Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2011; 17(36): 4135-4142
Published online Sep 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i36.4135
Published online Sep 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i36.4135
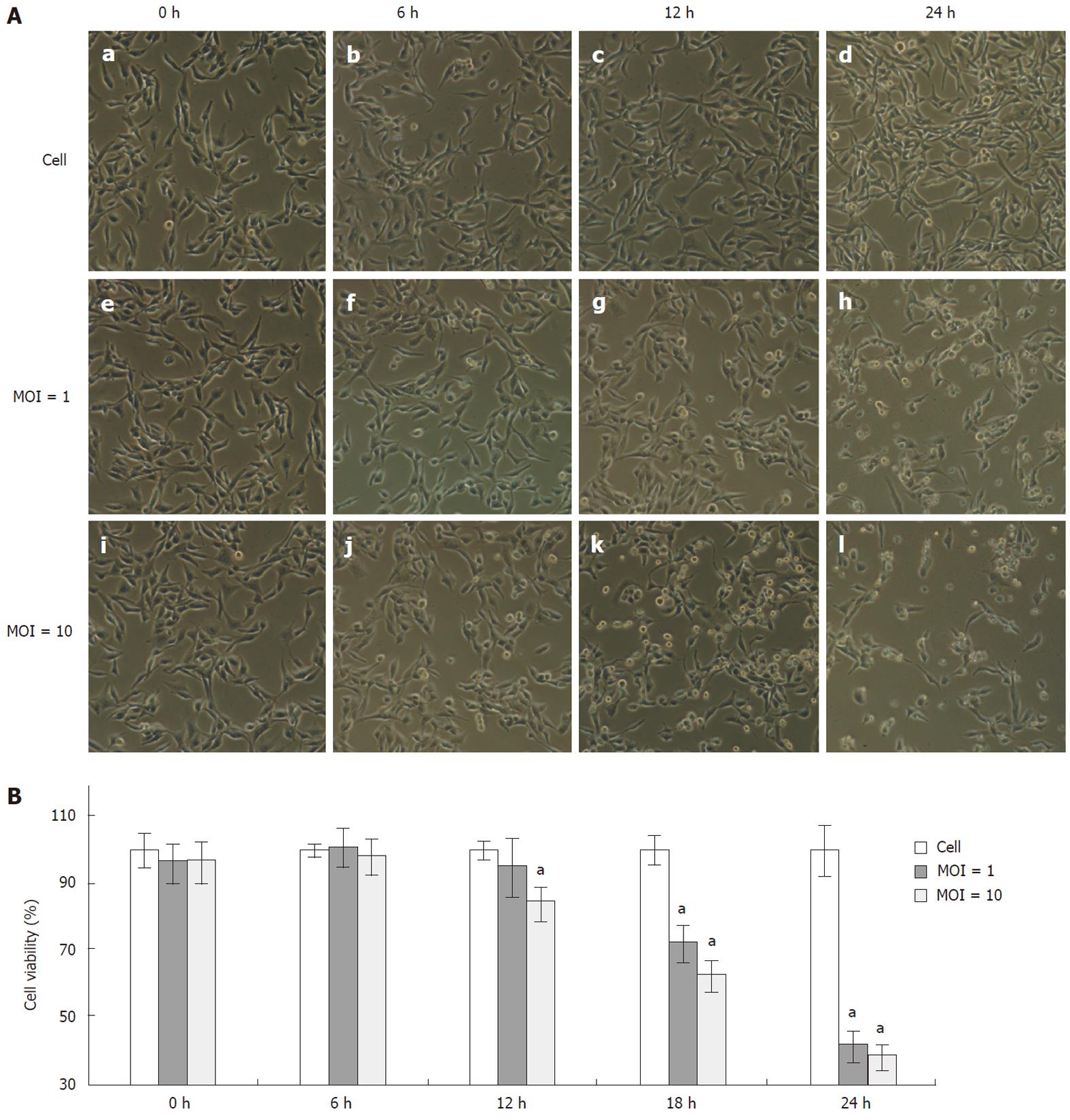
Figure 1 Cytopathic effects and kinetics of cell viability upon enterovirus 71 infection.
Rhabdomyosarcoma cells were infected with enterovirus 71 (EV71) at multiplicity of infection (MOI) 1 or MOI 10. A: The cytopathic effects were shown by cell morphological changes (original magnification, ×100); B: Cell viability was measured by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assays at different time points after EV71 infection. Data are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments, each carried out in triplicate. aP < 0.05.
