Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2011; 17(7): 938-945
Published online Feb 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i7.938
Published online Feb 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i7.938
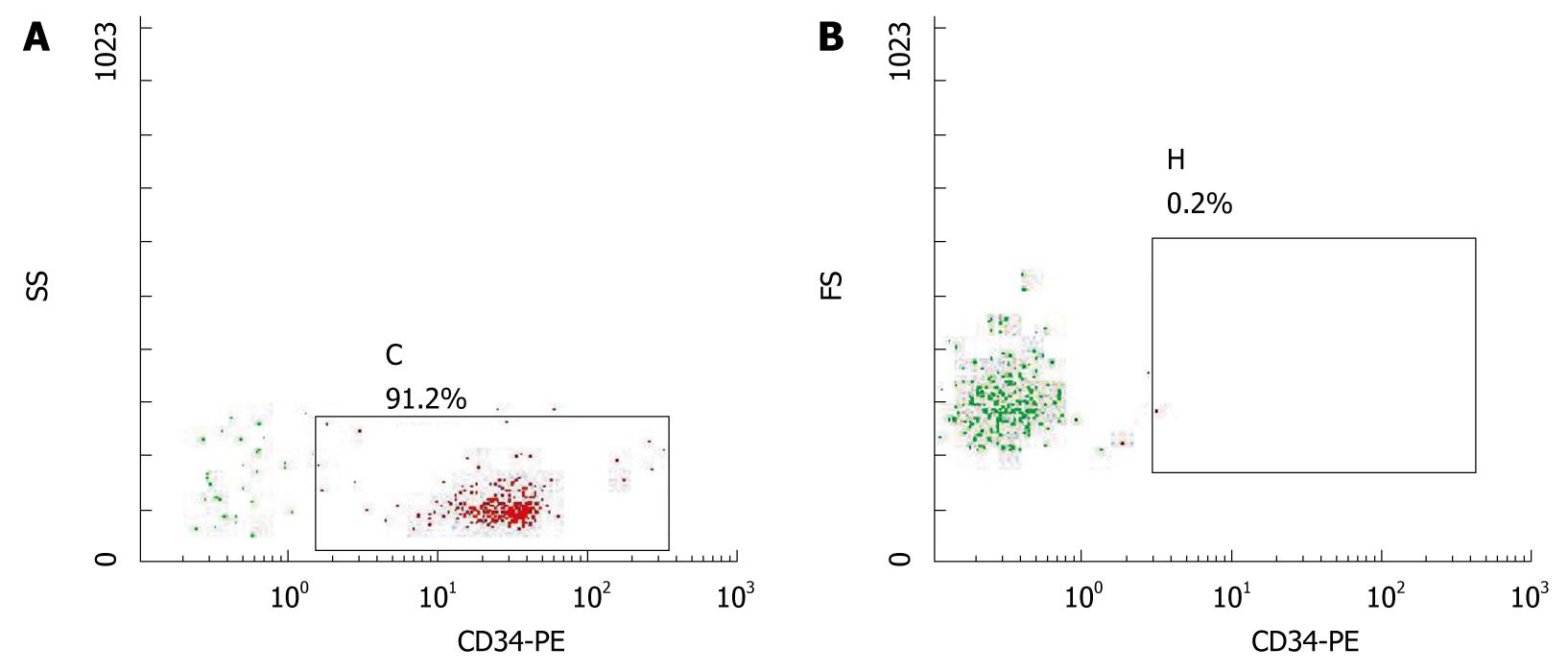
Figure 1 FACS determination of CD34+ cells.
A: Purity of CD34+ cells; B: Homotypic control cells.
