Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2010; 16(31): 3919-3927
Published online Aug 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i31.3919
Published online Aug 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i31.3919
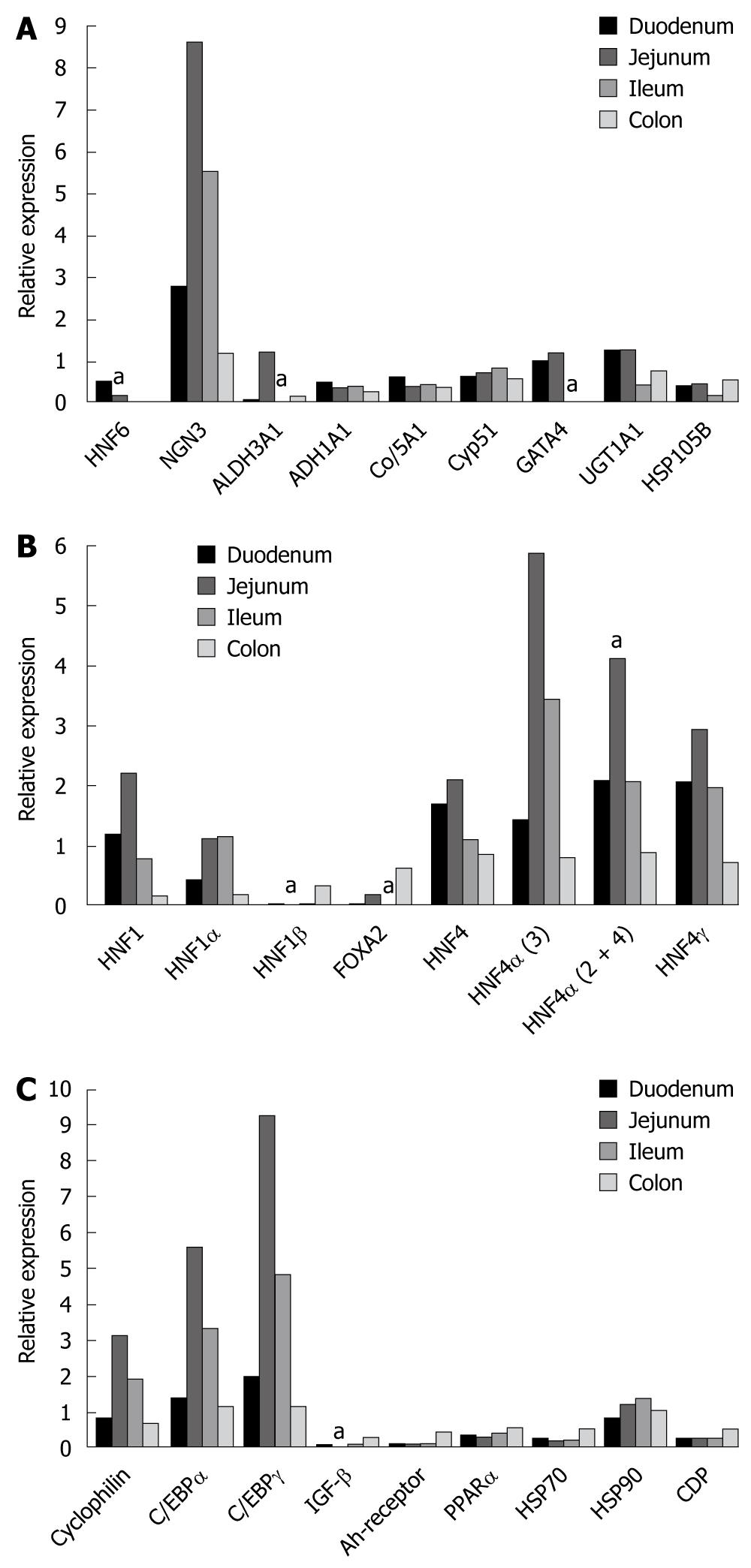
Figure 1 Gene expression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 and of other liver enriched transcription factors in the human intestine.
