Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2012; 18(19): 2344-2356
Published online May 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i19.2344
Published online May 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i19.2344
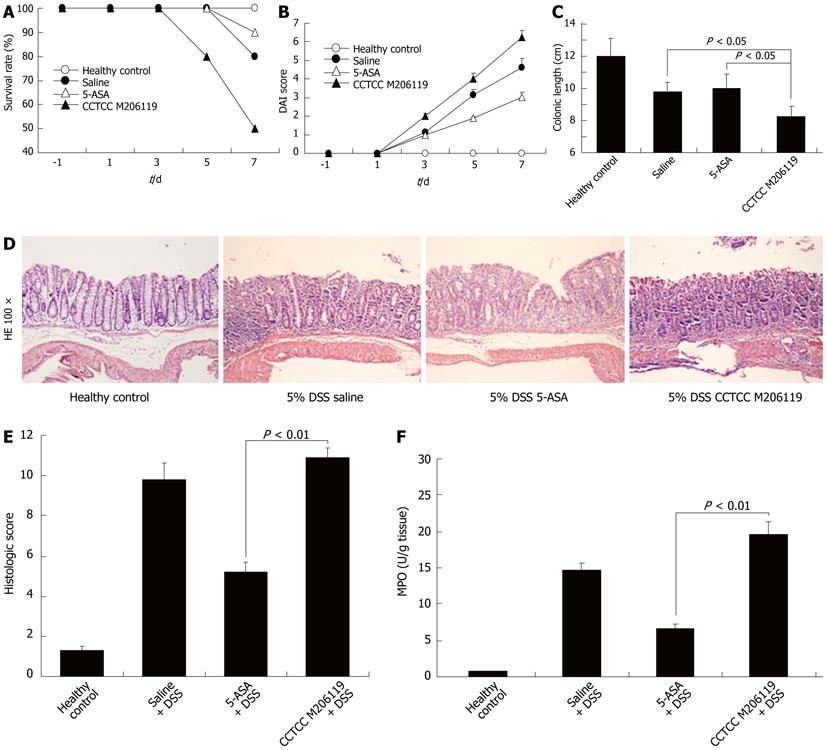
Figure 1 Colonic inflammation was aggravated in dextran sulfate sodium-colitis mice after China Center for Type Culture Collection M206119 treatment.
A: Survival rate changes of four age- and sex-matched BALB/c mouse groups (n = 10) [〇: Healthy controls; ●: 5% dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) plus saline treatment; △: 5% DSS plus 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) treatment; ▲: 5% DSS plus China Center for Type Culture Collection M206119] at the indicated time points; B: Disease activity index (DAI) changes among groups in (A) after 7 d 5% DSS treatment at the indicated time points. Each point represents the mean ± SE (n = 10); C: Mean colon length (cm) for the mice in (A); D: Histological analysis of representative colons from the mice in (A) (original magnification, hematoxylin and eosin staining, 100 ×); E: Summarized histological scores from colons of (D); F: Summarized myeloperoxidase (MPO) activities of colons from mice in (D).
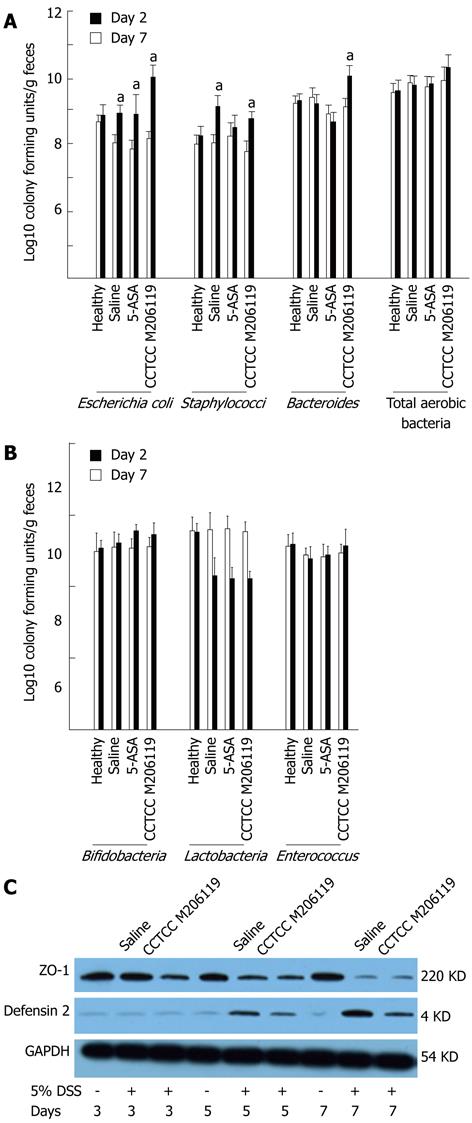
Figure 2 Alteration of fecal microflora in DSS-colitis mice after China Center for Type Culture Collection M206119 treatment.