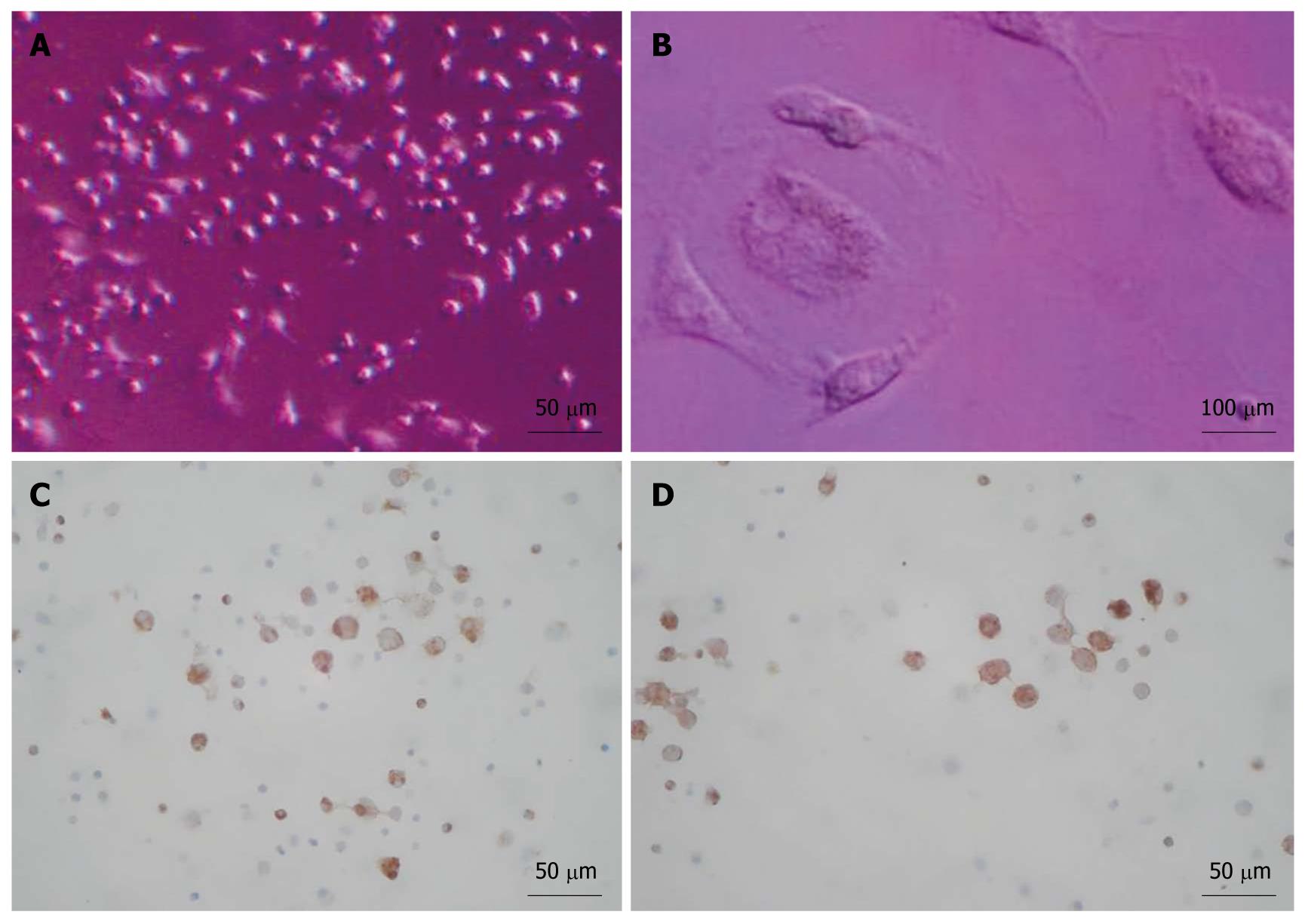
Figure 2 Cell culture and analyses.
A: After 16 d; B: A binucleated cell; C, D: Positive staining for albumin (C) and α-fetoprotein (D) after 16 d of indction.