A: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 (HNF6) and some of its target genes. Bars hallmarked by "a" refer to statistically significant changed expression (P < 0.05) when compared to other segments of the gut; B: Hepatic nuclear transcription factors. Bars hallmarked by "a" refer to statistically significant changed expression (P < 0.05) when compared to other segments of the gut; C: CAAT enhancer binding proteins and the transcription factors Ah-receptor, PPAR alpha as well as the heat shock proteins HSP70 and HSP90 and IGF-β. Bars hallmarked by "a" refer to statistically significant changed expression (P < 0.05) when compared to other segments of the gut.
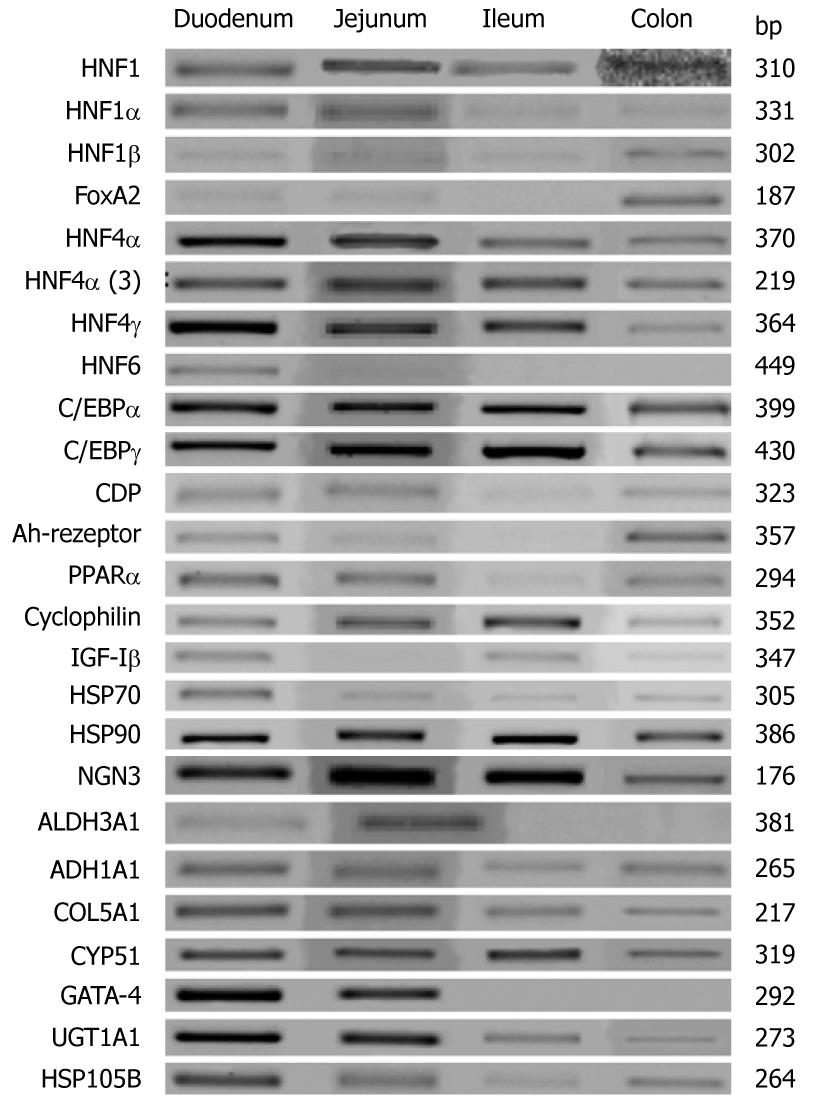
Figure 2 Representative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction gels of gene expression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 and of other liver-enriched transcription factors in the human intestine.
Note, all polymerase chain reaction reactions were done within the linear range of amplification.
Figure 3 Microscopic images of time depended sequence of Caco-2 cells.
