Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2010; 16(41): 5195-5202
Published online Nov 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i41.5195
Published online Nov 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i41.5195
Figure 1 Expression of β-catenin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissue samples (magnification × 400).
A: Immunohistochemical staining of β-catenin in cytoplasm and membrane of cancer cells (immunohistochemistry score: 15); B: Immunohistochemical staining of β-catenin in cytoplasm of cancer cells (immunohistochemistry score: 3).
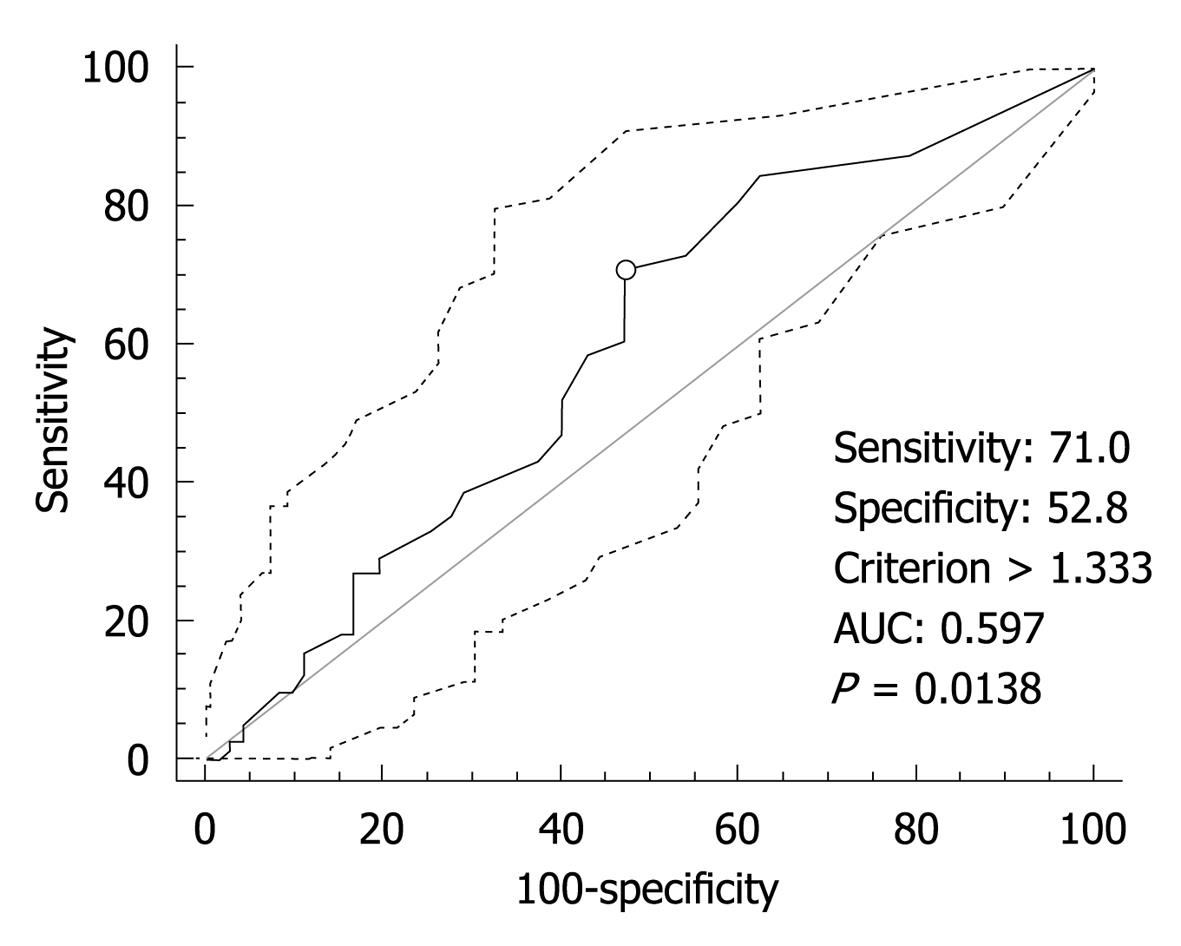
Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis of β-catenin and selection of cut-off score.
