Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2011; 17(47): 5203-5213
Published online Dec 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i47.5203
Published online Dec 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i47.5203
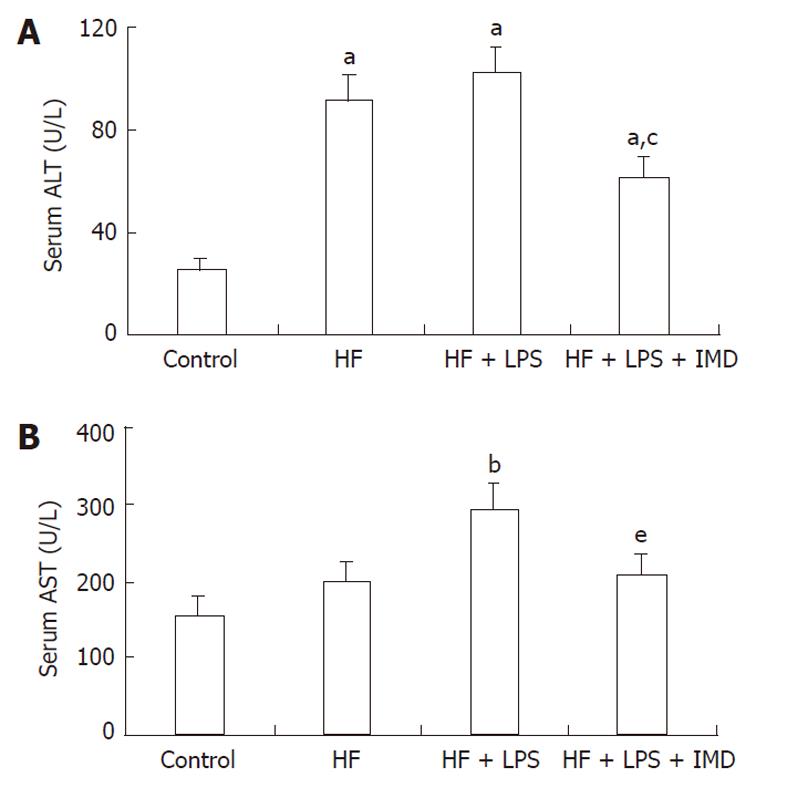
Figure 1 IKK2 inhibitor prevented HF + LPS-induced liver injury, as determined by serum ALT and AST levels.
The normal values for ALT and AST were 45 U/L and 160 U/L. Serum ALT (A) and AST (B) were measured in different groups (control group, HF group, LPS-induced HF group and IMD-treated group), data are expressed as mean ± SD. A: aP < 0.05 vs control group, cP < 0.05 vs the HF and LPS + HF groups; B: bP < 0.01 vs the control group, eP < 0.05 vs the LPS + HF group. HF: High-fat; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; IMD: IKK2 inhibitor; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase.
