Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2012; 18(25): 3303-3309
Published online Jul 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i25.3303
Published online Jul 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i25.3303
Figure 1 Circulating and tumor-infiltrating CD33+HLA-DR- myeloid-derived suppressor cells in colorectal carcinoma patients.
A: CD33+HLA-DR- myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) were present in the peripheral blood of colorectal carcinoma (CRC) patients and healthy donors, as well as in CRC tumor tissues; B: The percentage of CD33+HLA-DR- MDSCs was significantly increased in the blood and tumor tissues of CRC patients (aP < 0.05). PBMCs: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
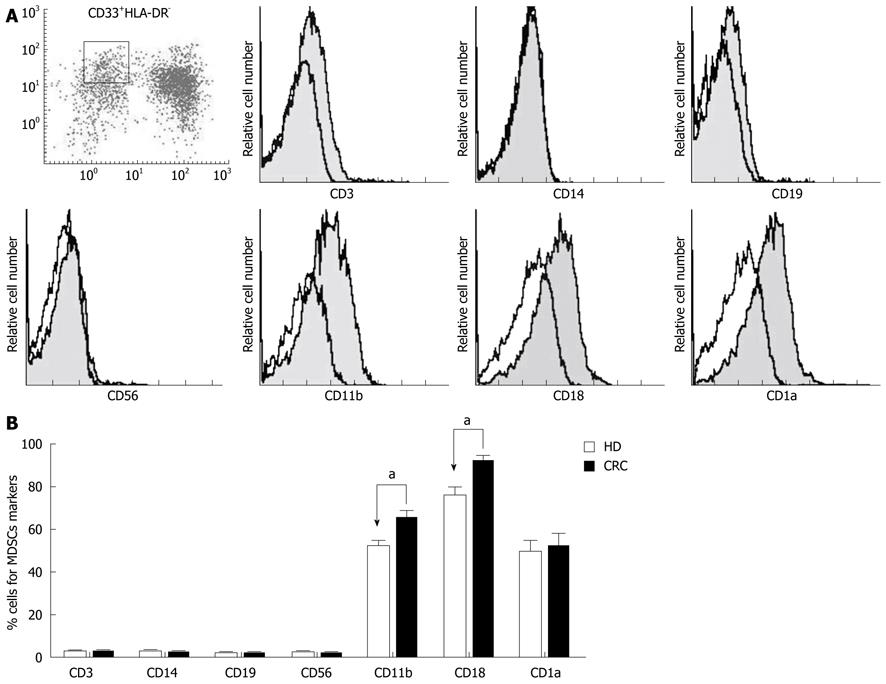
Figure 2 Phenotypic analyses of CD33+HLA-DR- myeloid-derived suppressor cells in colorectal carcinoma patients and healthy donors.
A: Cell surface markers of peripheral blood myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), obtained by gating on the CD33+HLA-DR- subset, were detected in colorectal carcinoma (CRC) patients; B: Percentages of cells positive for various markers on the CD33+HLA-DR- subset in healthy donors (HD) and CRC patients (aP < 0.05).
- Citation: Sun HL, Zhou X, Xue YF, Wang K, Shen YF, Mao JJ, Guo HF, Miao ZN. Increased frequency and clinical significance of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in human colorectal carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(25): 3303-3309
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i25/3303.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i25.3303