Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2011; 17(6): 691-696
Published online Feb 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i6.691
Published online Feb 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i6.691
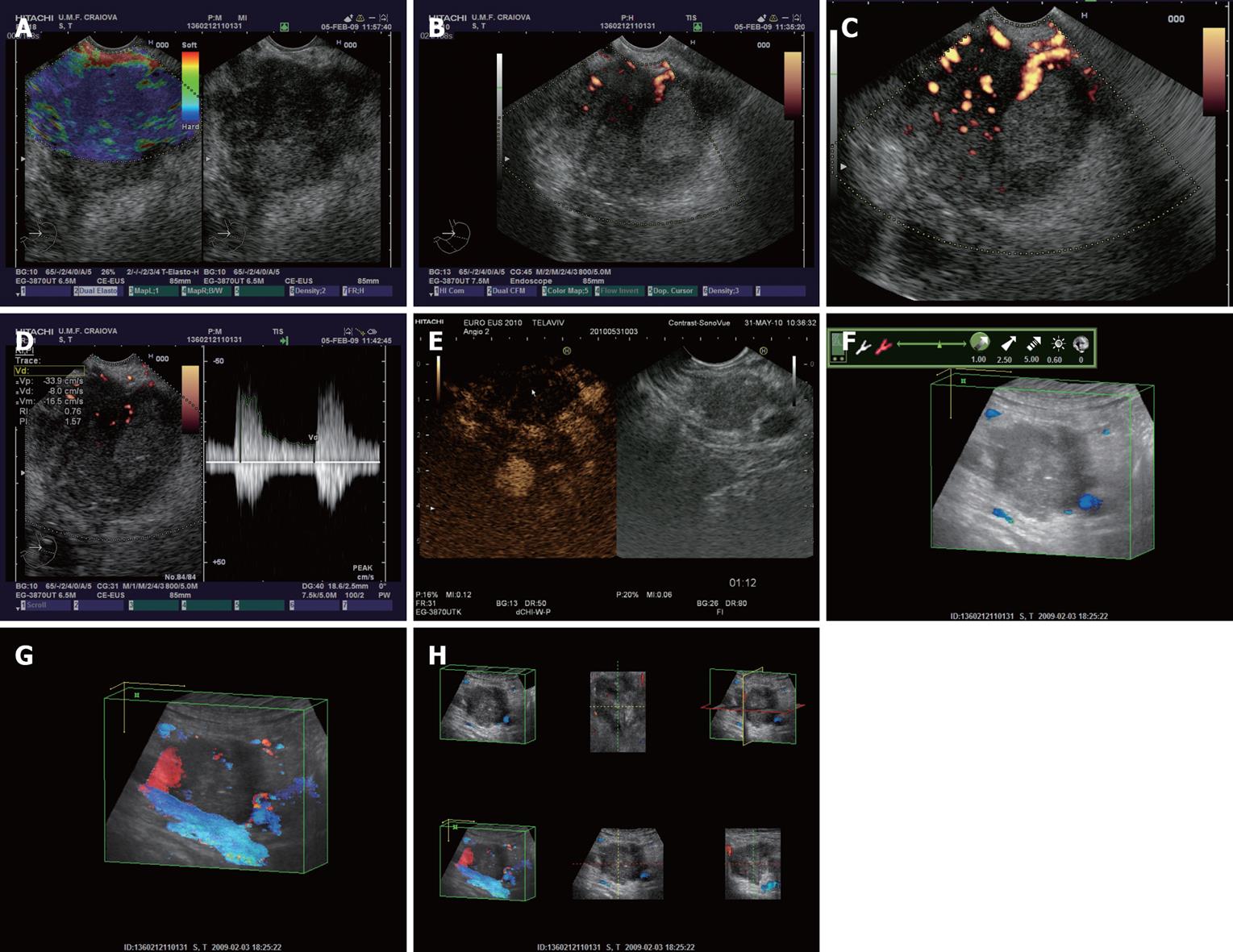
Figure 1 Pancreatic carcinoma at the level of pancreatic head depicted by different endoscopic ultrasound imaging techniques.
A: Real-time elastography showing an in-homogenous hard mass; B: Power Doppler endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) without contrast-enhancement; C: Power Doppler EUS after contrast-enhancement with Sono-Vue, showing a hypovascular mass; D: Pulsed Doppler (triplex mode) after contrast-enhancement, with high resistivity and pulsatility indexes of intratumoral arteries; E: Contrast-enhanced low-mechanical index EUS harmonic imaging, showing a hypovascular appearance in the late (venous) phase; F: Tridimensional EUS showing an enhanced image in the opacity mode; G: Transparency mode obtained after contrast-enhancement with Sono-Vue; H: Multiview tridimensional (3D)-EUS display of the pancreatic tumor.
- Citation: Săftoiu A. State-of-the-art imaging techniques in endoscopic ultrasound. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(6): 691-696
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i6/691.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i6.691