Bacterial counts of (A) aerobic (Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus, Bacteroides, total aerobic bacteria) and (B) anaerobic (Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, Enterococcus spp.) in colon luminal contents from healthy animals and dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-colitis mice treated by saline, 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), or China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) M206119 strain at day 2 and day 7 after DSS-treatment, as determined by culture. The data sets were pooled from two independent experiments. Significance levels were determined by U test. Underlined P values shown in black were calculated from comparisons of healthy vs diseased animals; C: Zonula occludens (ZO)-1 and defensin 2 expression from colons of DSS-colitis mice treated with saline or CCTCC M206119 and healthy mice was measured by western blotting at indicated time points; GAPDH was used as a loading control. The data represent at least three experiments. aP < 0.05 vs healthy group. GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
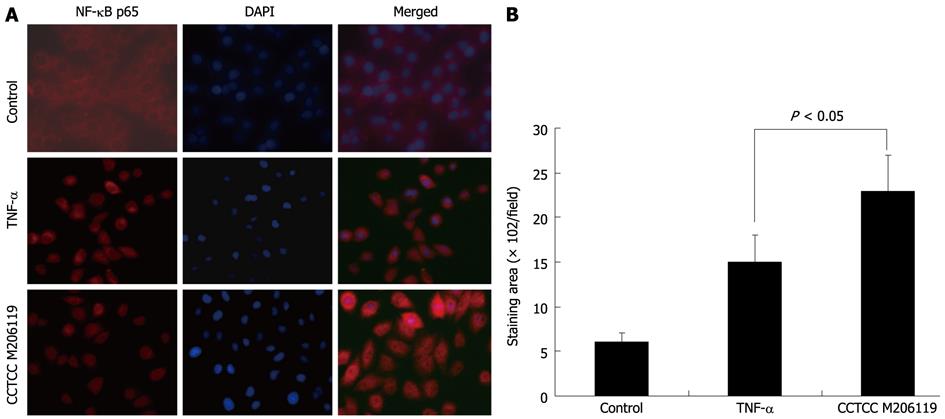
Figure 3 Effects of China Center for Type Culture Collection M206119 strain on epithelial injury and translocation of nuclear factor-κB in vitro.
Immunofluorescence staining for nuclear factor (NF)-κB p65 (red) and 4',6'-diamidino-2-phenylindole hydrochloride (DAPI) (blue) in HT-29 cells treated either by tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α or China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) M206119 (scale bars, 10 mm). A: Increased positive NF-κB p65 staining after CCTCC M206119 treatment; B: Positive staining areas were quantified as pixels per high-power microscopic field (400 ×) using Photoshop. Error bars indicate mean ± SD (n = 3).
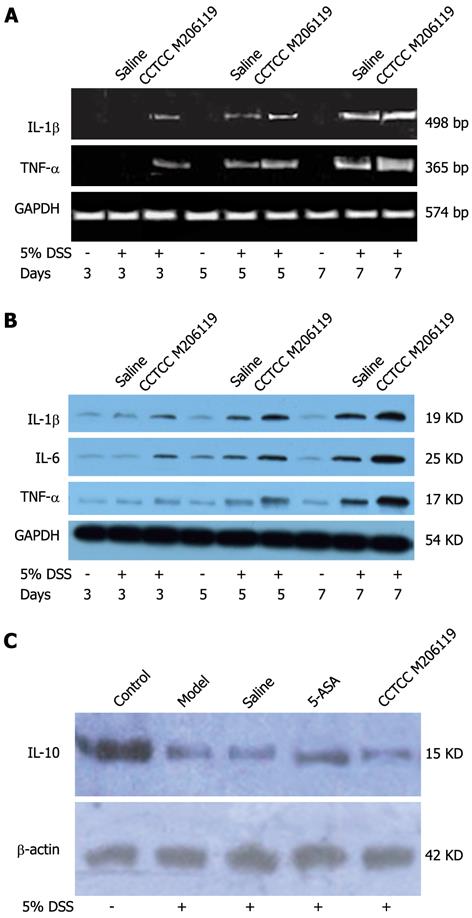
Figure 4 Colonic cytokines changes in China Center for Type Culture Collection M206119 or vehicle-treated dextran sulfate sodium-colitis mice.
