Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2011; 17(13): 1701-1709
Published online Apr 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i13.1701
Published online Apr 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i13.1701
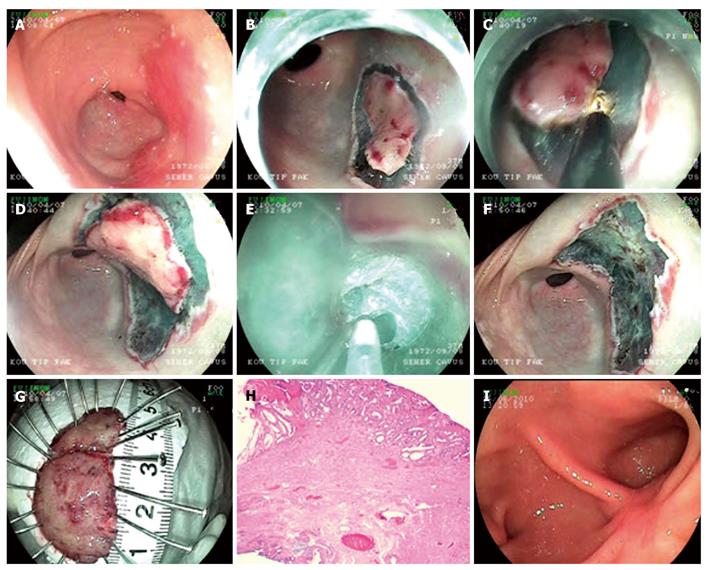
Figure 1 Endoscopic submucosal dissection procedure for adenoma with high grade dysplasia at antrum.
A: Endoscopic view flat adenoma at antrum; B: Cutting of the first piece of the lesion which was decided to be extracted in two pieces; C: Submucosal dissection of the first piece; D: Cutting of the second piece of the lesion; E: Submucosal dissection of the second piece; F: Endoscopic view after the lesion is being extracted; G: Microscopic view of the lesion; H: Histology; Adenoma including fields of marked glandular atypia and distortion (HE × 20); I: Endoscopic view ten weeks after the procedure.
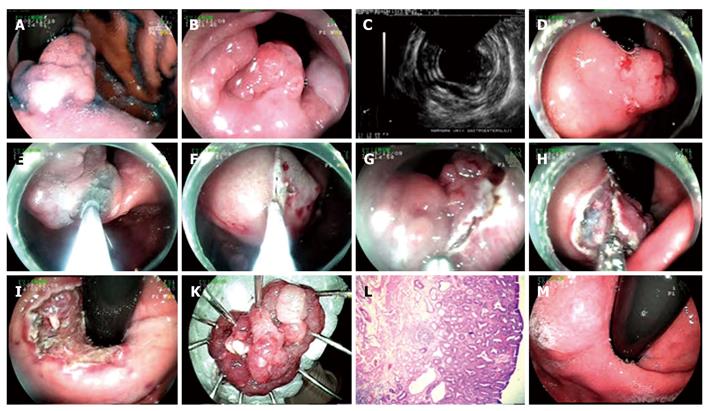
Figure 2 Endoscopic submucosal dissection procedure for adenoma with high grade dysplasia at cardia.
A: Adenoma at cardia; B: View of the lesion from esophageal aspect; C: Endosonographic image of the lesion; D, E: Marking the borders of the lesion with needle knife and lifting it; F, G: Cutting the lesion circumferentially with endo-cut above Z line, in retroflexion; H: Dissection of the submucosal area; I: Appearance of the mucosa after the lesion being extracted; K: Microscopic view of the lesion; L: Histology: mucosa, muscularis mucosa and superficial submucosa of stomach (HE × 20). Adenoma structure including adenomatous epithelium formed by irregular glands at mucosa; M: Endoscopic view six months after the procedure.
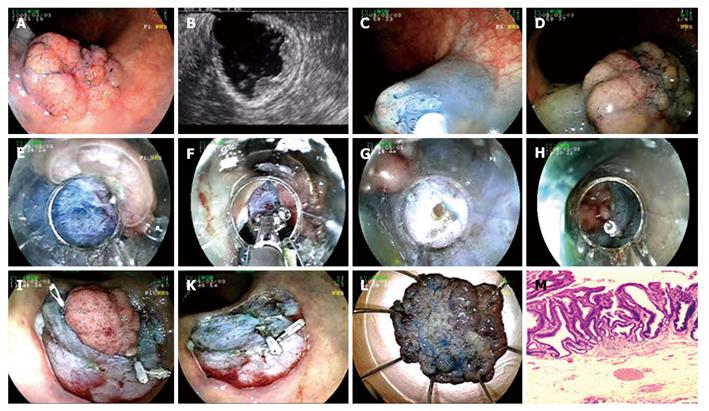
Figure 3 Endoscopic submucosal dissection procedure for tubulovillous adenoma with high grade dysplasia at sigmoid colon.
A: Adenoma at sigmoid colon; B: Endosonographic image of tubulovillous adenoma; C-D: Lifting the lesion; E: Cutting with endo-cut; F: Coagulation of submucosal vein with hemostatic forceps; G: Mini perforation during the procedure; H: Fixing perforation with hemoclip; I: Hemoclip application to control bleeding that occured after cutting the lesion circumferentially with endo-cut; K: Appearance of the mucosa after the lesion being extracted; L: Microscopic view of the lesion; M: Histology; tubulovillous adenoma with high grade dysplasia (HE × 40).
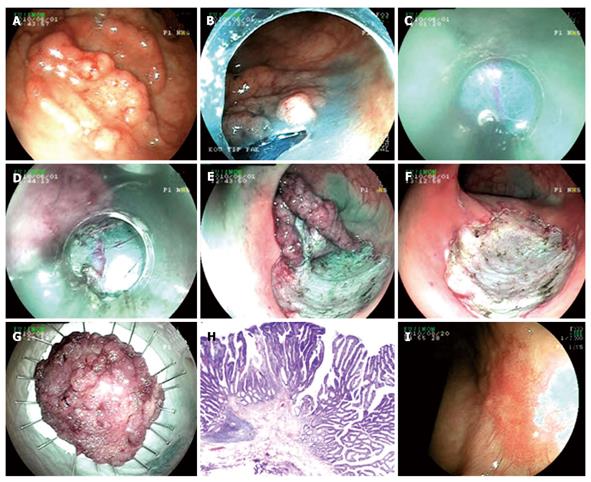
Figure 4 Endoscopic submucosal dissection procedure for pseudo-depressed type lateral spreading tumor with high grade dysplasia at rectum.
A: Pseudo-depressed type lateral spreading tumor at rectum; B: Cutting the lesion circumferentially with endo-cut; C, D: Submucosal dissection with semipermeable cap; E: Endoscopic view just before completing submucosal dissection; F: Appearance of the mucosa after the lesion being extracted; G: Microscopic view of the lesion; H: Histology; tubulovillous adenoma including fields of focal pattern loss and dysplasia (HE × 20); I: Endoscopic view ten weeks after the procedure.
- Citation: Hulagu S, Senturk O, Aygun C, Kocaman O, Celebi A, Konduk T, Koc D, Sirin G, Korkmaz U, Duman AE, Bozkurt N, Dindar G, Attila T, Gurbuz Y, Tarcin O, Kalayci C. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for premalignant lesions and noninvasive early gastrointestinal cancers. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(13): 1701-1709
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i13/1701.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i13.1701