Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2012; 18(14): 1695-1699
Published online Apr 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i14.1695
Published online Apr 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i14.1695
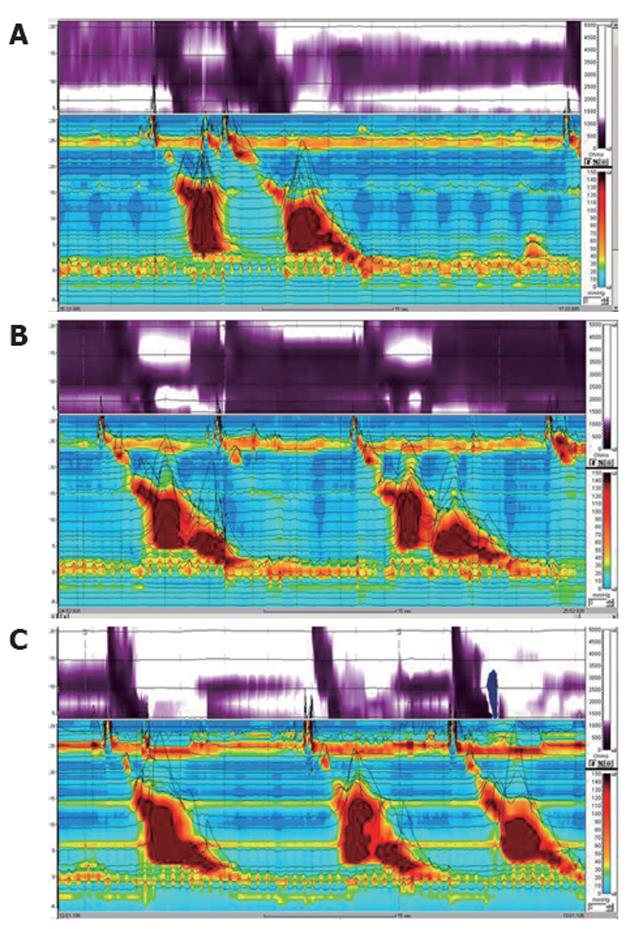
Figure 1 High resolution impedance manometry findings using the standard protocol.
A: Liquid swallowing at admission reveals high amplitude, simultaneous contractions of esophageal body with incomplete lower esophageal sphincter relaxation, and incomplete bolus transit; B: Viscous swallowing at admission demonstrates higher amplitude, repetitive contractions and incomplete bolus transit; C: After injection of botulinum toxin, the isocontour of impedance shows considerably improved bolus transit compared with those at admission during saline swallows (Figure 1A), but spasms are still seen on the isocontour of manometry.
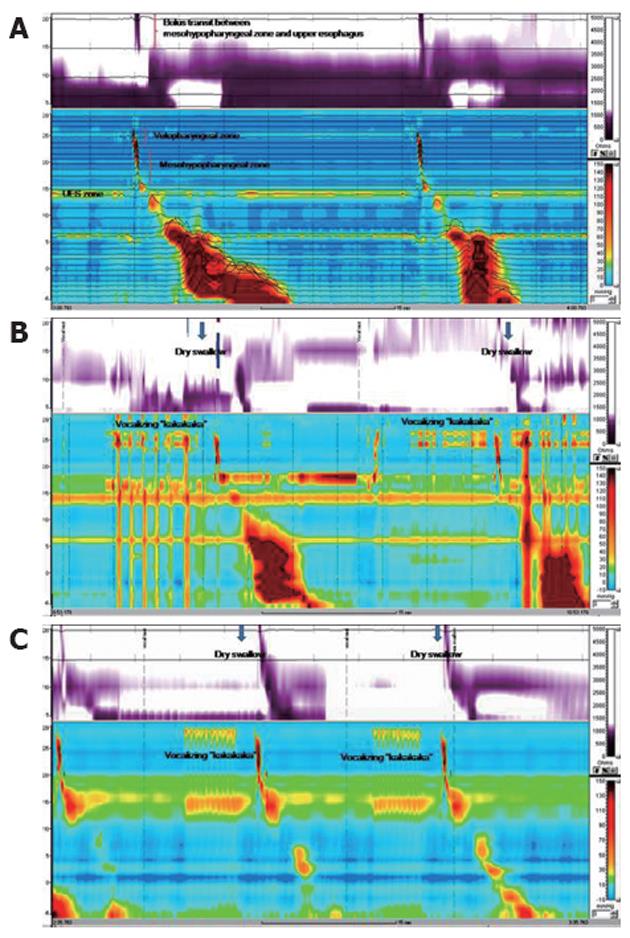
Figure 2 High resolution impedance manometry findings using modified protocol.
A: Patient; unremarkable peristaltic contraction and bolus transit between the hypopharynx and upper esophagus are seen after pull back of the catheter; B: Patient; irregular contractions are seen at the velopharyngeal zone, and simultaneous contraction between velopharyngeal and mesohypo- pharyngeal zone accompanying impaired bolus transit of pharyngo-upper esophageal segment after vocalizing “kakakaka”; C: Healthy subject without dysphagia; regular contractions are noted at the velopharyngeal zone, and peristaltic contractions of pharyngo-upper esophageal segment are normal as well as bolus transit after vocalizing “kakakaka”.
- Citation: Lee TH, Lee JS, Kim WJ. High resolution impedance manometric findings in dysphagia of Huntington’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(14): 1695-1699
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i14/1695.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i14.1695