Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2010; 16(14): 1688-1695
Published online Apr 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i14.1688
Published online Apr 14, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i14.1688
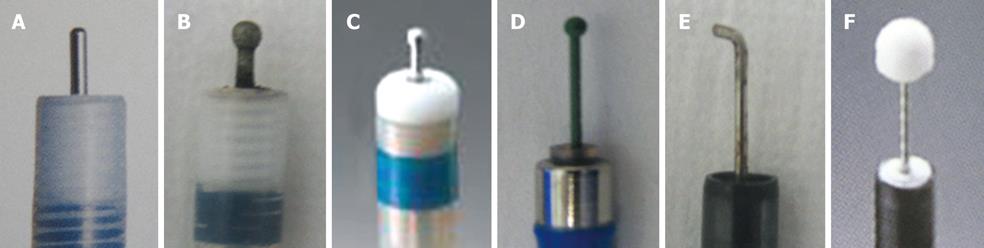
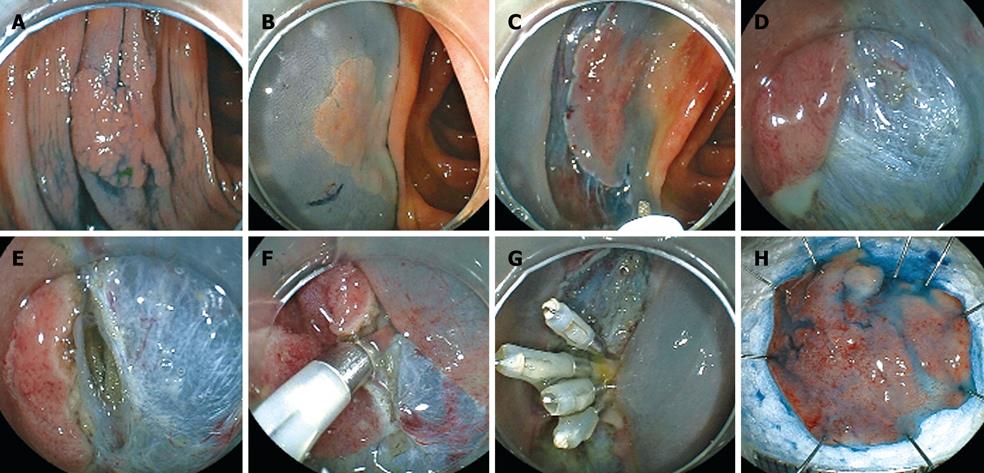
Figure 1 Various knives used in endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for colorectal tumors.
A: Flush knife; B: Flush knife with ball tip; C: Dual knife; D: B-knife with ball tip; E: Hook knife; F: Insulated tipped (IT) knife.
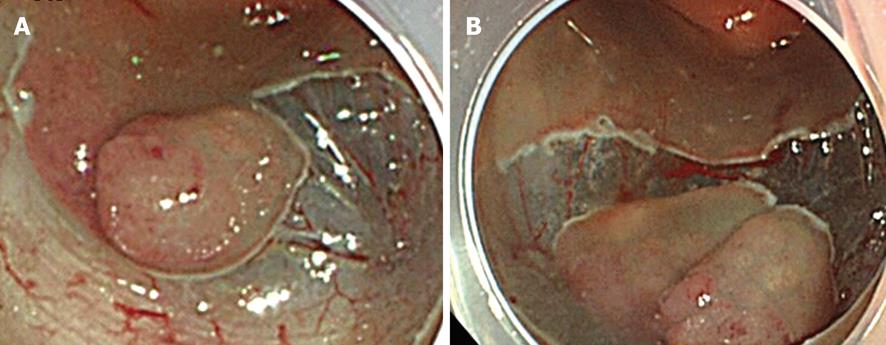
Figure 2 Mucosal incision.
A: Partial circumferential incision; B: Initial complete circumferential incision.
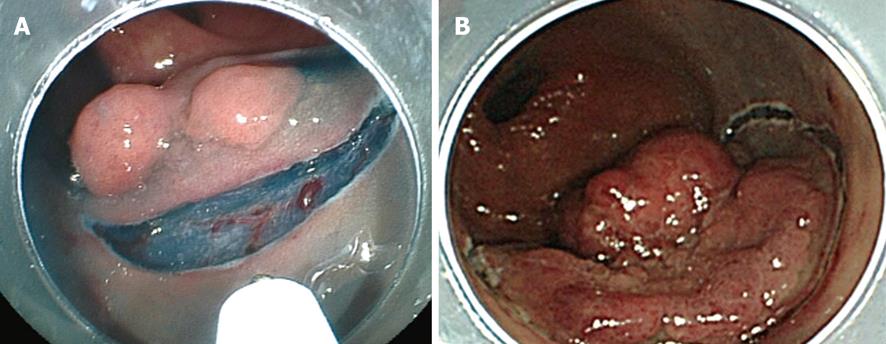
Figure 3 A case of the tumor perpendicular to the endoscope.
A: Colonic tumor, 0-IIa 20 mm in the ascending colon; B: The position of the tumor became vertical with respect to the endoscope following injection into the proximal side.
