sequential treatment reduced the levels of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) (A) and hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) (B) most strongly at 16 d in the treatment period. aP < 0.05 vs control group, cP < 0.05 vs lamivudine group, eP < 0.05 vs cytokine group.
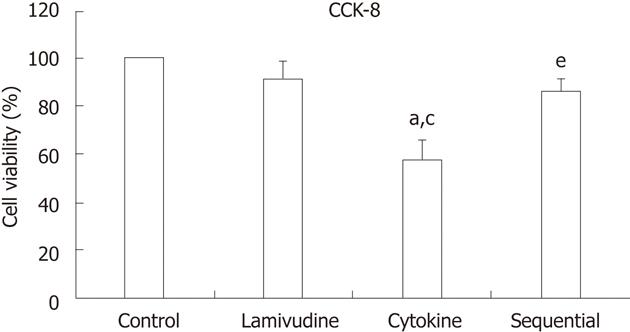
Figure 3 Lamivudine pretreatment significantly reduces interferon-γ + tumor necrosis factor-α-mediated toxicity of HepG2.
2.15 cells. Percent cell survival was analyzed with the cell counting kit (CCK)-8 assay following exposure of HepG2.2.15 cells to the four treatments. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD from three individual experiments. aP < 0.05 vs control, cP < 0.05 vs lamivudine group, eP < 0.05 vs cytokine group.
- Citation: Shi H, Lu L, Zhang NP, Zhang SC, Shen XZ. Effect of interferon-γ and tumor necrosis factor-α on hepatitis B virus following lamivudine treatment. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(27): 3617-3622
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i27/3617.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i27.3617