Note, HNF6 gene expression increased with time and cell culture confluency up to day 11 but declined thereafter (see Figure 2 for gene expression data). A: 0 d; B: 3 d; C: 5 d; D: 7 d; E: 11 d; F: 17 d.
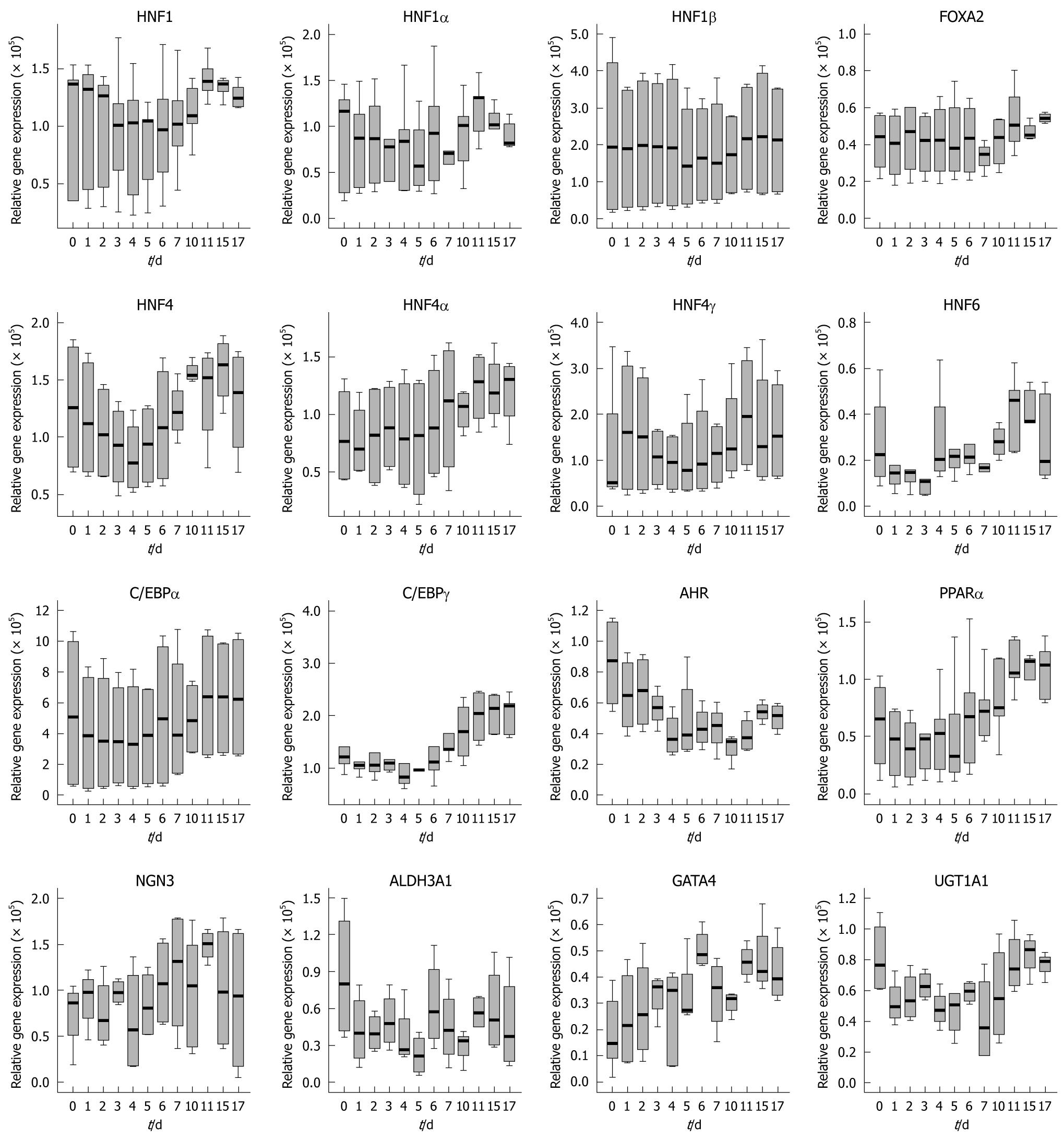
Figure 4 Time-dependent gene expression of liver-enriched transcription factors and some of its target genes in cultures of Caco-2 cells.
