Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2011; 17(36): 4055-4062
Published online Sep 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i36.4055
Published online Sep 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i36.4055
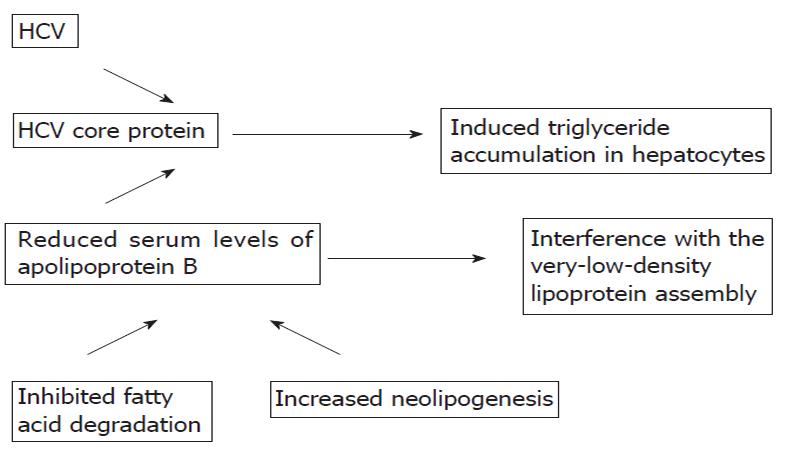
Figure 1 Underlying mechanisms of the complex interaction resulting in steatosis in patients with hepatitis C virus.
HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
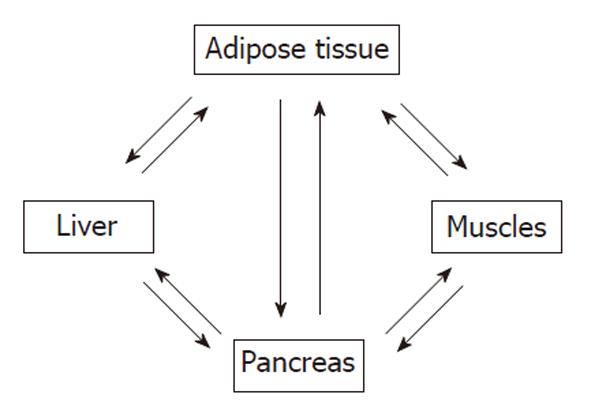
Figure 2 Cross-talk among the insulin sensitive organs.
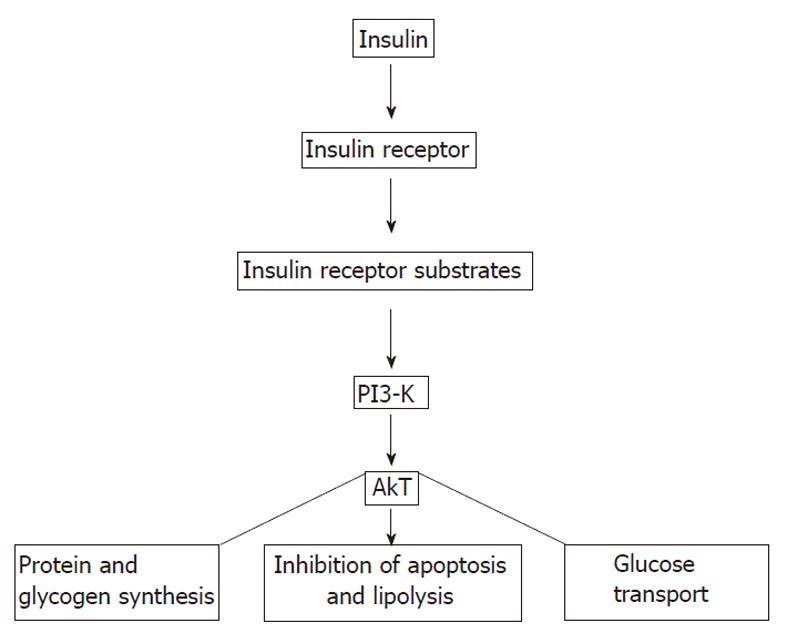
Figure 3 Insulin signaling pathways.
PI3-K: Phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase; AkT: A serine/threonine protein kinase.
