Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2012; 18(15): 1806-1813
Published online Apr 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i15.1806
Published online Apr 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i15.1806
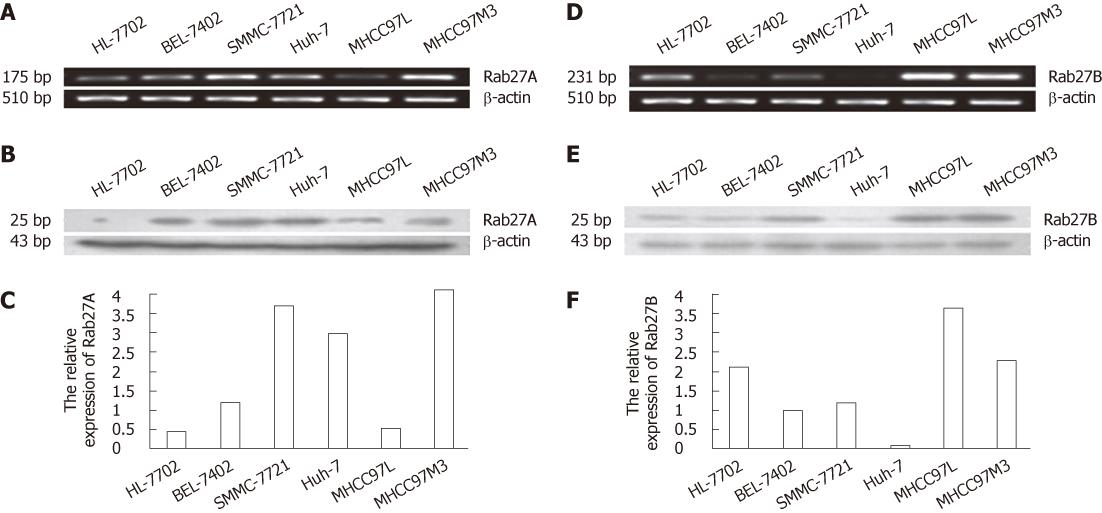
Figure 1 Detection of Rab27A and Rab27B mRNA and protein in 6 human cell lines.
A and C: Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and real-time PCR, respectively, of Rab27A in 5 hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines and the human HL-7702 line; D and F: RT-PCR and real-time PCR, respectively, of Rab27B; B and E: Western blotting of Rab27A and Rab27B protein levels, respectively. β-actin served as an internal control.
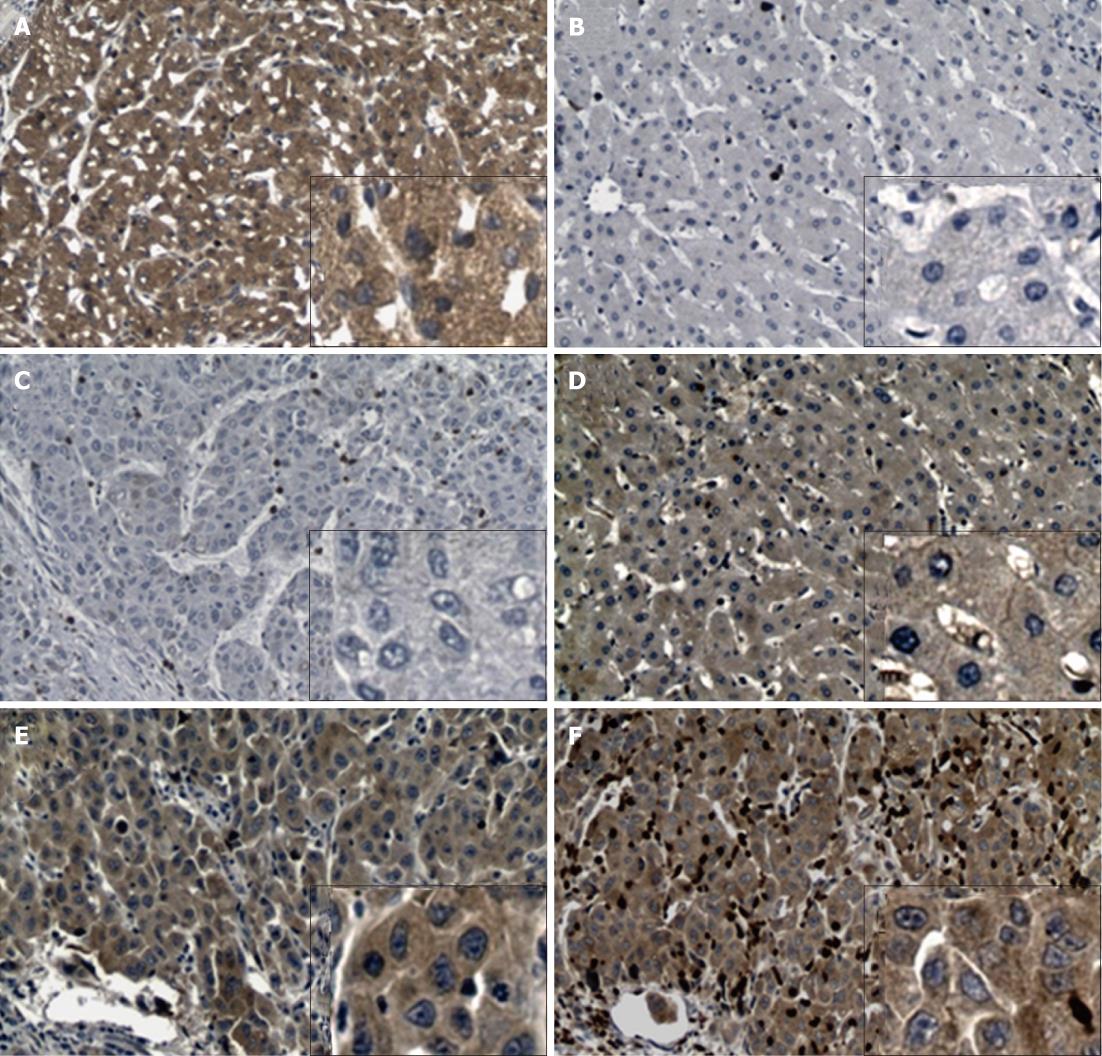
Figure 2 Differential expression of Rab27A and Rab27B in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
A: Positive staining of Rab27A in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissue; B: Negative staining of Rab27A in adjacent tissue; C: Negative staining of Rab27B in