Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2010; 16(22): 2771-2779
Published online Jun 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i22.2771
Published online Jun 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i22.2771
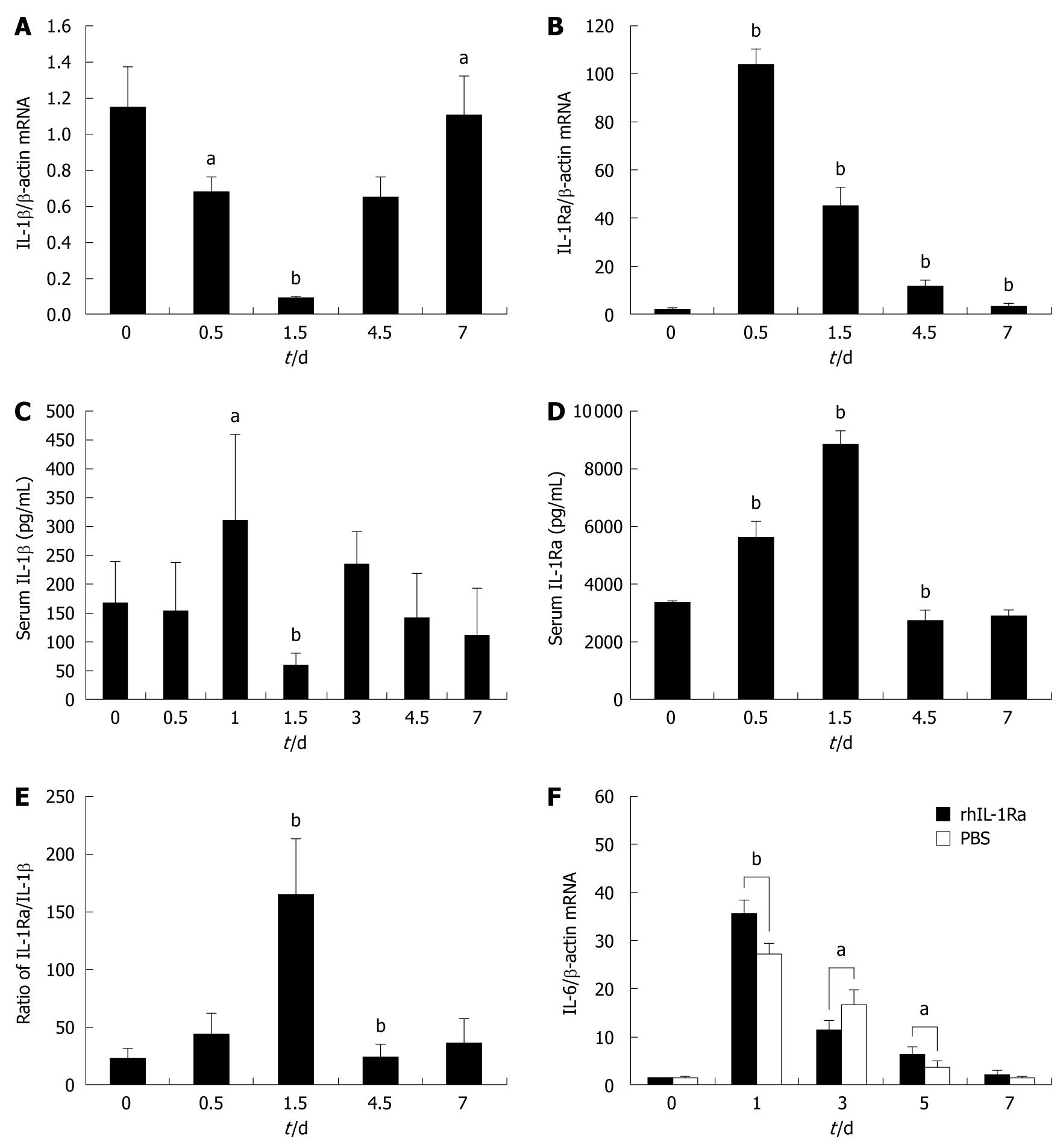
Figure 1 Interleukin (IL)-1β, interleukin 1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) and IL-6 expression after carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) (1 mL/kg) administration.