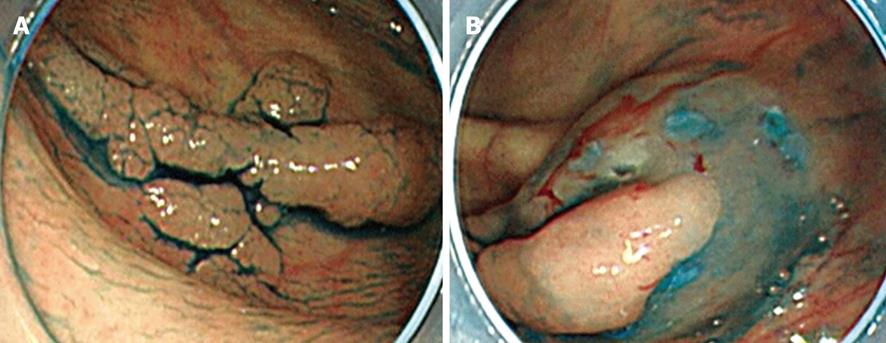
Figure 4 Another case of the tumor perpendicular to the endoscope.
A: Residual mucosa on the oral side pulled the tumor upward; B: The substance caused by the residual mucosa was lost during full mucosal resection, and the position of the tumor became vertical with respect to the endoscope.
Figure 5 A unique use of hemostat forceps.
A: Thick vessels were detected in the submucosa; B: The vessels were grasped by the hemostat forceps; C: The vessels and surrounding submucosa were coagulated and became whitish. The view of the submucosa was obscured; D: The coagulated vessels and submucosa were resected using the hemostat forceps, following which the view was restored.
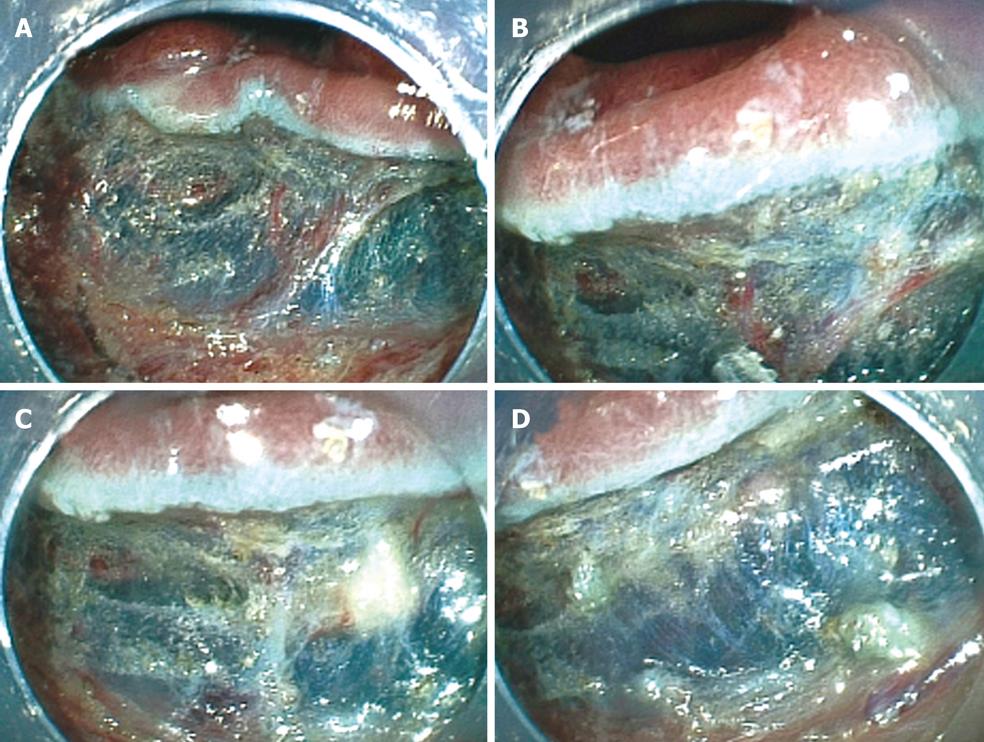
Figure 6 A case with perforation.
A: The tumor in this patient was graded 0-IIa, measured 20 mm, and was located in the ascending colon. The surface of the tumor was slightly depressed and the deformity of the colonic wall was detected with indigo carmine dye; B: Injection was performed on the anal side of the tumor. However, the elevation of the tumor following the injection was poor on the oral side of the tumor; C: Mucosal incision and submucosal dissection below the tumor were performed with the Flush knife from the anal side of the tumor; D: Mucosal incision on the oral side of the tumor was performed. Severe fibrosis was detected on the oral side of the tumor; E: Submucosal dissection was then performed with the Hook knife. However, owing to the thin submucosa, perforation occurred during hooking; F: Endoscopic clipping was performed minimally as clipping did not prevent the resection of the tumor; G: Several endoscopic clippings were performed after resection of the tumor; H: The resected specimen was fixed and the tumor was diagnosed by histopathological examination as early colonic cancer. The tumor was 20 mm in diameter. Tumor invasion was limited to the mucosa. Lateral and vertical margins of the tumor were histopathologically free of the tumor.
- Citation: Yoshida N, Yagi N, Naito Y, Yoshikawa T. Safe procedure in endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors focused on preventing complications. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(14): 1688-1695
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i14/1688.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i14.1688