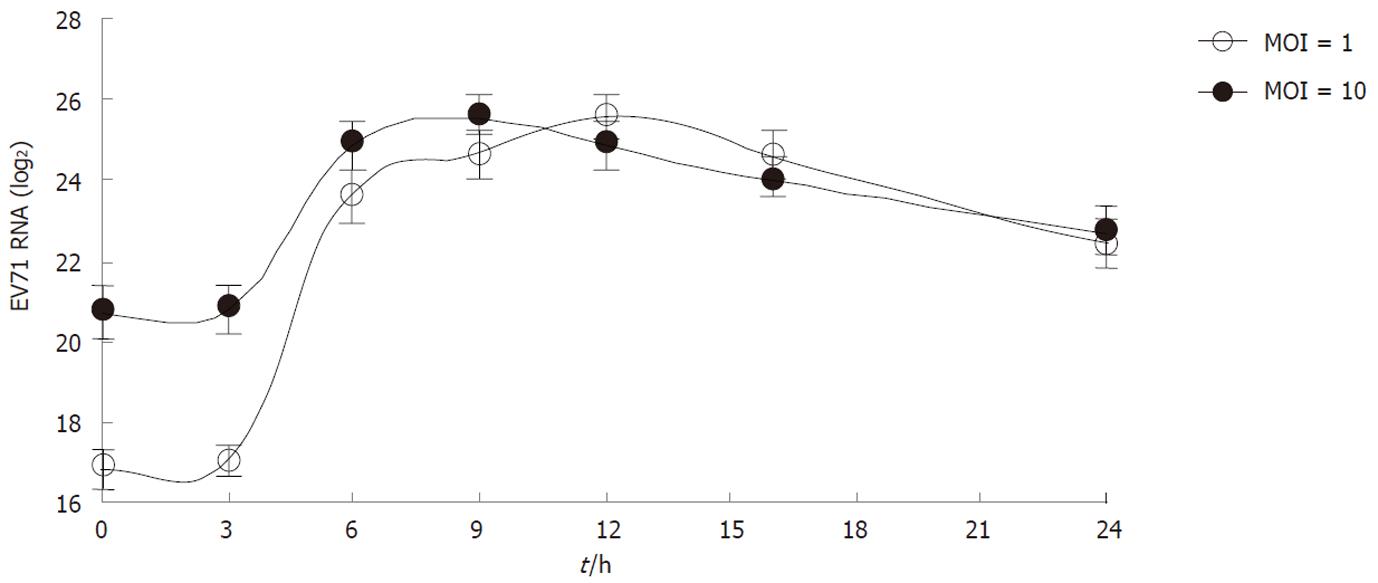
Figure 2 The kinetics of enterovirus 71 Replication.
Rhabdomyosarcoma cells were infected with enterovirus 71 (EV71) virus at multiplicity of infection (MOI) = 1 or MOI = 10. At the indicated time points, the levels of total intracellular viral RNA were measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Data are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments; each carried out in triplicate.
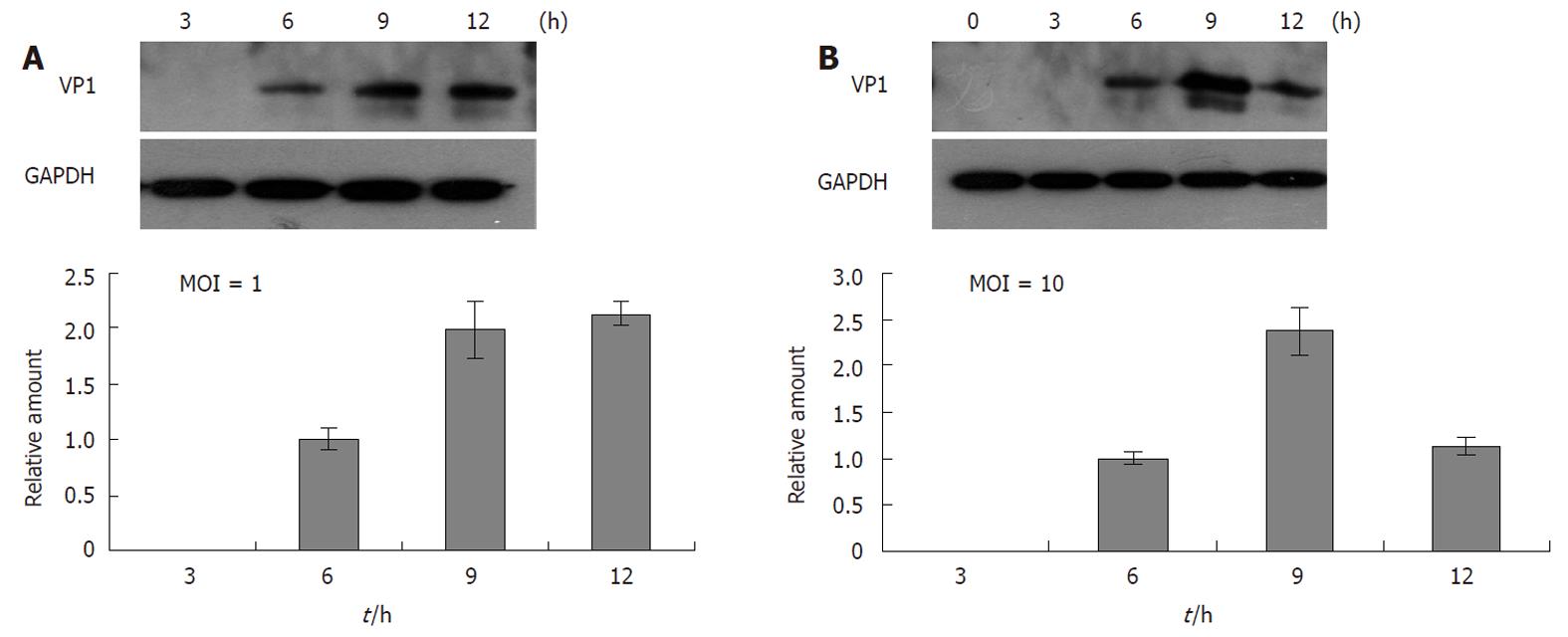
Figure 3 The kinetics of virus VP1 protein synthesis.