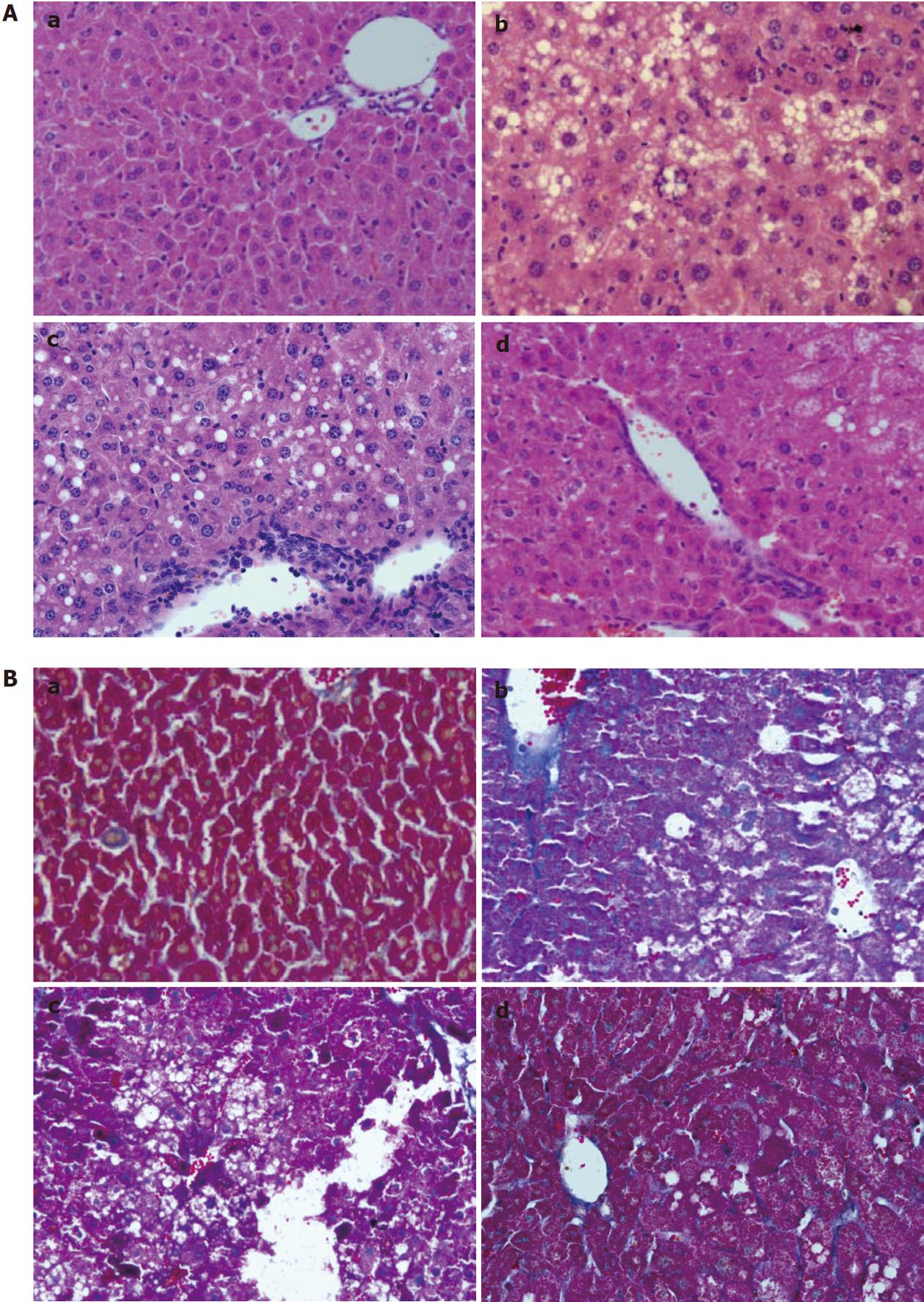
Figure 2 Hematoxylin and eosin stain and Masson staining in sections of (a) control group; (b) HF group; (c) HF + LPS group; and (d) HF + LPS + IMD group.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin stain. Macrovesicular steatosis, lobular inflammation and balloon degeneration of hepatocytes were observed in liver sections of HF-treated mice and HF + LPS + treated mice with a significantly large amount of inflammatory cell infiltration surrounding the centrilobular veins of the liver. Significant amelioration was observed in the group treated with IMD (d); B: Masson staining. A thin lining of collagen was observed in the HF group, HF + LPS group and HF + LPS + IMD group. With LPS treatment, there was an increase in the amount of collagen accumulated along the central vein with the presence of collagen in the pericellular area. Treatment with IMD reduced LPS-induced collagen accumulation. HF: High-fat; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; IMD: IKK2 inhibitor.