HCC tissue; D: Positive staining of Rab27B in adjacent tissue; E and F: Positive staining of Rab27A and Rab27B, respectively, in the same HCC tissue. Both Rab27A and Rab27B were observed in the cytoplasm and plasma membrane of human cells. Original magnification × 100; the inset boxes are at original magnification × 400.
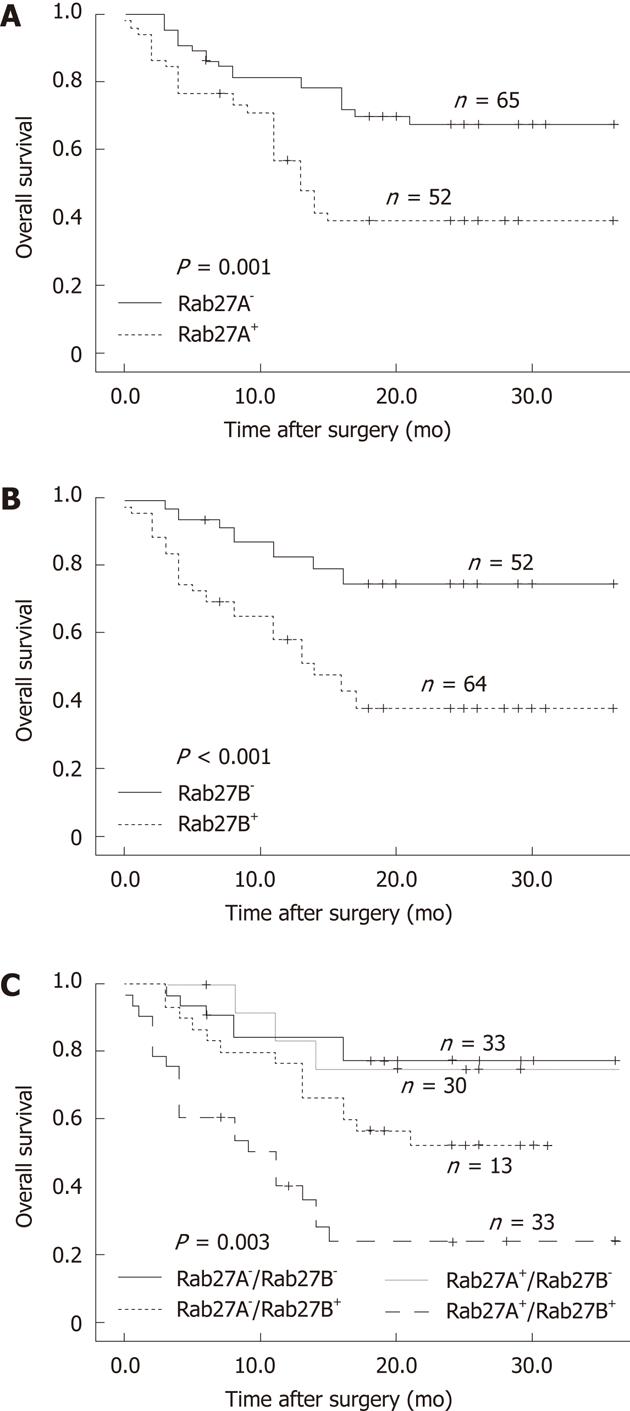
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier overall survival analysis of Rab27A and Rab27B in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
A: Survival analysis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients by expression of Rab27A; B: Survival analysis by expression of Rab27B; C: Survival analysis with expression of Rab27A and Rab27B as covariables.
- Citation: Dong WW, Mou Q, Chen J, Cui JT, Li WM, Xiao WH. Differential expression of Rab27A/B correlates with clinical outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(15): 1806-1813
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i15/1806.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i15.1806