HNF: Hepatocyte nuclear factor.
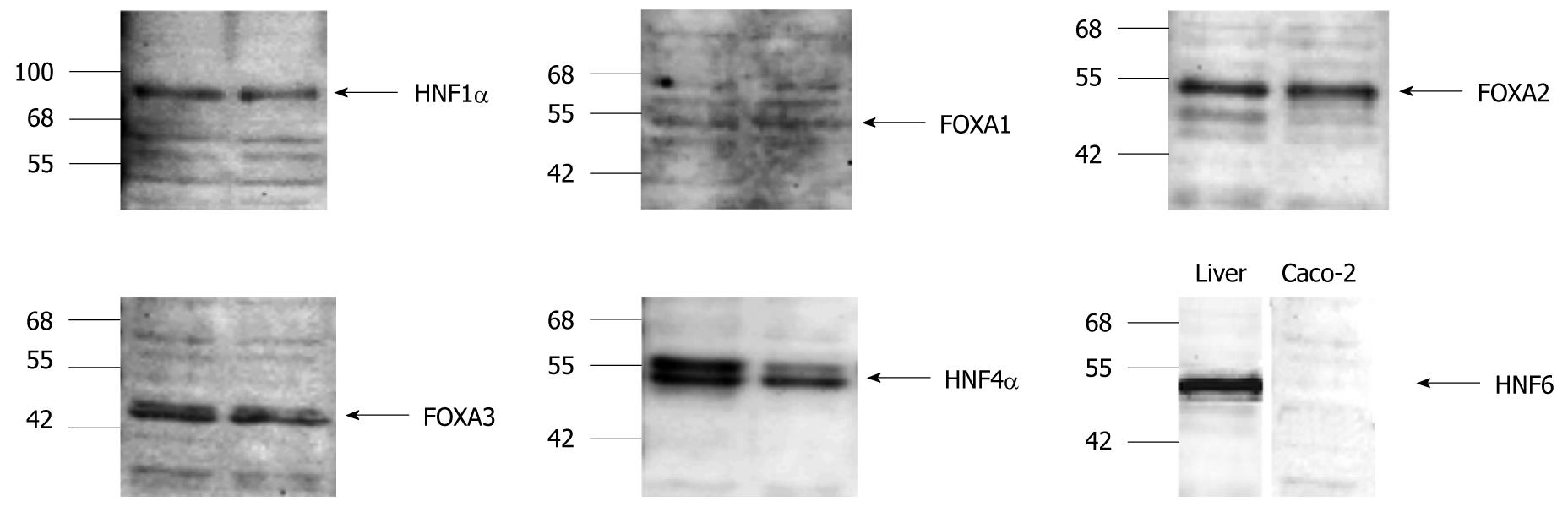
Figure 5 Western blotting of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α, FOXA1, FOXA2, FOXA3, hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α and hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 in different human colon carcinoma Caco-2 cell line cultures.
Note, in case of hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF) 6 healthy human liver serves as control.
