Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2011; 17(17): 2241-2247
Published online May 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i17.2241
Published online May 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i17.2241
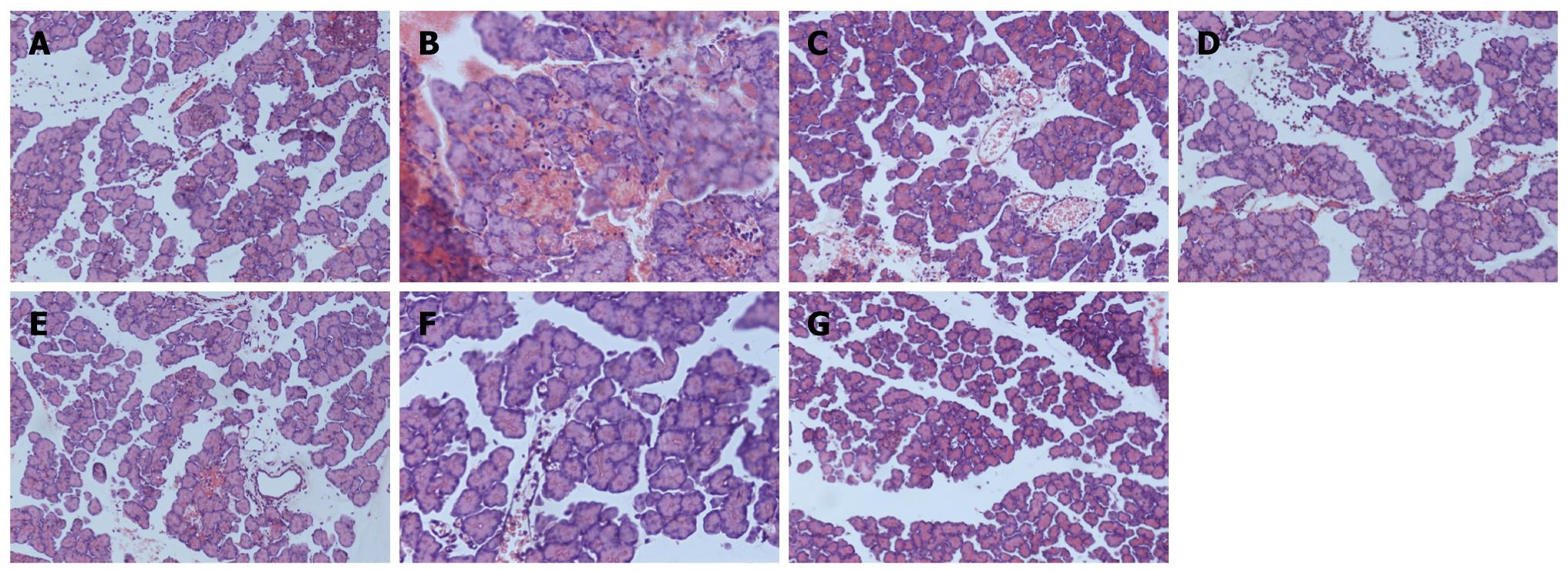
Figure 1 Pathological change of pancreatic tissues (HE staining, × 200).
A: Sham-operation group; B: Severe acute pancreatitis group; C: DMSO group; D: 2.5 mg/kg BN52021 group; E: 5.0 mg/kg BN52021 group; F: 10 mg/kg BN52021 group; G: 20 μg/kg Sandostatin group.
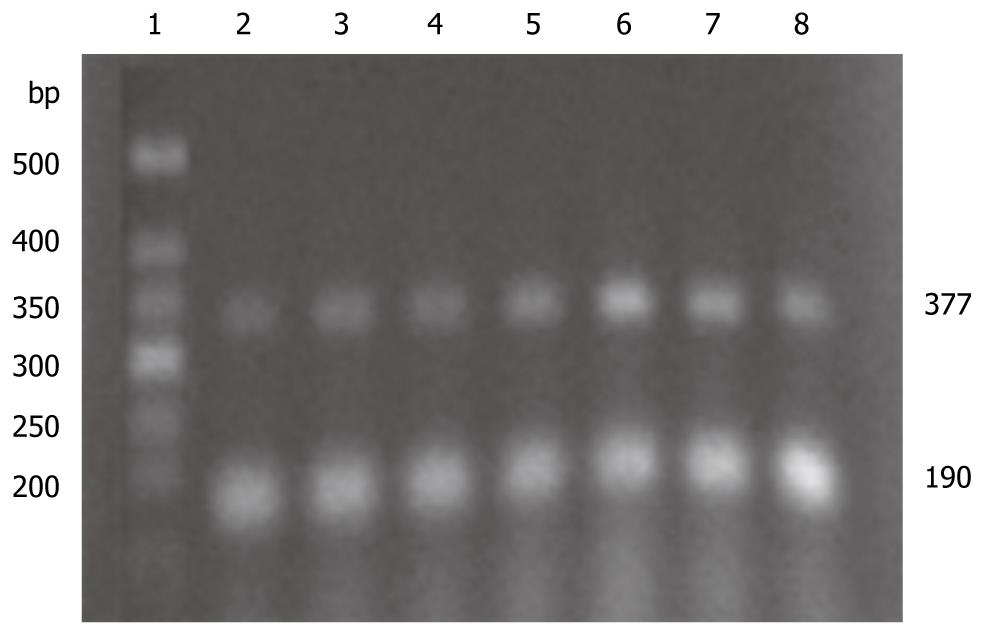
Figure 2 Expression of platelet activating factor receptor mRNA in pancreatic tissues by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.