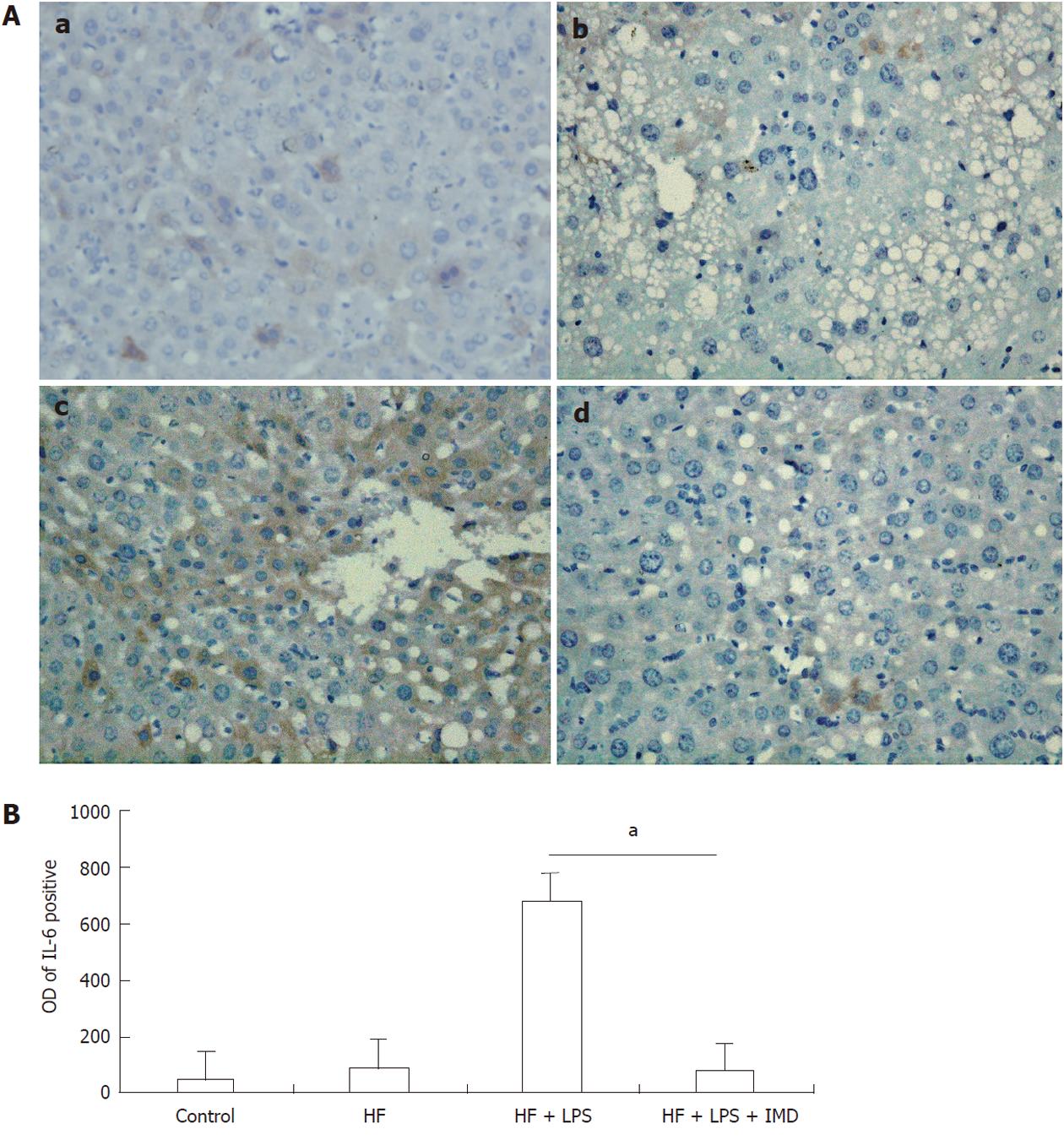
Figure 3 Interleukin-6 expression was assessed by immunohistochemistry.
A: Positive staining was observed in hepatocytes in the control group (a), HF group (b), LPS-induced HF group (c) and IMD-treated group (d). B: The optical density (OD) of interleukin-6 (IL-6)-positive areas was measured with ImageProplu6.0 (aP < 0.05). HF: High-fat; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; IMD: IKK2 inhibitor.
