Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2010; 16(3): 392-394
Published online Jan 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i3.392
Published online Jan 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i3.392
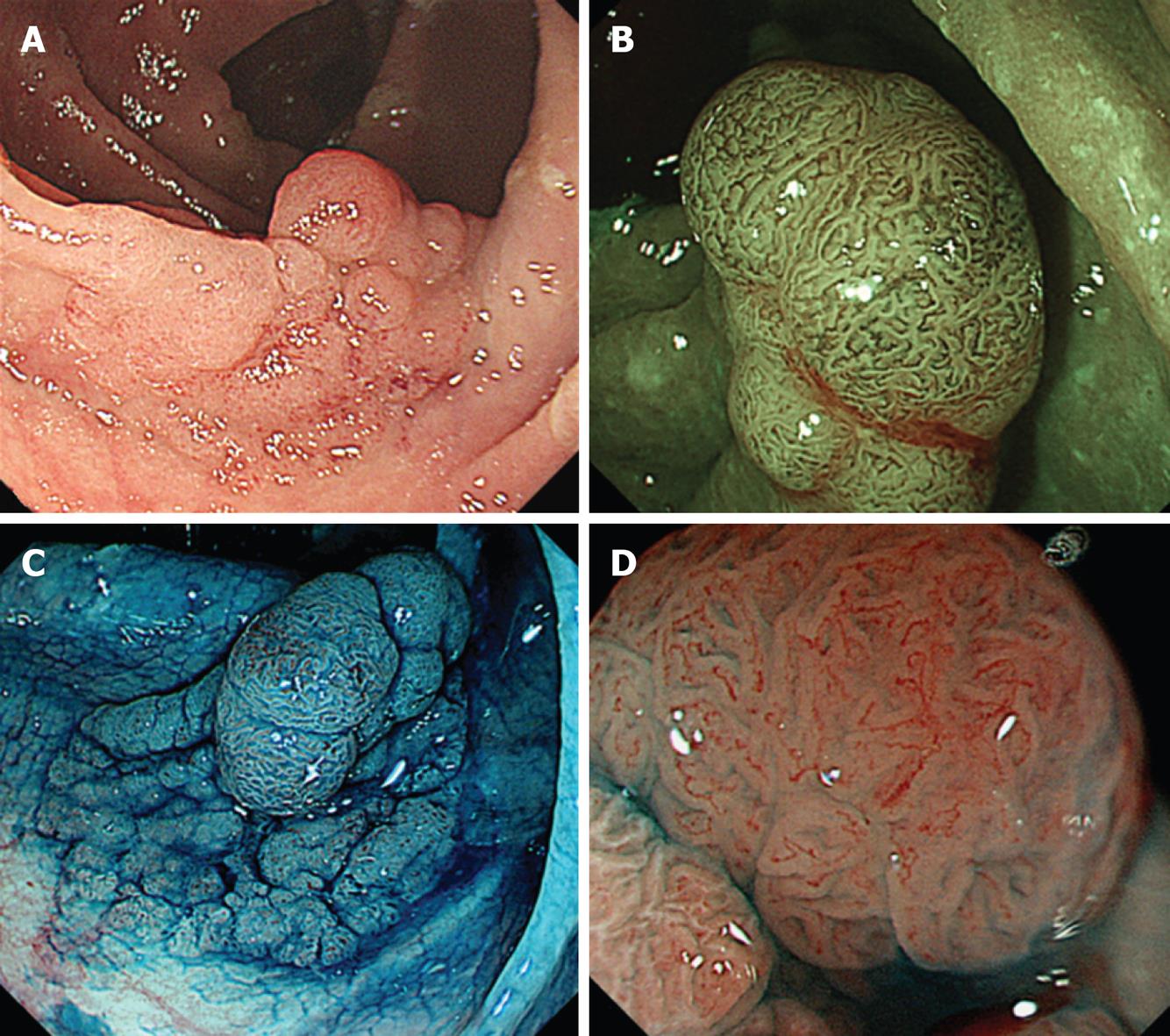
Figure 1 A laterally-spreading tumor of granular type (LST-G) in the colonic interposition was shown at colonoscopy.
Narrow-band imaging with magnification revealed a capillary pattern type II. Magnifying chromoendoscopy using 0.4% indigo carmine revealed a type IV pit pattern. A: Conventional view; B: Narrow-band imaging with magnification; C: Chromoendoscopy with 0.4% indigo carmine; D: Magnifying chromoendoscopy using 0.4% indigo carmine dye spraying.
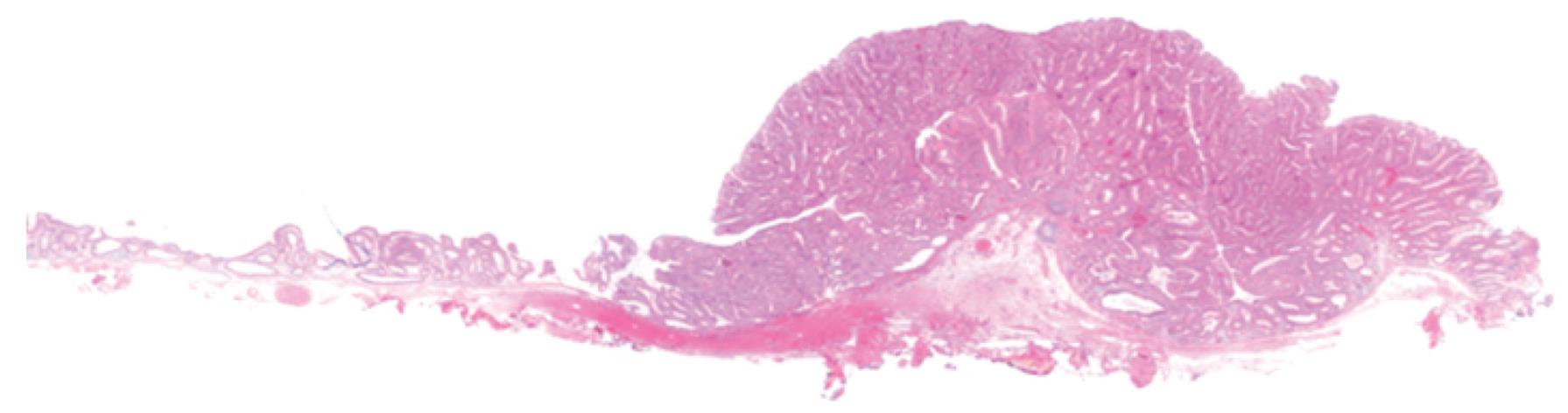
Figure 2 Histologically, the resected specimen showed an intramucosal adenocarcinoma in a tubular adenoma.
Cross sectional view (HE, magnification × 5).
- Citation: Bando H, Ikematsu H, Fu KI, Oono Y, Kojima T, Minashi K, Yano T, Matsuda T, Saito Y, Kaneko K, Ohtsu A. A laterally-spreading tumor in a colonic interposition treated by endoscopic submucosal dissection. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(3): 392-394
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i3/392.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i3.392