1: Marker; 2: Sham-operation group; 3: Severe acute pancreatitis group; 4: DMSO group; 5: 2.5 mg/kg BN52021 group; 6: 5.0 mg/kg BN52021 group; 7: 10 mg/kg BN52021 group; 8: 20 μg/kg Sandostatin group.
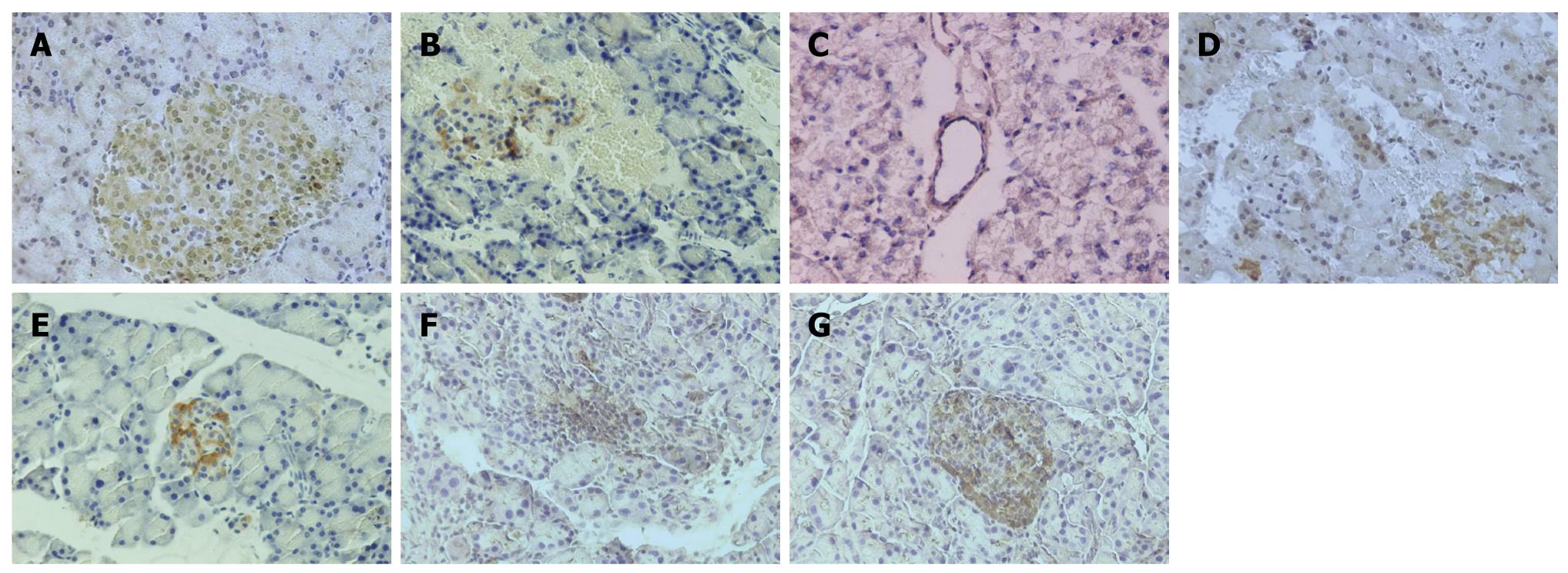
Figure 3 Expression of platelet activating factor receptor in pancreatic tissues by immunohistochemistry (HE staining, × 200).
A: Sham-operation group; B: Severe acute pancreatitis group; C: DMSO group; D: 2.5 mg/kg BN52021 group; E: 5.0 mg/kg BN52021 group; F: 10 mg/kg BN52021 group; G: 20 μg/kg Sandostatin group.