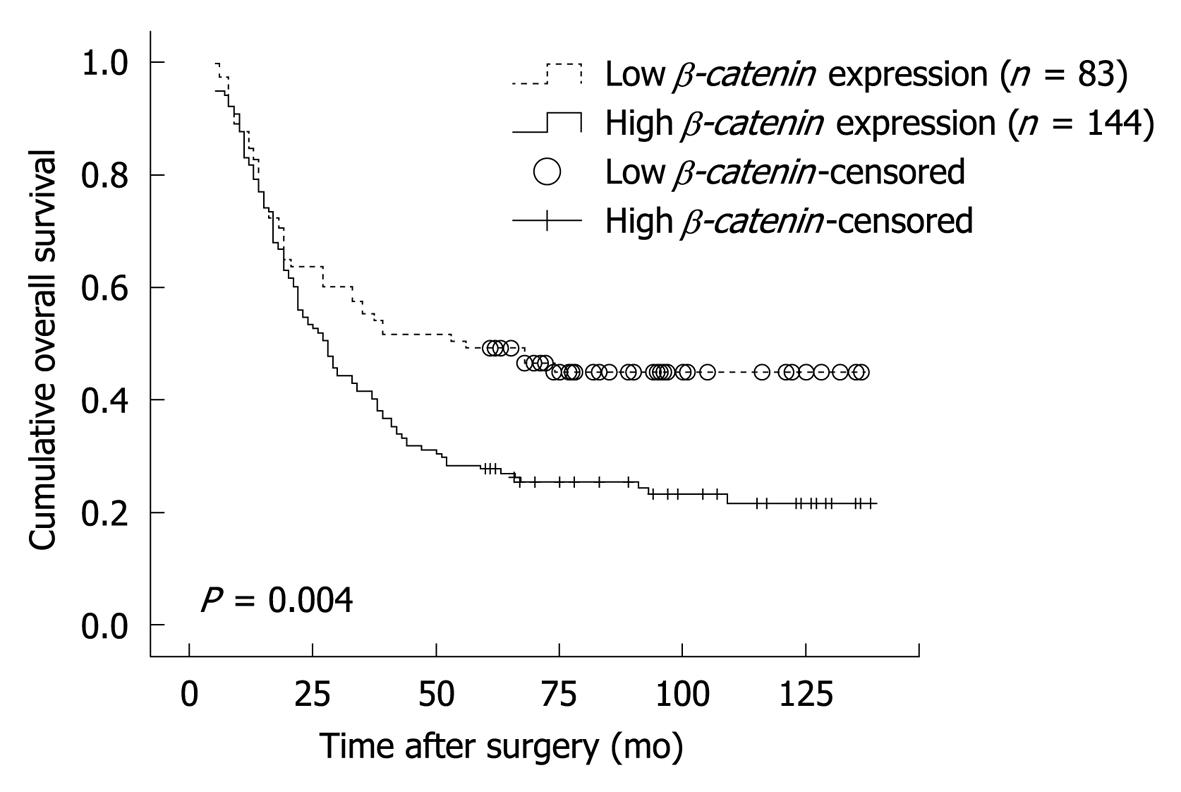
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier survival curves for patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma at stage T2-3N0M0 according to β-catenin expression.
