Copyright
copy;2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2010; 16(39): 4913-4921
Published online Oct 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i39.4913
Published online Oct 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i39.4913
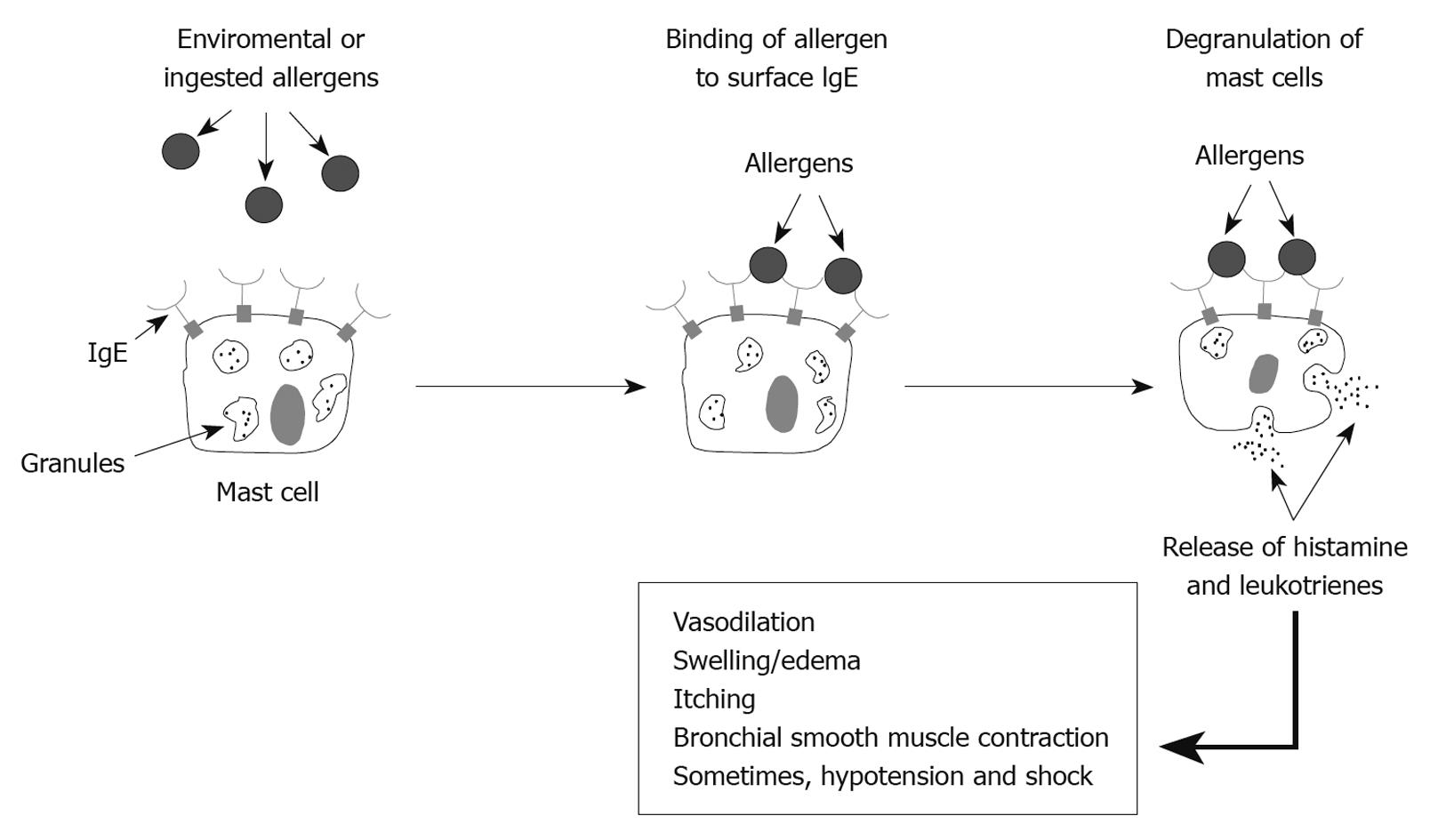
Figure 1 Allergic angioedema pathway.
