Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2010; 16(45): 5716-5721
Published online Dec 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i45.5716
Published online Dec 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i45.5716
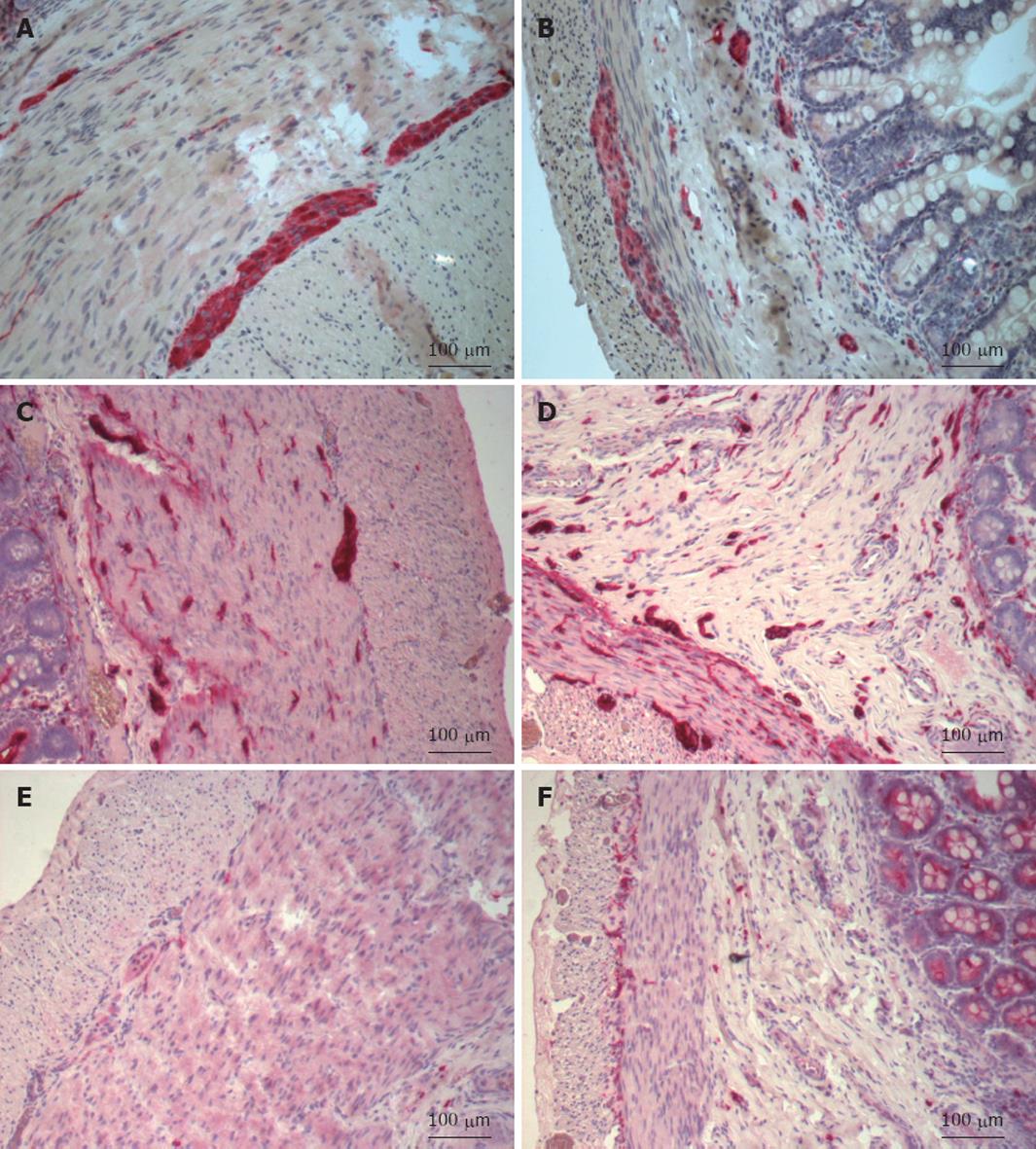
Figure 1 Immunohistochemistry of a full-thickness section of the ileum.
A: Protein gene product (PGP) 9.5 in the ileum proximal to the atresia shows a dense innervation within the submucosal and myenteric plexus; B: PGP 9.5 in the ileum distal to the atresia shows a normal innervation pattern of the submucosal and myenteric plexuses; C: S-100 in the ileum proximal to the atresia shows numerous fibers and large ganglia (> 20 μm) within the submucosal plexus and normal innervation within the myenteric plexus; D: S-100 in the ileum distal to the atresia shows a normal innervation pattern within the submucosal and myenteric plexuses; E: c-kit in the ileum proximal to the atresia shows that myenteric and muscular interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) are almost absent; F: c-kit in the ileum distal to the atresia shows normal distribution of myenteric and muscular ICCs.
- Citation: Gfroerer S, Metzger R, Fiegel H, Ramachandran P, Rolle U. Differential changes in intrinsic innervation and interstitial cells of Cajal in small bowel atresia in newborns. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(45): 5716-5721
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i45/5716.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i45.5716