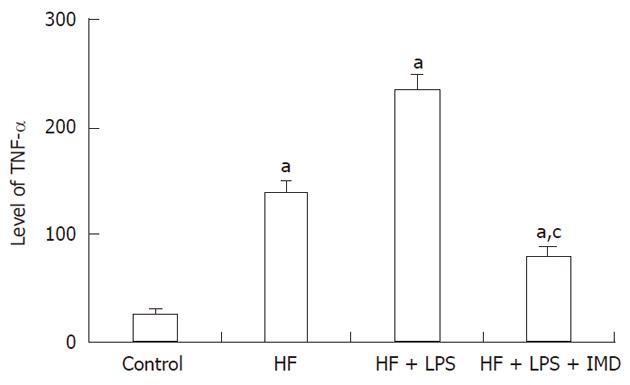
Figure 4 The levels of nuclear factor-κB-dependent pro inflammatory cytokines and tumor necrosis factor-alpha were measured in livers obtained from the control group, HF group, HF + LPS group and HF + LPS + IMD group.
aP < 0.05, compared with the control group. cP < 0.05, significant compared with both the HF and LPS + HF exposed groups. HF: High-fat; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; IMD: IKK2 inhibitor; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
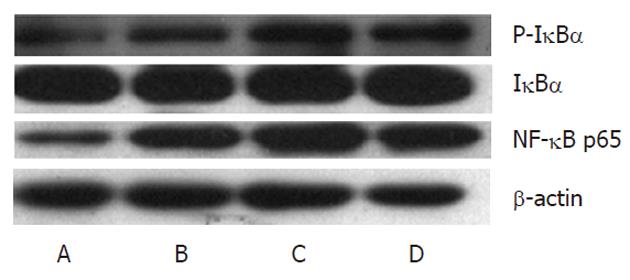
Figure 5 IKK2 inhibitor decreased lipopolysaccharide-induced nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-κB p65 and P-IκBα in livers.
Nuclear levels of the p65 subunit of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) were measured by Western blotting in different groups (A: Control; B: HF group; C: HF + LPS group; D: HF + LPS + IMD group). β-actin was used as a loading control. Administration of IMD at 30 mg/kg doses decreased the DNA binding activity of NF-κB, which was induced by HF and LPS in mice livers. HF: High-fat; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; IMD: IKK2 inhibitor.
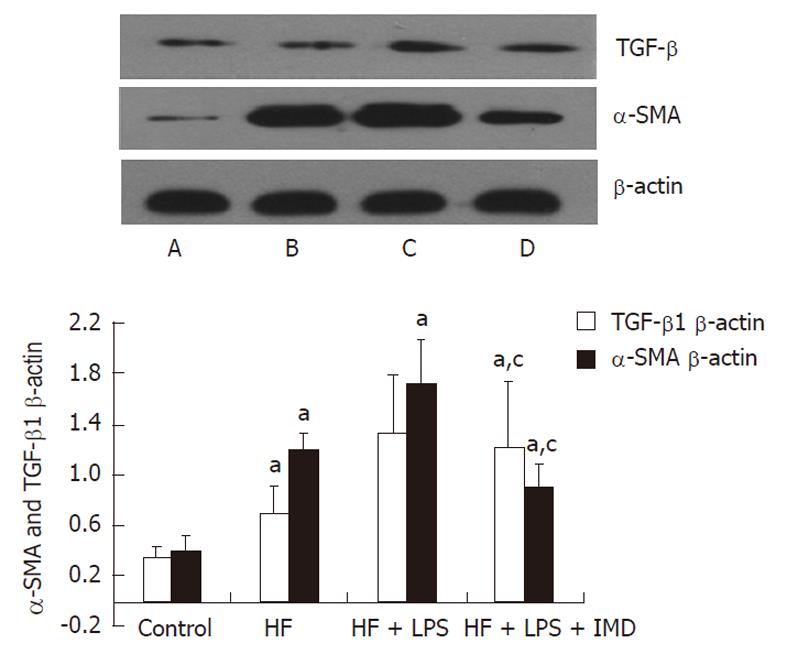
Figure 6 Western blotting analysis of tumor growth factor-beta1, alpha-smooth muscle actin proteins were measured that were involved in IKK2-nuclear factor-κB pathways in the liver in different groups (A: Control; B: HF group; C: HF + LPS group; D: HF + LPS + IMD group).