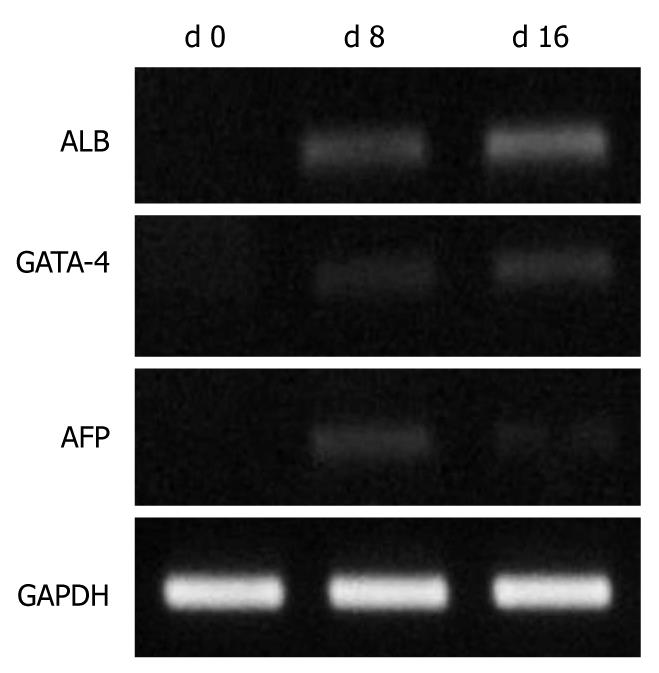
Figure 3 Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis of umbilical cord blood CD34+ cells cultured in vitro d 0, d 8 and d 16.
ALB: Albumin; AFP: α-fetoprotein.
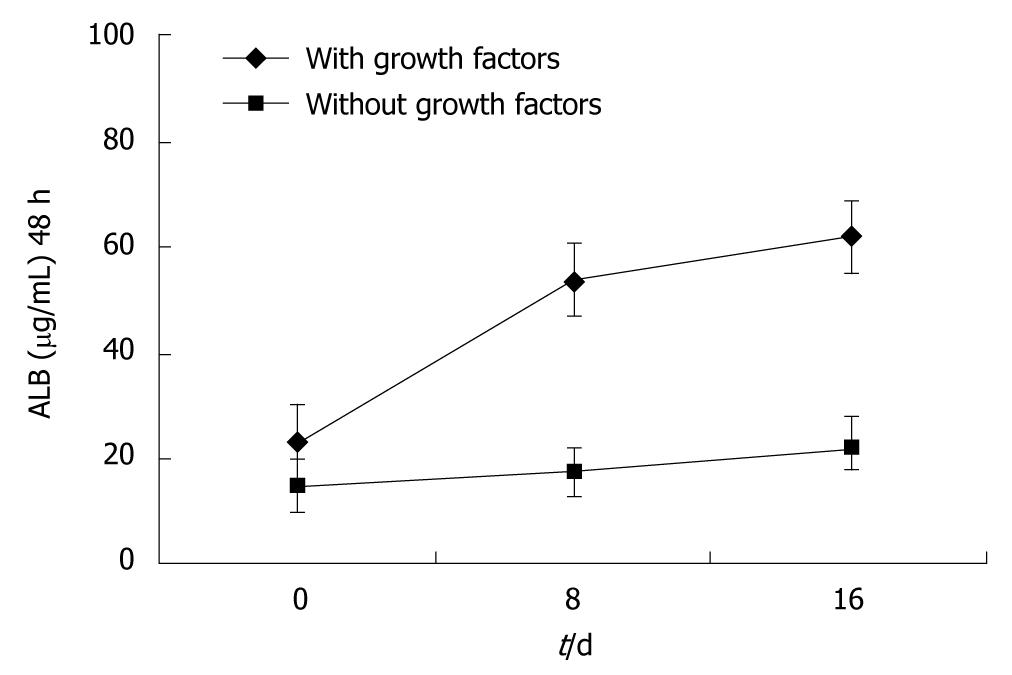
Figure 4 Determination of albumin expression by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay.
ALB: Albumin.
