Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2010; 16(48): 6145-6150
Published online Dec 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i48.6145
Published online Dec 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i48.6145
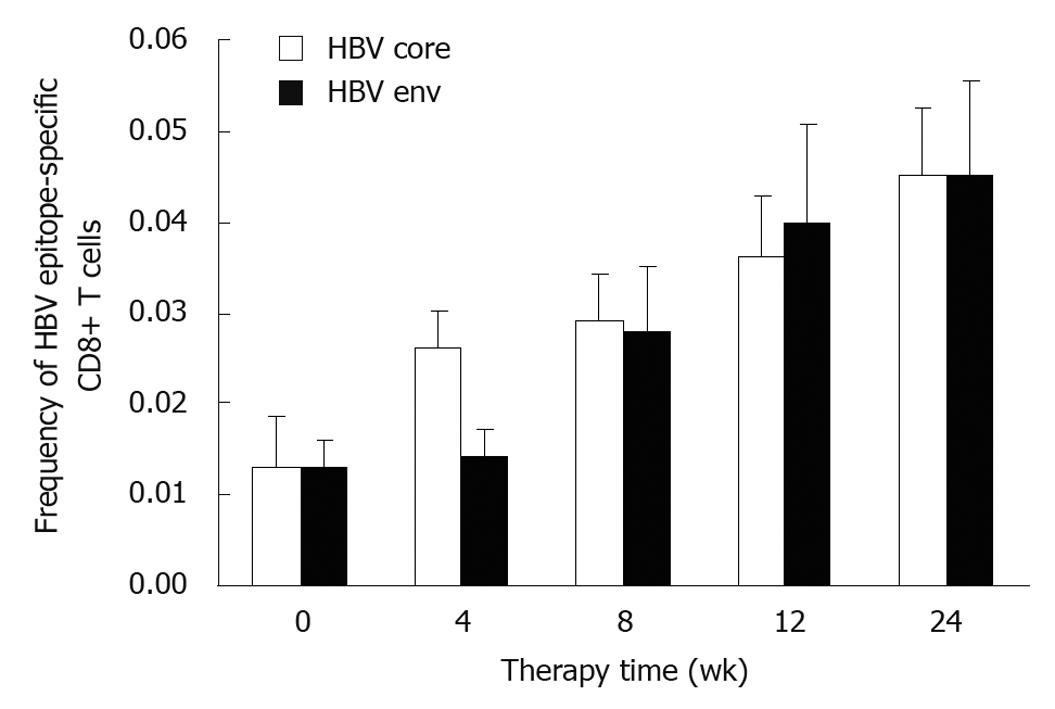
Figure 1 Frequency of hepatitis B virus epitope tetramer+/CD8+ T cell after pegylated interferon α-2b treatment.
The frequency of hepatitis B virus (HBV) specific CD8+ T cells was increased connectively at weeks 4, 8, 12 and 24 after pegylated interferon α-2b treatment with no difference in frequency of HBV core specific CD8+ T cells and HBV env specific T cells.
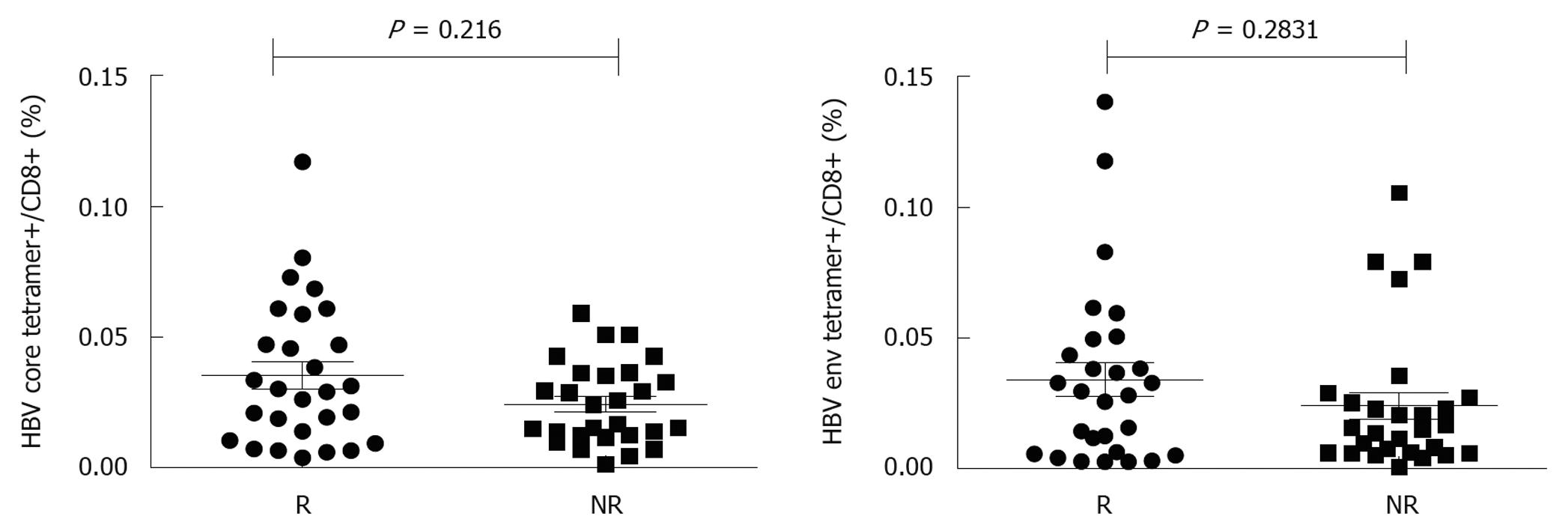
Figure 2 No correlation between increased hepatitis B virus epitope-specific CD8+ T cells and treatment outcome.