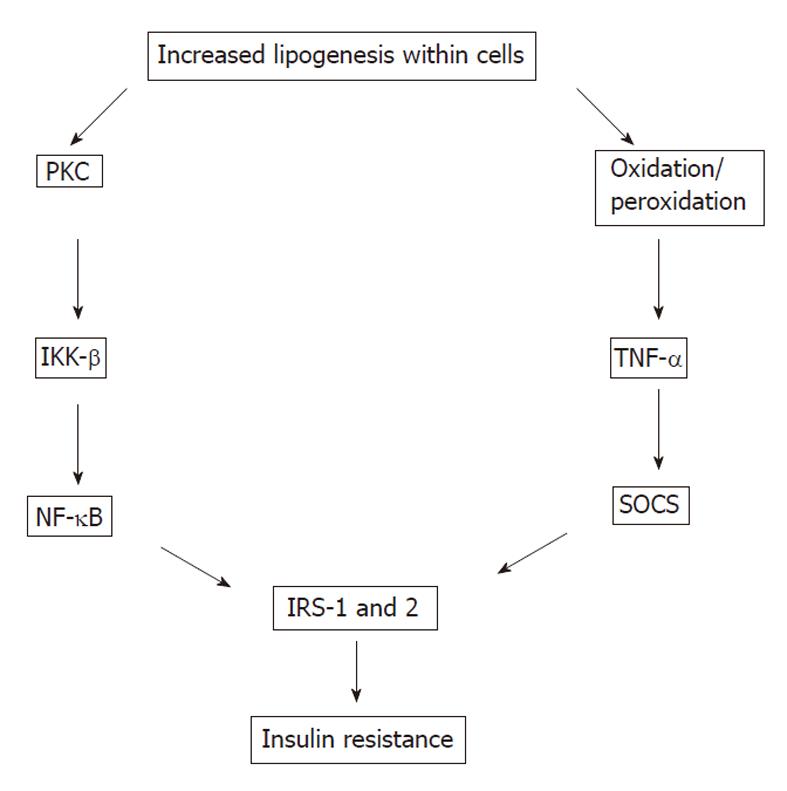
Figure 4 Pathways to insulin resistance.
PKC: Protein kinase C; IKK: Inhibitor κB kinase; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; NF: Nuclear factor; SOCS: Suppressors of cytokine signaling; IRS: Insulin receptor substrate.
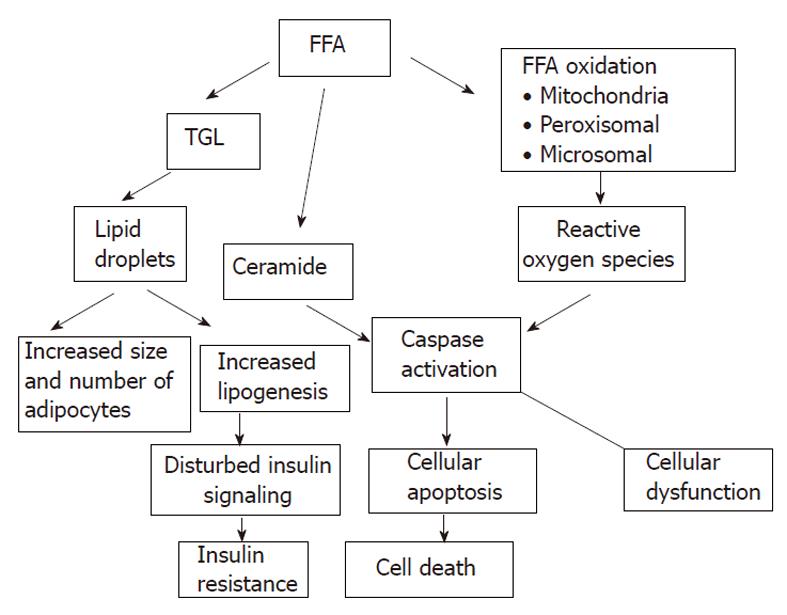
Figure 5 Insulin resistance and cell death.
FFA: Free fatty acids; TGL: Tryglycerides.
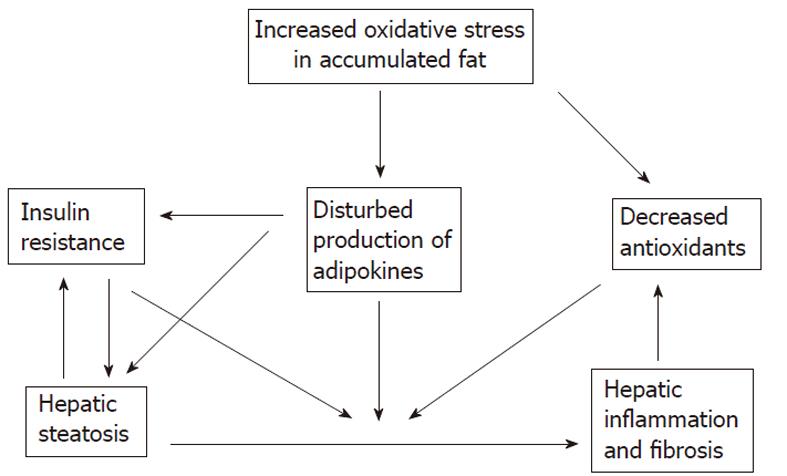
Figure 6 Fate of accumulated fat within hepatocytes.
- Citation: Basaranoglu M, Basaranoglu G. Pathophysiology of insulin resistance and steatosis in patients with chronic viral hepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(36): 4055-4062
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i36/4055.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i36.4055