A: Quantification of IL-1β mRNA levels; B: IL-1Ra mRNA levels; C: Serum IL-1β; D: Serum IL-1Ra; E: Ratio of serum level of IL-1Ra to IL-1β; F: Quantification of IL-6 mRNA levels of the livers treated with recombinant human IL-1Ra (rhIL-1Ra) or PBS. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
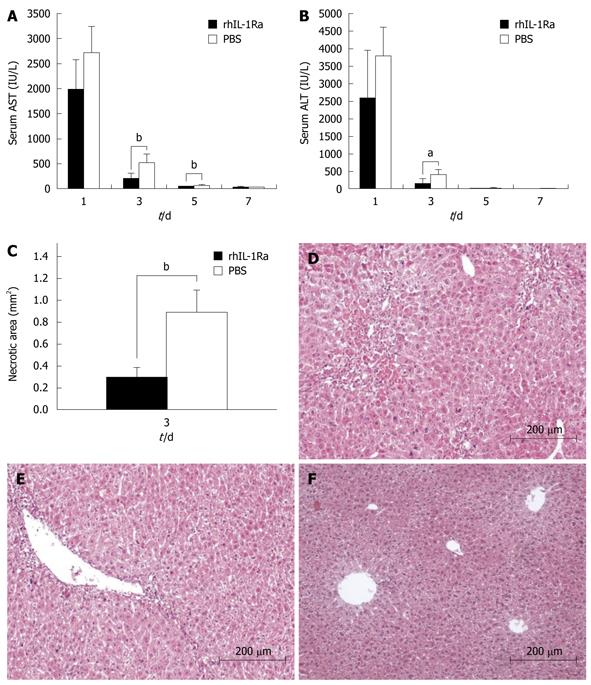
Figure 2 Acute liver injury (1 mL/kg CCl4 administration) ± rhIL-1Ra.
A: Serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST); B: Serum alanine amino transferase (ALT), with rhIL-1Ra or PBS; C: Necrotic areas. Representative findings from at least 12 mm2 tissue sections were counted for each mouse; D-F: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) stained liver sections; D: Group received PBS at day 3 after CCl4 administration, shows necrosis with clusters of inflammatory cells around central vein (original magnification, × 100); E: Group received rhIL-1Ra at day 3 after CCl4 administration, demonstrates mostly histological recovery with only inconspicuous necrosis still remaining around central vein and very few inflammatory cells are present (original magnification, × 100); F: Normal liver histology with rhIL-1Ra treatment, which shows no difference from normal liver tissue histology. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
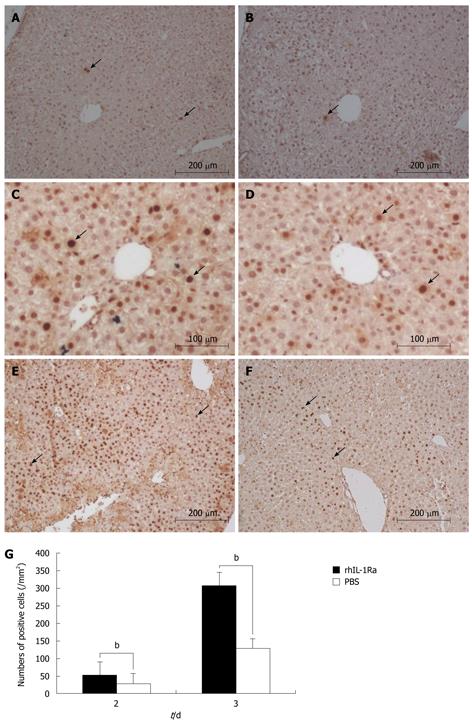
Figure 3 Immunostaining of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) shows rhIL-1Ra promotes hepatocyte proliferation.