The frequency of hepatitis B virus (HBV) core or env epitope-specific CD8+ T cells was higher in non-responders (NR) than in responders (R).
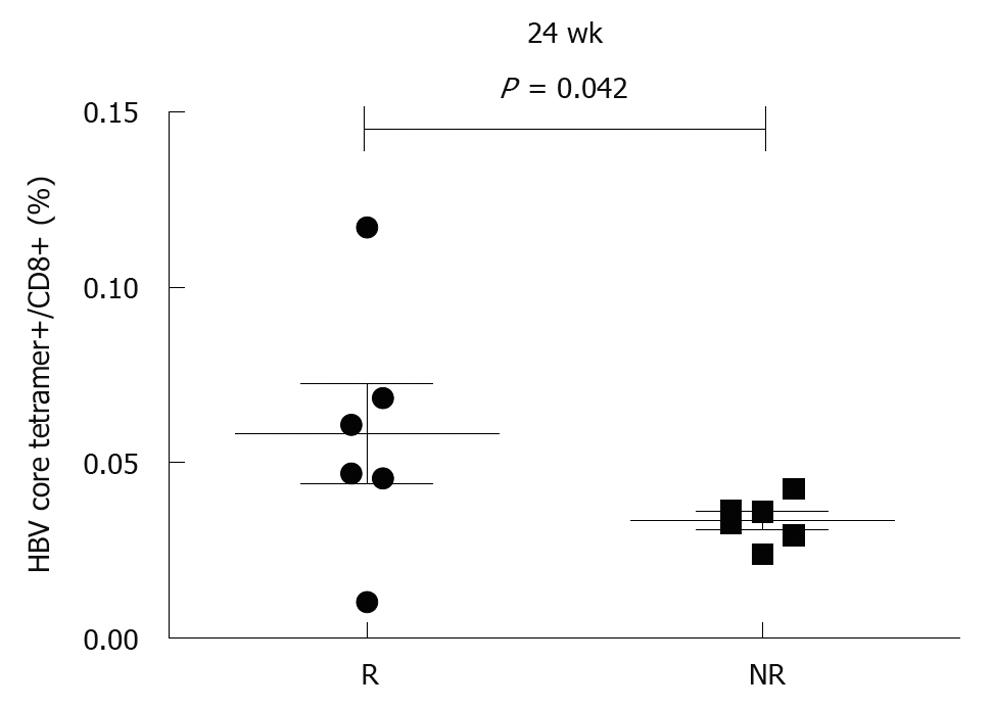
Figure 3 Correlation between increased hepatitis B virus specific T cells and treatment response 24 wk after therapy.
The frequency of hepatitis B virus (HBV) core epitope-specific CD8+ T cells at week 24 was higher in responders (R) than in non-responders (NR).