Expression of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α from the colons of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-colitis mice treated with China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) M206119 or saline was measured by (A) RT-PCR and (B) western blotting at indicated time points; GAPDH was used as a loading control; C: IL-10 expression from colons of DSS-colitis mice treated with saline, 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), or CCTCC M206119 was measured by western blotting at indicated time points; β-actin was used as a loading control. The data represent at least three experiments. GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
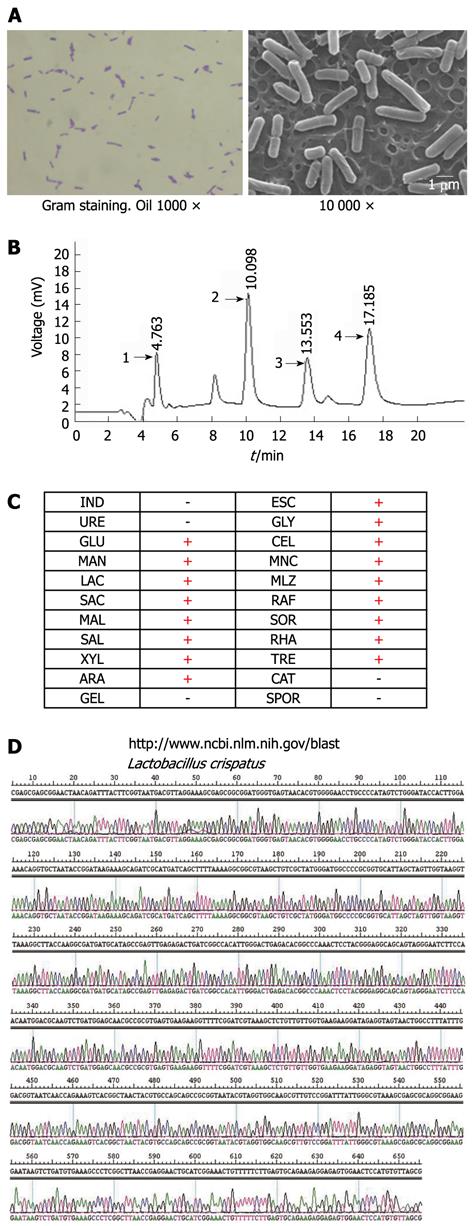
Figure 5 Characteristics of China Center for Type Culture Collection M206119 strain.
China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) M206119 strain was identified by (A) microscopy (Gram staining, oil 1000 ×) and scanning electron microscopy (10 000 ×); (B) Gas chromatography ratio (high performance liquid chromat); (C) biochemical reaction; and (D) sequence analyses of 16S rRNA gene fragments amplified from DNA eluted from CCTCC M206119 genomic DNA.
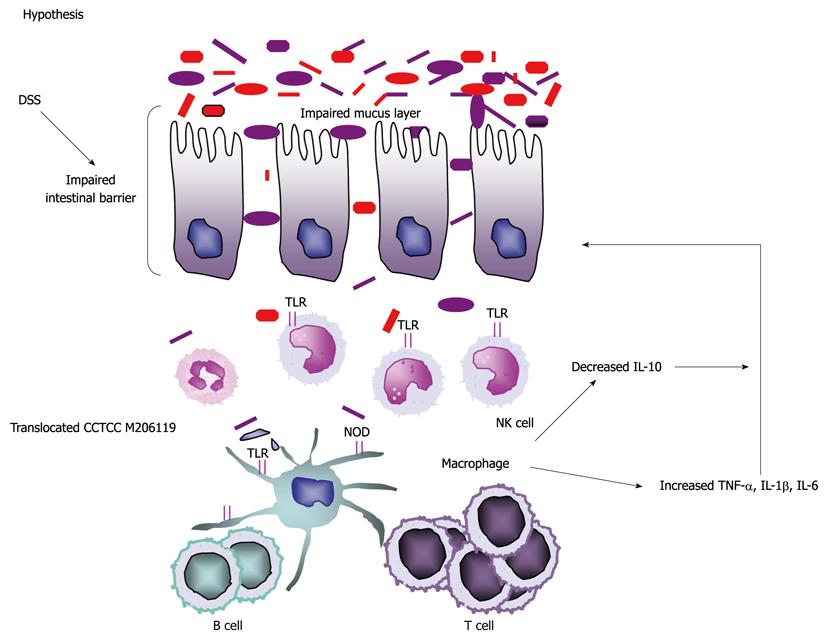
Figure 6 Model illustrating how China Center for Type Culture Collection M206119strain leads to aggravated phenotype in dextran sulfate sodium-colitis mice.
DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; TLR: Toll-like receptor; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; NOD: Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain; NK: Natural killer.
-
Citation: Zhou FX, Chen L, Liu XW, Ouyang CH, Wu XP, Wang XH, Wang CL, Lu FG.
Lactobacillus crispatus M206119 exacerbates murine DSS-colitis by interfering with inflammatory responses. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(19): 2344-2356 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i19/2344.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i19.2344