Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2011; 17(8): 1036-1044
Published online Feb 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i8.1036
Published online Feb 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i8.1036
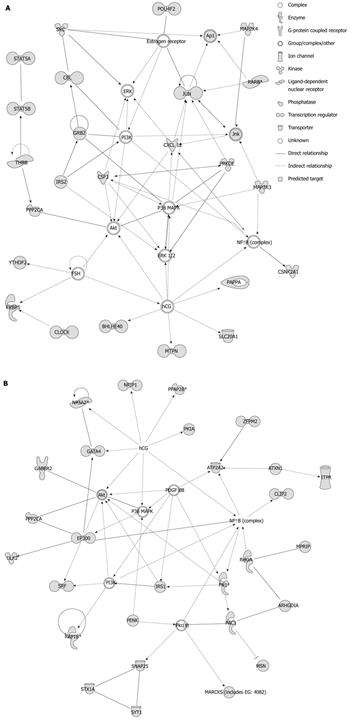
Figure 1 Top associated network functions for miR-141 and miR-200c.
A: Ingenuity Pathway Analysis predicted that the top associated network functions for miR-141 were gene expression, cell death and cell cycle (P = 1 × 10-35). B: The top associated network functions for miR-200c were cell morphology, cellular assembly and organization, cellular function and maintenance (P = 1 × 10-38). Predicted targets of miR-141 or miR-200c are highlighted in grey. Uncolored entries represent molecules that are associated with the pathway but are not predicted miR-141 or miR-200c targets. The P values were derived from a right-tailed Fisher’s exact test to calculate the probability that each predicted miRNA target matches the ascribed network function due to chance alone.
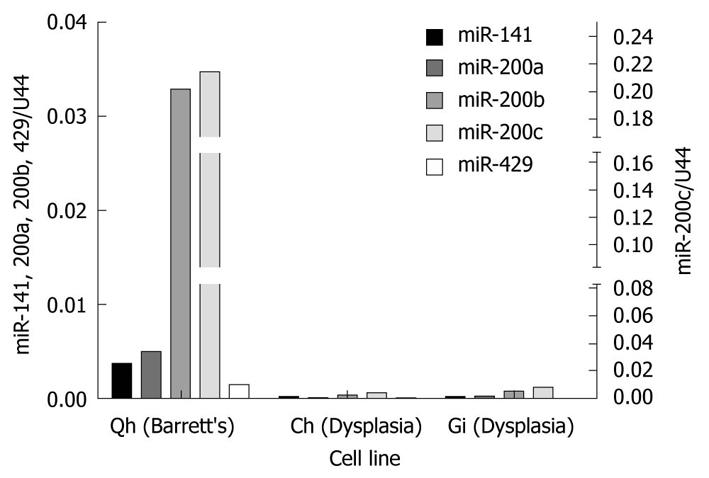
Figure 2 miR-200 family expression in benign Barrett’s and dysplastic cell lines.
Relative expression of all miR-141, miR-200a, miR-200b and miR-429, normalized to U44 expression is shown on the left hand y axis. Relative expression of miR-200c is shown on the right hand y axis. The pattern of relative expression of miR-200 members in the Qh (benign Barrett’s) cell line closely resembled that in benign Barrett’s esophagus mucosa (see relative expression values in Table 1).
- Citation: Smith CM, Watson DI, Leong MP, Mayne GC, Michael MZ, Wijnhoven BP, Hussey DJ. miR-200 family expression is downregulated upon neoplastic progression of Barrett’s esophagus. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(8): 1036-1044
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i8/1036.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i8.1036