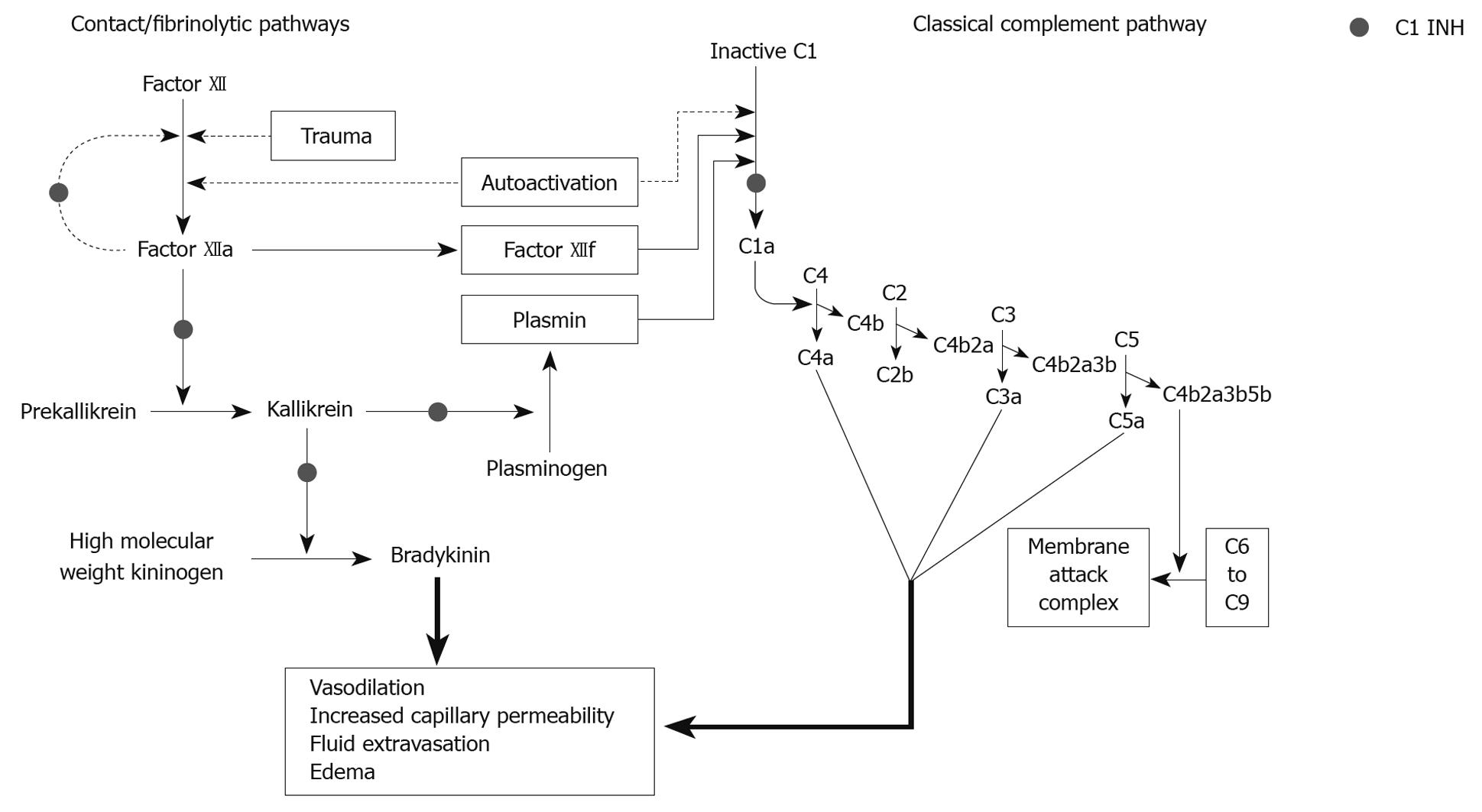
Figure 2 Pathways Involved in hereditary angioedema and acquired angioedema.
C1 INH: C1 esterase inhibitor.
Figure 3 Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced angioedema pathway.
NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; COX-1: Cyclooxygenase-1.
- Citation: Nzeako UC. Diagnosis and management of angioedema with abdominal involvement: A gastroenterology perspective. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(39): 4913-4921
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i39/4913.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i39.4913