β-actin was used as a loading control. The levels of tumor growth factor-beta1 (TGF-β1) and alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) measured in livers were increased in the HF and HF + LPS groups. IKK2 inhibitor significantly inhibited LPS and HF-induced expression of TGF-β1 and α-SMA in mouse livers. The ratio of TGF-β1 and α-SMA/β-actin in the liver was increased in other groups, compared with the control group, aP < 0.05. IKK2 inhibitor normalized TGF-β1 and α-SMA significantly compared with the HF or LPS + HF groups. cP < 0.05. HF: High-fat; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; IMD: IKK2 inhibitor.
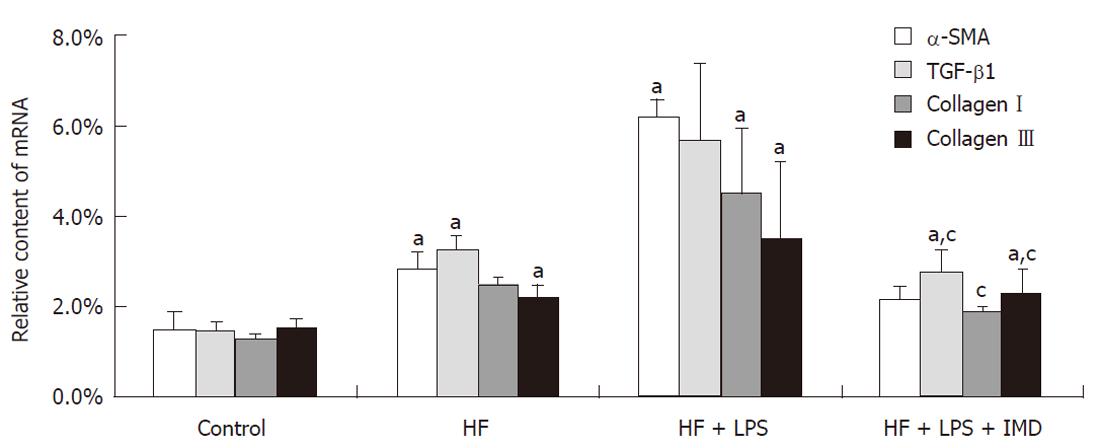
Figure 7 The IKK2 inhibitor inhibited LPS and HF-induced increases in pro inflammatory cytokine levels in mouse livers.
The level of tumor growth factor-beta1 (TGF-β1) was measured in the livers of mice in the control, HF, HF + LPS and HF + LPS + IMD groups. Also, expression of the fibrosis index, such as alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), typeIcollagen and type III collagen, were detected in the four groups by real-time polymerase chain reaction. The level of TGF-β1 measured in livers was increased in the HF and HF + LPS groups, compared with the control group, aP < 0.05. The mRNA content of typeIcollagen in the HF group and type III collagen in the HF + LPS group were significantly higher, aP < 0.05, compared with the control group. Intraperitoneally administered IKK2 inhibitor normalized the expression of TGF-β1, as well as the contents of α-SMA, typeIand type III collagen mRNA, compared with the HF or LPS + HF groups. aP < 0.05, compared with the control group. cP < 0.05, compared with both HF group and LPS + HF exposed group. HF: High-fat; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; IMD: IKK2 inhibitor.
- Citation: Wei J, Shi M, Wu WQ, Xu H, Wang T, Wang N, Ma JL, Wang YG. IκB kinase-beta inhibitor attenuates hepatic fibrosis in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(47): 5203-5213
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i47/5203.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i47.5203