Rhabdomyosarcoma cells were infected with enterovirus 71 (EV71) virus at multiplicity of infection (MOI) = 1 (A) and MOI = 10 (B). The intracellular viral protein VP1 was measured by Western blotting. The relative VP1 levels (the density of VP1/GAPDH) were calculated and are shown as solid bars.
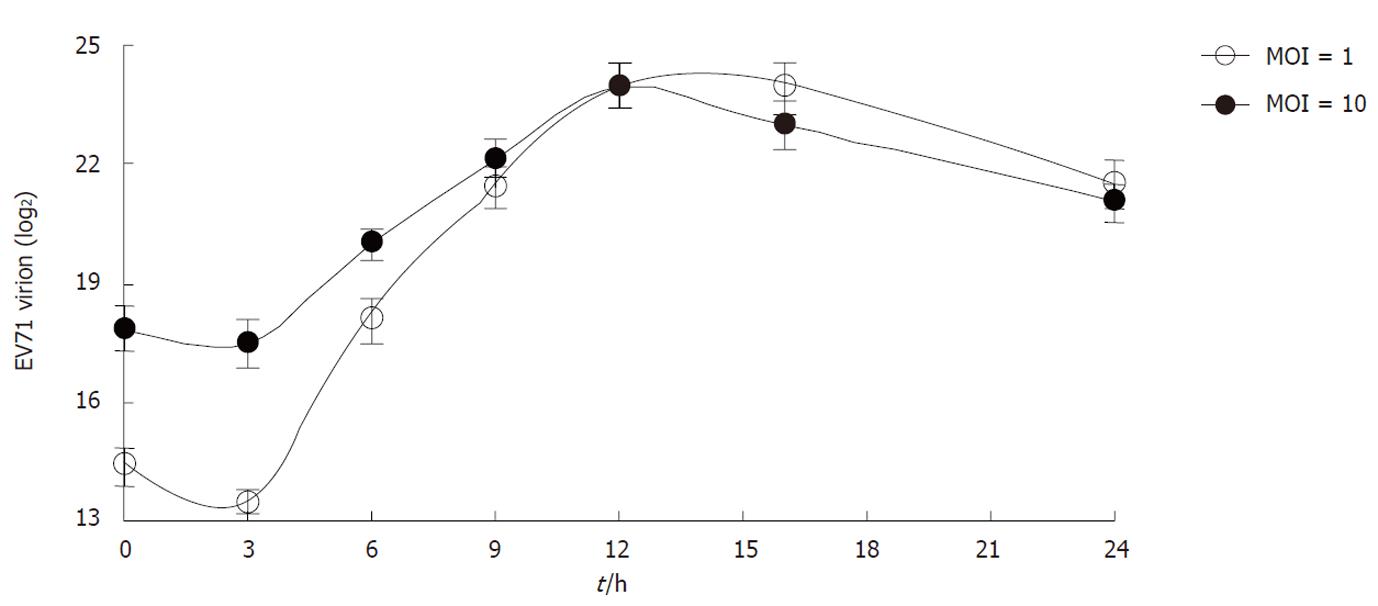
Figure 4 The kinetics of enterovirus 71 virus package.
Rhabdomyosarcoma cells were infected with enterovirus 71 (EV71) virus at multiplicity of infection (MOI) = 1 or MOI = 10. The intracellular virus particles were isolated to measure the virion RNA by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Data are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments; each carried out in triplicate.