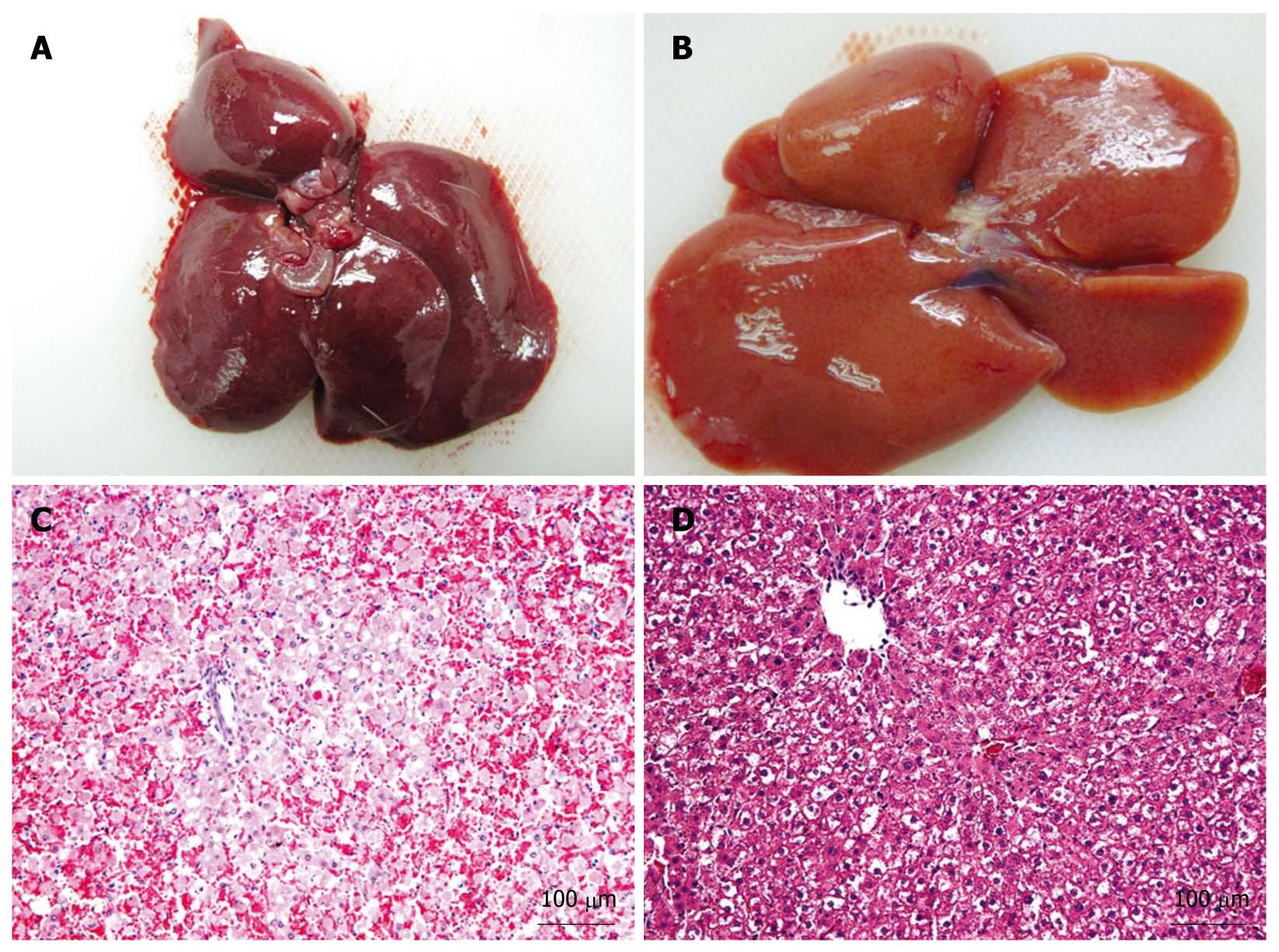
Figure 5 Pathological changes in the livers of acute hepatic failure rats.
A: Liver at 48 h after injection of D-galactosamine; B: Liver at 48 h after microcapsule transplantation; C: HE staining of the liver shown in section (A); D: HE staining of the liver shown in section (B).