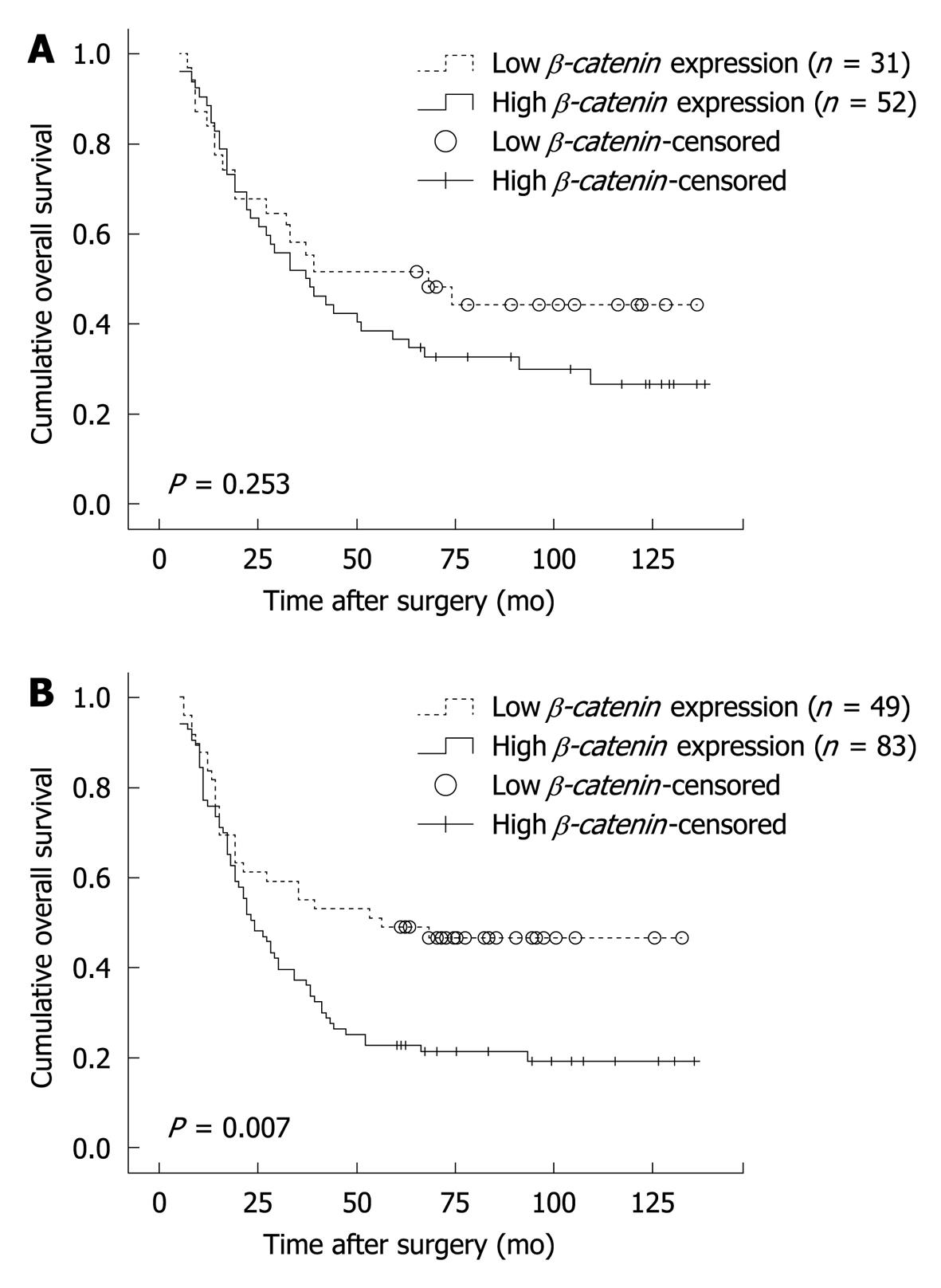
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier survival curves for patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma according to β-catenin expression.
A: Correlation between β-catenin expression and post-operative survival rate of patients with T2 lesions; B: Correlation between β-catenin expression and post-operative survival rate of patients with T3 lesions.
Figure 5 Kaplan-Meier survival curves for patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma stratified for pathological stage according to β-catenin expression.
A: Correlation between β-catenin expression and post-operative survival rate of patients with IIA diseases; B: Correlation between β-catenin expression and post-operative survival rate of patients with IIB diseases.
-
Citation: Situ DR, Hu Y, Zhu ZH, Wang J, Long H, Rong TH. Prognostic relevance of
β-catenin expression in T2-3N0M0 esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(41): 5195-5202 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i41/5195.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i41.5195