Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2011; 17(43): 4817-4824
Published online Nov 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i43.4817
Published online Nov 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i43.4817
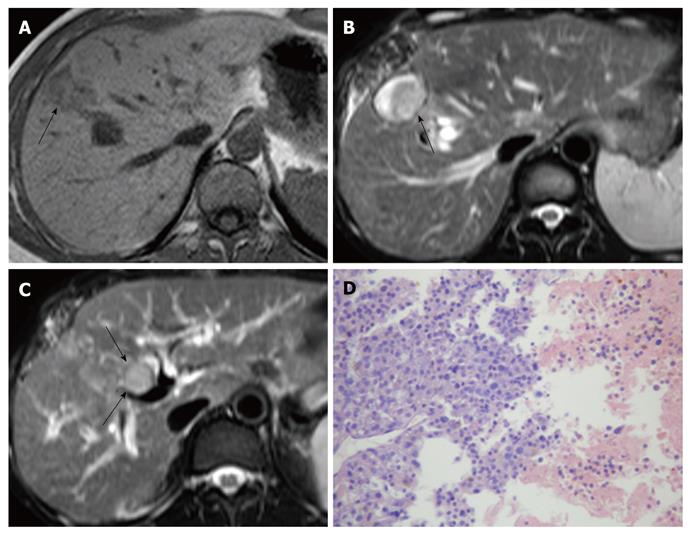
Figure 1 Small hepatocellular carcinoma in a 35-year-old male.
A: T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) shows primary sHCC (arrow) in segment VIII; B: T2-weighted MRI shows an intrahepatic recurrent tumor (arrow) at the margin of the residual cavity following resection of primary sHCC; C: A BDTT (arrows) extending through the intrahepatic bile duct into the common bile duct is depicted in a T2-weighted image; D: Histologically, intrahepatic recurrent tumor and BDTT are moderately differentiated HCC [hematoxylin and eosin (HE), × 100]. sHCC: Small hepatocellular carcinoma; BDTT: Bile duct tumor thrombus; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
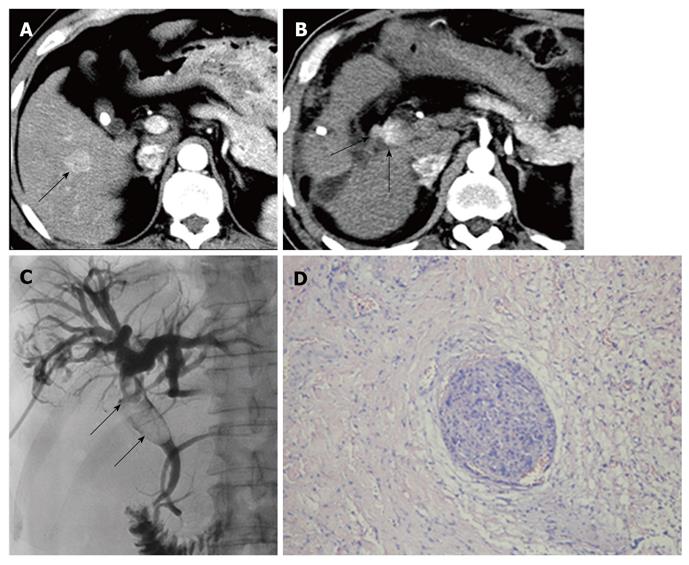
Figure 2 Small hepatocellular carcinoma in a 57-year-old male.
A: Computed tomography (CT) shows primary sHCC (arrow) in segment V at the hepatic arterial phase; B: Forty-seven months after the initial operation, CT reveals a BDTT (arrows) with characteristics of early enhancement at the hepatic arterial phase; C: Tumor thrombus (arrows) extending through the common hepatic duct into the common bile duct is demonstrated during PTCD; D: Cancer nest invasion into the bile duct wall is observed histologically (HE, × 100). sHCC: Small hepatocellular carcinoma; BDTT: Bile duct tumor thrombus; HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; PTCD: Percutaneous transhepatic cholangial drainage.
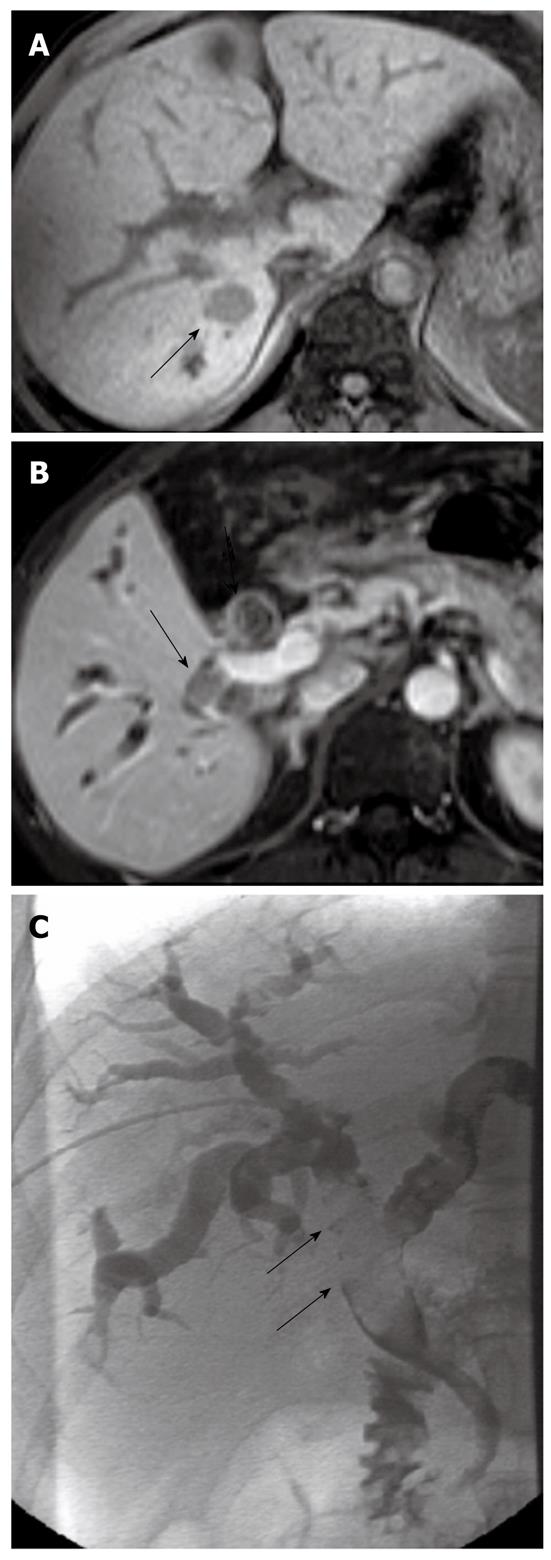
Figure 3 Small hepatocellular carcinoma in a 41-year-old male.
A: T1-weighted MRI shows primary sHCC (arrow) in segment VI; B: A BDTT (arrows) in the right intrahepatic bile duct and the common bile duct is noted on contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRI; C: Filling defect (arrows) in the biliary tree is depicted during percutaneous transhepatic cholangial drainage. MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; sHCC: Small hepatocellular carcinoma; BDTT: Bile duct tumor thrombus.
- Citation: Liu QY, Lai DM, Liu C, Zhang L, Zhang WD, Li HG, Gao M. A special recurrent pattern in small hepatocellular carcinoma after treatment: Bile duct tumor thrombus formation. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(43): 4817-4824
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i43/4817.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i43.4817