Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2011; 17(20): 2536-2542
Published online May 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i20.2536
Published online May 28, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i20.2536
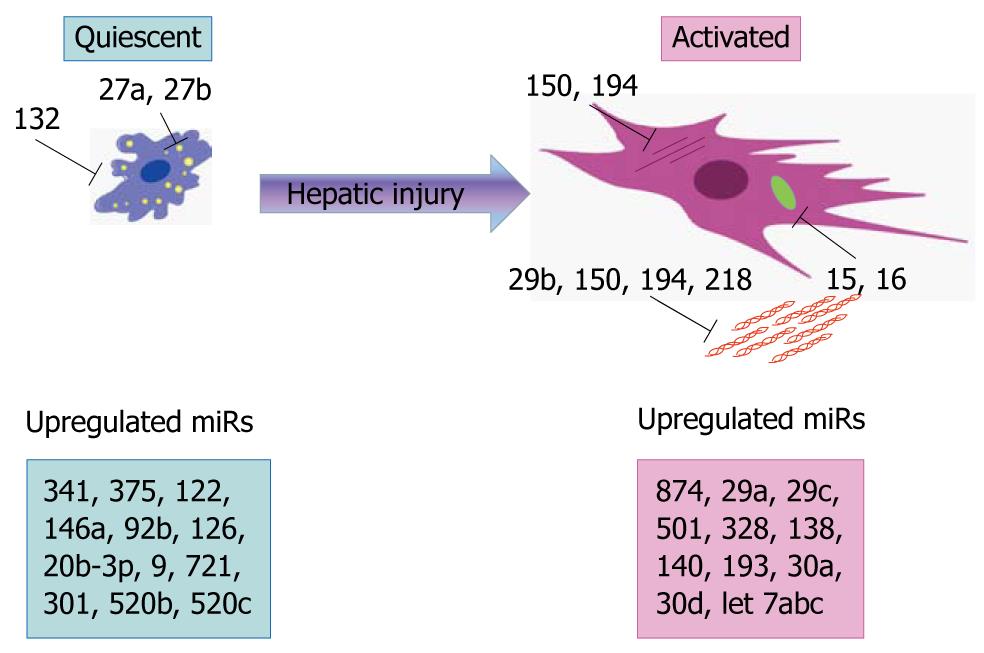
Figure 1 microRNAs involved in hepatic stellate cell transdifferentiation.
Functional manipulation studies utilizing mimics and/or antagomirs have demonstrated that the miRs depicted in the above schematic regulate key genes/functions in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). (Quiescent HSC: yellow circles represent cytoplasmic lipid droplets; activated HSC: purple lines indicate cytoskeletal protein smooth muscle alpha actin; green oval represents Bcl-2; red fibrils represent collagen). Additional profiling studies have shown upregulation of several microRNAs (miRs) in both phenotypes, some of which are already associated with hepatic disease (boxes contain a small fraction of published miRs). References[38-43,47] were used to generate the contents of this figure with design software BioDraw Ultra 12.0.
- Citation: Lakner AM, Bonkovsky HL, Schrum LW. microRNAs: Fad or future of liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(20): 2536-2542
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i20/2536.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i20.2536