A: Normal liver (original magnification, × 100); B: Normal liver in rhIL-1Ra treated mice (original magnification, × 100); C: Group received rhIL-1Ra at day 2 after CCl4 administration, numerous PCNA+ hepatocytes in centrilobular areas and scattered PCNA+ hepatocytes at the edge of hepatocellular necrosis (original magnification, × 200); D: Group received PBS at day 2 after CCl4 administration, few PCNA+ hepatocytes in centrilobular areas at day 2 (original magnification, × 200); E: Group received rhIL-1Ra at day 3 after CCl4 administration, numerous positive cells in centrilobular areas around central vein (original magnification, × 100); F: Group received PBS at day 3 after CCl4 administration shows fewer numbers of positive cells (original magnification, × 100); G: Numbers of PCNA+ cells after CCl4 administration with rhIL-1Ra or PBS, at least 12 mm2 tissue sections were counted for each mouse. Arrows point to PCNA+ hepatocytes. bP < 0.01.
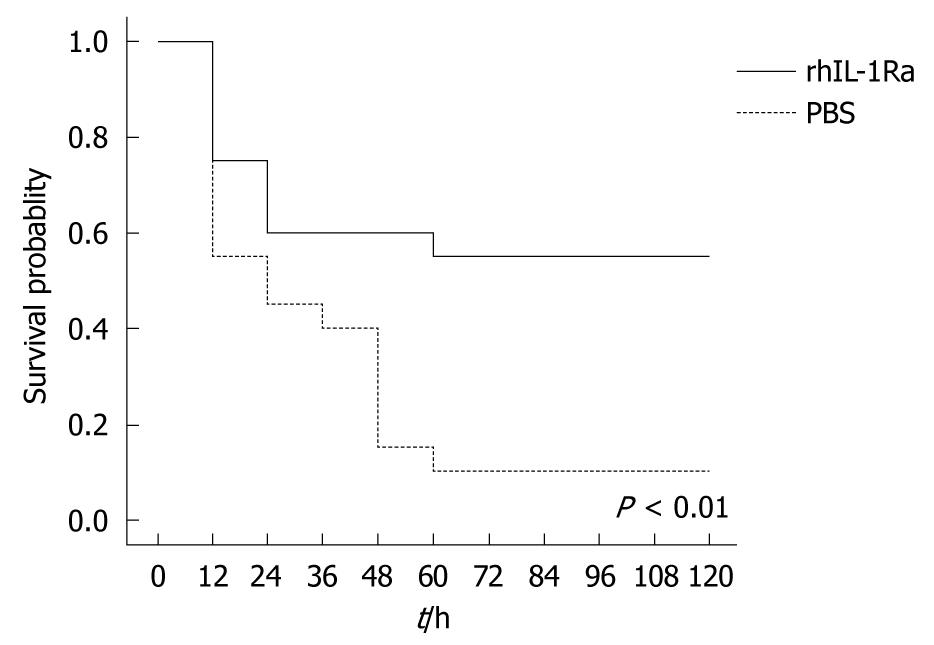
Figure 4 rhIL-lRa treatment increased probability of survival after a lethal dose administration of CCl4 (2.
6 mL/kg). Mice were administered with either PBS as a control (n = 20) or rhIL-1Ra (n = 20) twice a day for 5 d. Survivals were scored twice a day for 5 d, and the results were analyzed using the log-rank test and expressed as the Kaplan-Meier survival curves. P = 0.006.
- Citation: Zhu RZ, Xiang D, Xie C, Li JJ, Hu JJ, He HL, Yuan YS, Gao J, Han W, Yu Y. Protective effect of recombinant human IL-1Ra on CCl4-induced acute liver injury in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(22): 2771-2779
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i22/2771.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i22.2771