Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2009; 15(6): 732-736
Published online Feb 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.732
Published online Feb 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.732
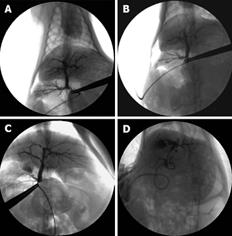
Figure 1 Cholangiography of the four groups 4 wk after operation.
A (SO): The image of the intra-hepatic bile duct was normal. No biliary stricture or dilation was observed; B (ABO-1 h): The image of the intrahepatic bile duct resembled that of SO, no intrahepatic biliary lesion was visualized either; C (ABO-2 h): All the branches of the intrahepatic bile duct appeared loose, with the “string beads manifestation” in part of them; D (ABO-3 h): The image of the intrahepatic bile duct was obviously abnormal, with a loose appearance and severe damage.
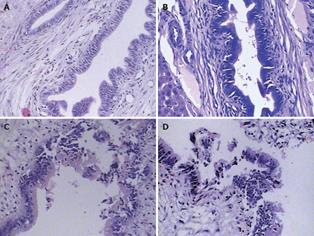
Figure 2 Histopathological manifestations of the four groups 4 wk after operation.
A (SO): The intrahepatic bile duct epithelial cells were eumorphic and no cell necrosis was observed; B (ABO-1 h): The intrahepatic bile duct epithelial cells were almost normal. Small amounts of bile duct epithelial cells sloughed into the bile duct lumen; C (ABO-2 h): The intrahepatic bile duct epithelial cells were damaged obviously, and some of them were necrotic and sloughed into the bile duct lumen; D (ABO-3 h): The intrahepatic bile duct epithelial cells were damaged severely; many of them were necrotic and sloughed into the bile duct lumen. The normal epithelial structures disappeared (HE, × 200).
- Citation: Sheng QS, Chen DZ, Lang R, He Q, Yang YJ, Qu ZW, Zhao DF, Zhang XS. Establishment of an animal model of ischemic type intrahepatic biliary lesion in rabbits. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(6): 732-736
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i6/732.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.732