Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2010; 16(42): 5388-5390
Published online Nov 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i42.5388
Published online Nov 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i42.5388
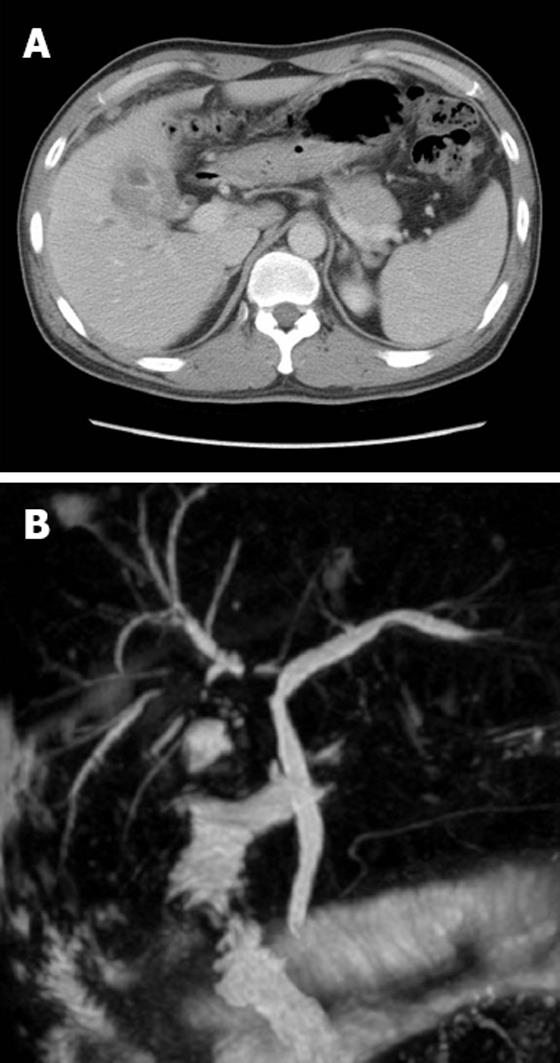
Figure 1 Abdominal computed tomography.
A: Diffuse low-attenuated wall thickening of the gallbladder; B: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography reveals a severe segmental stricture of the right intrahepatic bile duct with mild upstream duct dilatation.
Figure 2 Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography shows severe narrowing of the right proximal intrahepatic bile duct and slight narrowing of the common hepatic duct.
Figure 3 Endoscopic images.
A: A C2 catheter in the duodenum; B: A view of end-to-end contact between the tips of the guidewire-preloaded sphincterotome and C2 catheter (arrows) at the ampulla’s orifice.
Figure 4 Fluoroscopic views.
A: The guidewire passed into the right intrahepatic bile duct through the C2 catheter after end-to-end contact (arrows); B: Simultaneously, the sphincterotome was pushed into the common bile duct and the C2 catheter was pulled out (arrows); C: Finally, the C2 catheter was removed.
- Citation: Lee TH, Park SH, Lee SH, Lee CK, Lee SH, Chung IK, Kim HS, Kim SJ. Modified rendezvous intrahepatic bile duct cannulation technique to pass a PTBD catheter in ERCP. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(42): 5388-5390
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i42/5388.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i42.5388