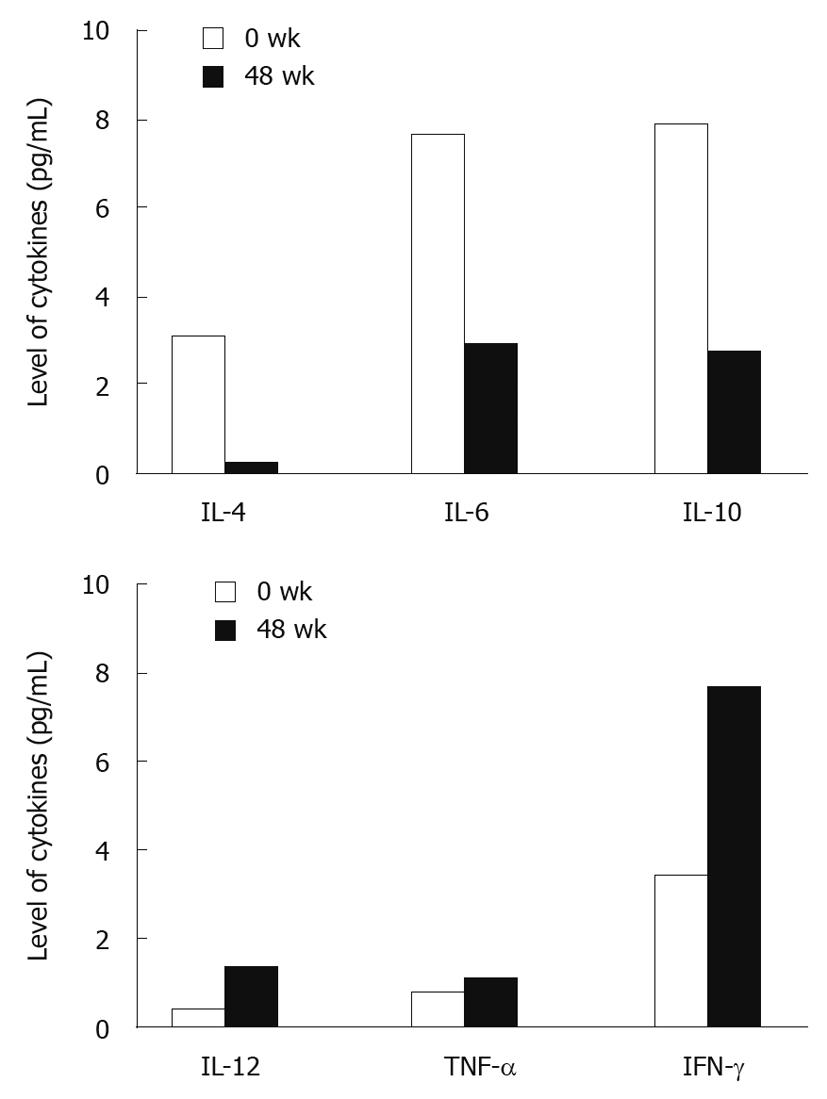
Figure 4 Level of cytokines after treatment.
The levels of Th1-type cytokines [interleukin (IL)-12, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interferon (IFN)-γ] were higher, while the levels of Th2-type cytokines (IL-4, IL-6 and IL-10) were lower at week 48 after treatment.
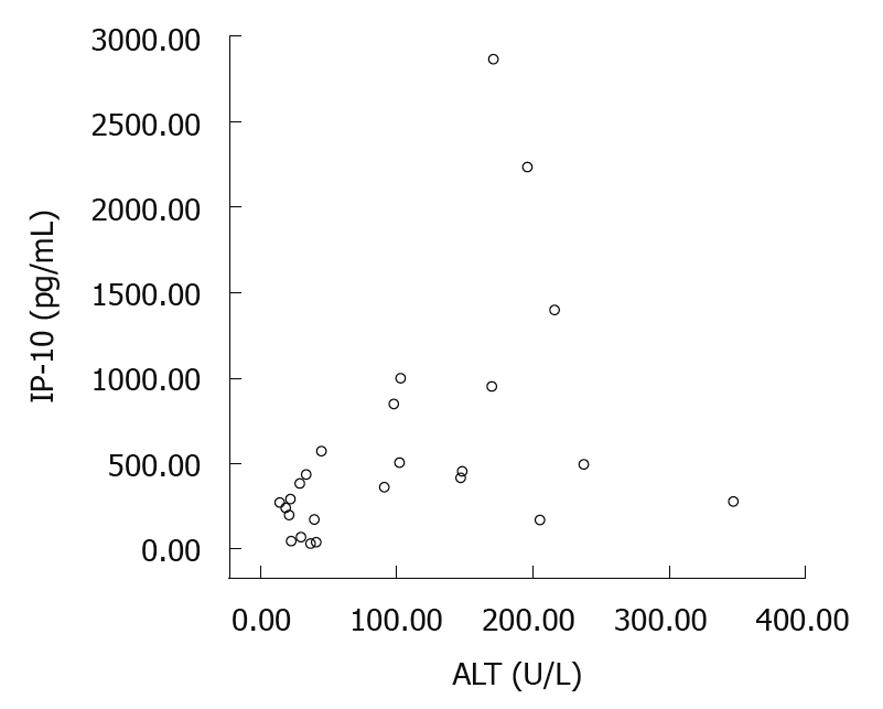
Figure 5 Positive correlation between alanine aminotransferase and inducible protein-10 levels (r = 0.
545, P = 0.005). ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; IP-10: Inducible protein-10.
- Citation: Chen J, Wang Y, Wu XJ, Li J, Hou FQ, Wang GQ. Pegylated interferon α-2b up-regulates specific CD8+ T cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(48): 6145-6150
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i48/6145.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i48.6145