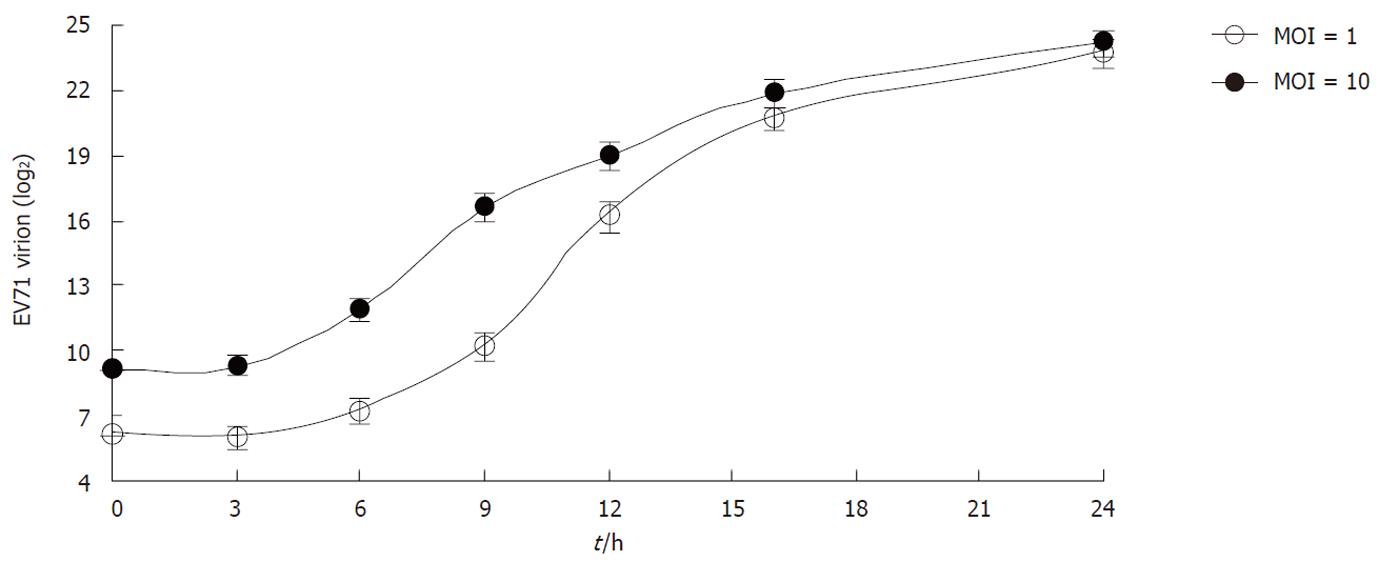
Figure 5 The kinetics of enterovirus 71 virus secretion.
Rhabdomyosarcoma cells were infected with enterovirus 71 (EV71) virus at multiplicity of infection (MOI) = 1 or MOI = 10. Extracellular EV71 virions in the culture media were measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction at different time points post infection. Data are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments; each carried out in triplicate.
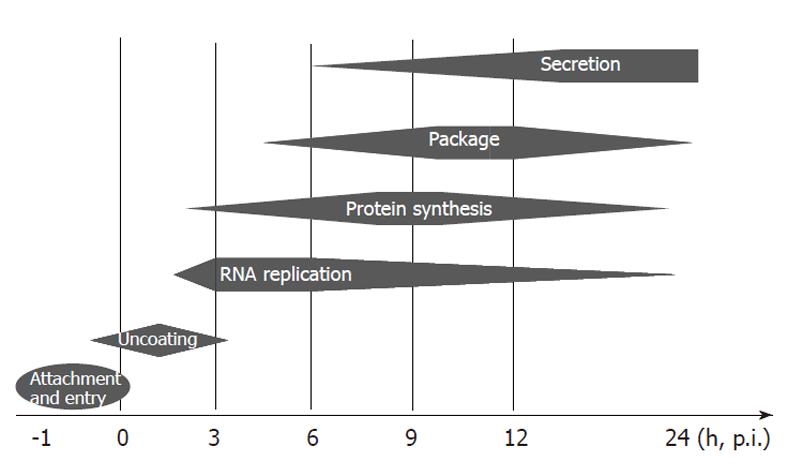
Figure 6 Schematic view of enterovirus 71 activities in rhabdomyosarcoma cells.
Within one hour of inoculation, enterovirus 71 would first attach and enter into the host cell via its specific receptors. The virus was then uncoated in the first 3 h and started to synthesize the essential viral proteins for replication. From 3 to 6 h p.i., the virus rapidly replicated its genomic RNA and initiated structure protein synthesis. Fast viral package was observed from 6 to 12 h p.i. and virion secretion increased from 6 h p.i. to the end of the observation period.
- Citation: Lu J, He YQ, Yi LN, Zan H, Kung HF, He ML. Viral kinetics of Enterovirus 71 in human abdomyosarcoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(36): 4135-4142
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i36/4135.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i36.4135