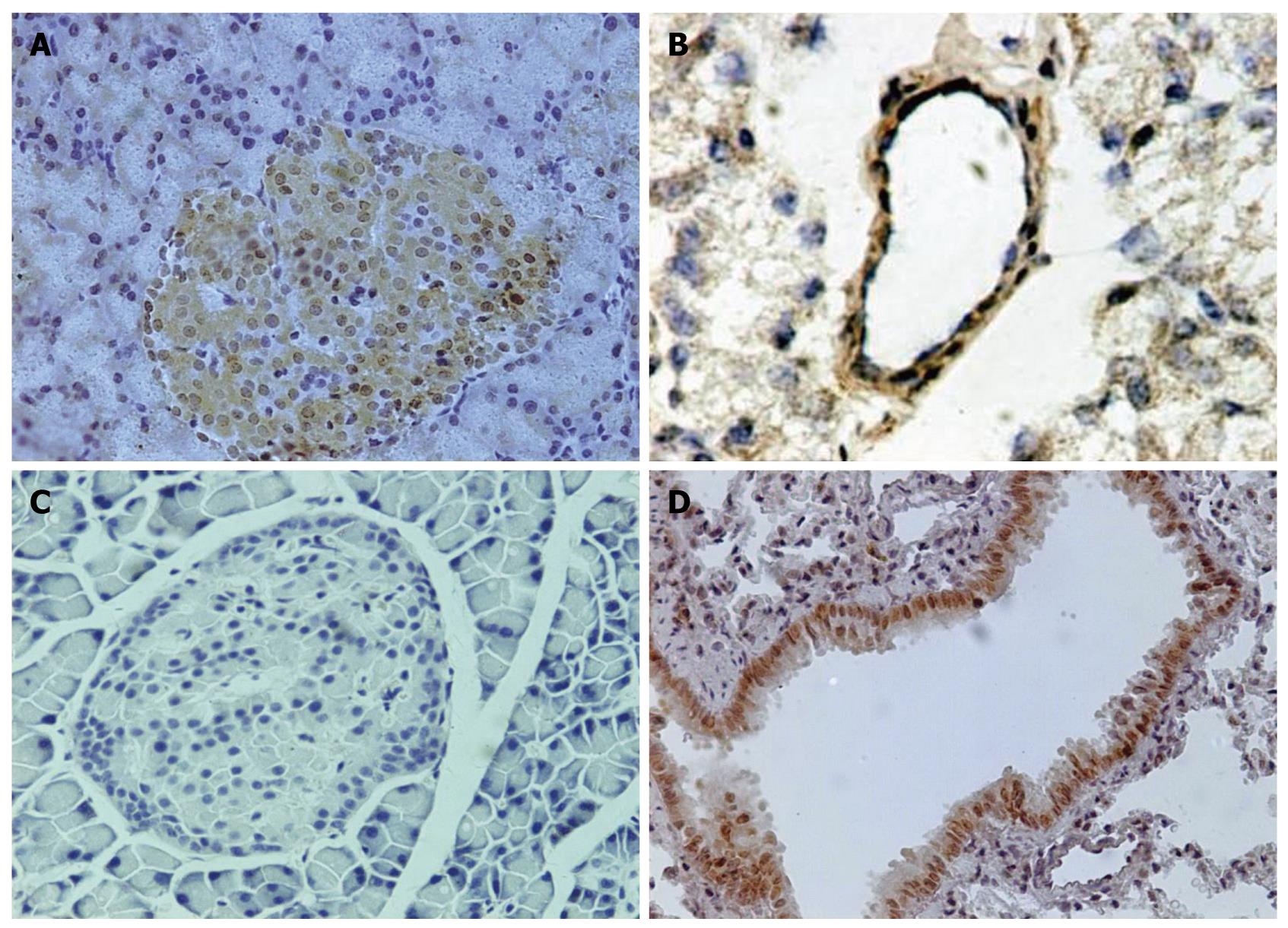
Figure 4 Location of platelet activating factor receptor in pancreatic and lung tissues in sham-operation group shown by immunohistochemistry (HE staining, × 200).
A: Paraffin slice of pancreatic tissues; B: Frozen slice of pancreatic tissues; C: Negative control of pancreatic tissues; D: Positive control of lung tissues.
- Citation: Ji RL, Xia SH, Di Y, Xu W. Mechanism and dose-effect of Ginkgolide B on severe acute pancreatitis of rats. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(17): 2241-2247
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i17/2241.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i17.2241