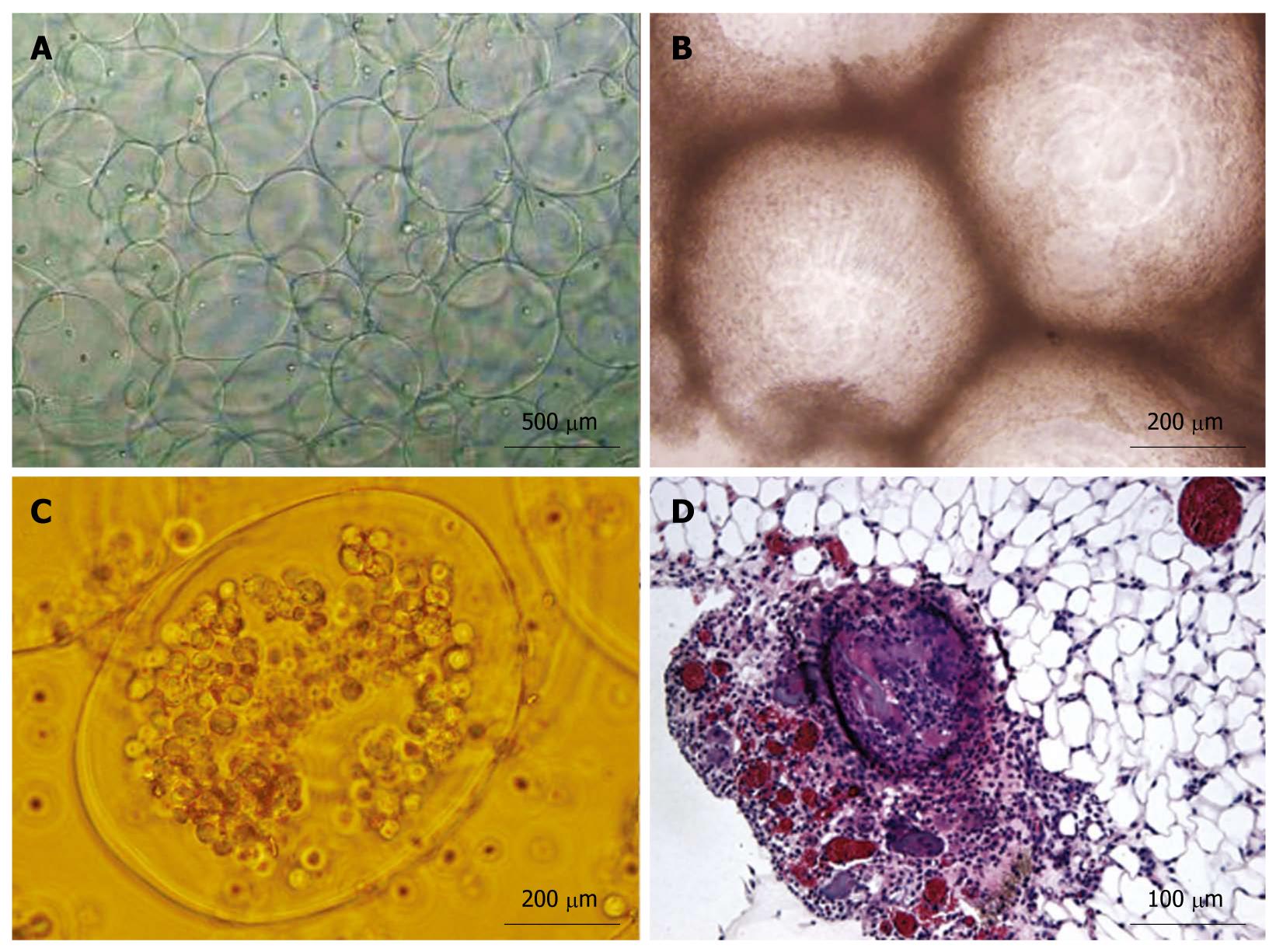
Figure 6 Encapsules observation.
A: Microcapsules created by the Alginate-poly-l-lysine-alginate microencapsulation method; B: Microcapsule masses in the peritoneal lavage fluid; C: Free microcapsules in the peritoneal lavage fluid; D: HE staining shows microcapsules in the greater omentum.
- Citation: Zhang FT, Wan HJ, Li MH, Ye J, Yin MJ, Huang CQ, Yu J. Transplantation of microencapsulated umbilical-cord-blood-derived hepatic-like cells for treatment of hepatic failure. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(7): 938-945
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i7/938.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i7.938