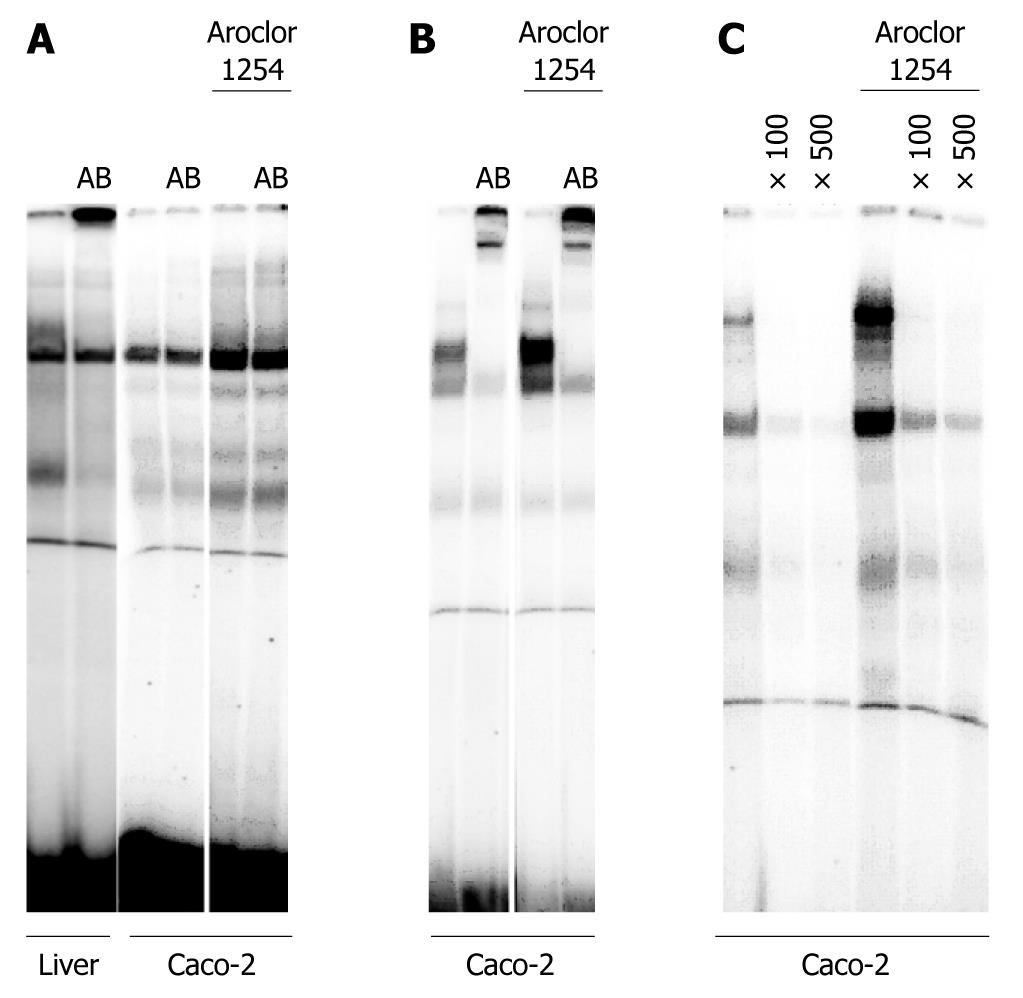
Figure 6 Electromobility shift assay with nuclear extracts of the human colon carcinoma Caco-2 cell line.
A: Demonstrates the DNA binding of HNF6 to an optimized oligonucleotide probe using either nuclear protein extract of human liver tissue or Caco-2 cells. Note, the lane labeled as AB refers to the addition of a hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 antibody to demonstrate specificity of the DNA binding assay; B: Demonstrates the DNA binding of HNF4α to an optimized oligonucleotide probe using either nuclear protein extract of human liver tissue or Caco-2 cells. Note, the lane labeled as AB refers to the addition of a HNF4α antibody to demonstrate specificity of the DNA binding assay; C: Demonstrates the DNA binding of NGN3 (a HNF6 target gene) to an optimized oligonucleotide probe using either nuclear protein extract of human liver tissue or Caco-2 cells. Note, the lane labeled as × 100 or × 500 refers to competition assays with excess of unlabeled probe.
- Citation: Lehner F, Kulik U, Klempnauer J, Borlak J. Mapping of liver-enriched transcription factors in the human intestine. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(31): 3919-3927
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i31/3919.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i31.3919