Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2009; 15(5): 615-621
Published online Feb 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.615
Published online Feb 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.615
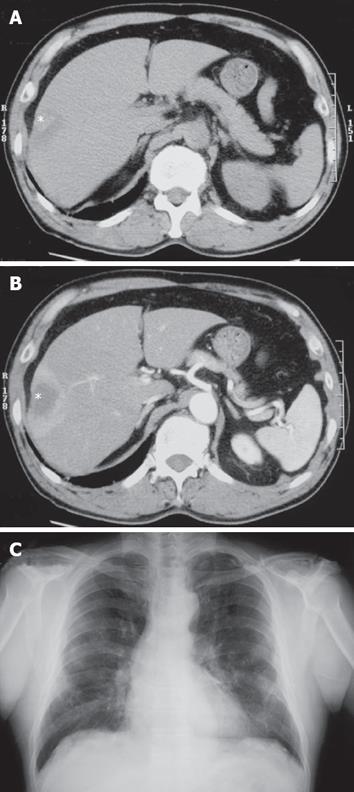
Figure 1 Radiological findings.
A: Plain CT showed a low-density mass (asterisk) in S8 segment of the liver; B: The periphery of the mass (asterisk) was enhanced in the early phase of enhanced CT, suggesting abundant blood supply; C: Chest X-ray showed pulmonary asbestosis and pleural thickening, but there were no new lesions suggesting lung cancer or pleural mesothelioma.
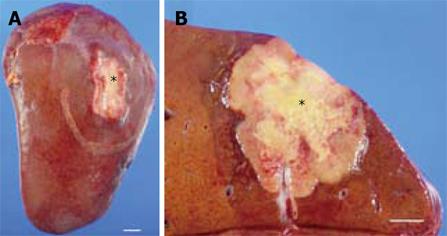
Figure 2 Gross appearance of the tumor.
A: A firm, white and slightly depressed lesion (asterisk) measuring 4.2 cm × 3 cm was identified on the liver surface. B: Cross section of the tumor in the liver. A yellowish-white tumor of 4.4 cm × 3.8 cm was identified just under the hepatic capsule (asterisk). The tumor had well-defined borders and an area of central necrosis. Bar indicates 1 cm.
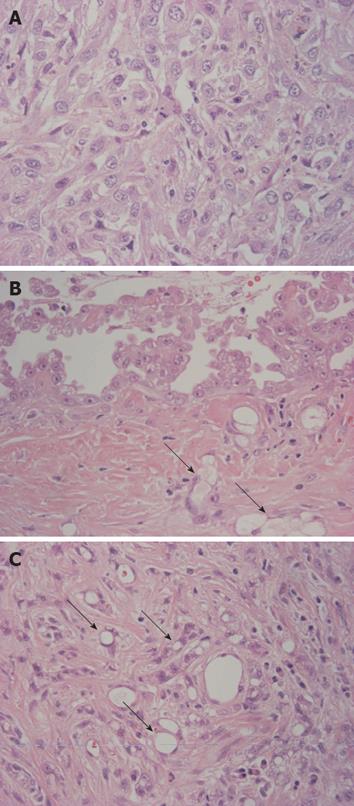
Figure 3 Histologic features of the tumor.
A: Sarcomatoid component was predominant and was composed of tumor cells with abundant eosinophilic or clear cytoplasm, indistinct cytoplasmic borders, round and atypical nuclei with vesicular fine chromatin and variably sized nucleoli; B: Papillary proliferation of epithelioid tumor cells was identified on the surface of the tumor. Epithelioid cells had eosinophilic cytoplasm with bland nuclei and distinct nucleoli. Arrows indicate microcystic (microglandular or adenomatoid) component; C: In the area near the surface, a microcystic (microglandular or adenomatoid) component showing microcystic structures with lace-like, adenoid cystic or signet ring appearance was detected (arrows) (HE × 400).
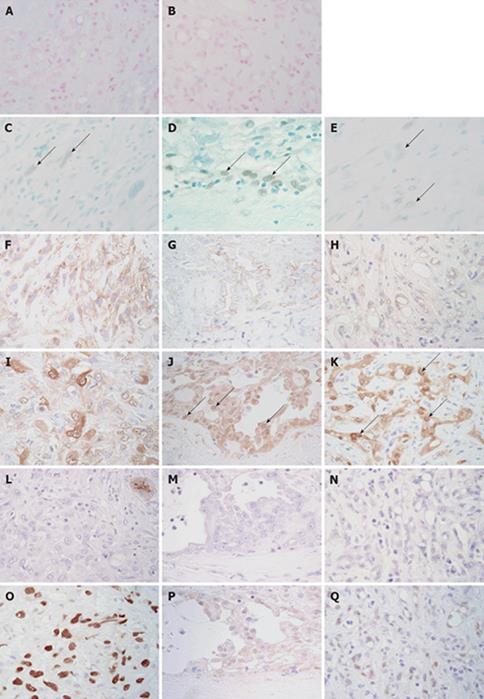
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical and special stains.
Alcian blue (pH 2.5) showed positive staining on the lumen of adenomatoid tumors (A). This positive staining was sensitive to digestion with hyaluronidase (B). Nuclear WT-1 immunoreactivity (arrows) was detected focally in sarcomatoid (C), papillary epithelioid (D) and microcystic (E) components. Immunostaining for WT-1 and methyl green. Sarcomatoid tumor cells showed focal membranous immunoreactivity for D2-40 (F). Membranous D2-40 immunoreactivity was detected in the papillary epithelioid (G) and microcystic (H) components. Immunostaining for D2-40 and hematoxylin. Sarcomatoid tumor cells showed focal and rather weak immunoreactivity for calretinin (I). Nuclear calretinin immunoreactivity (arrows) was detected in the papillary epithelioid (J) and microcystic (K) components. Immunostaining for calretinin and hematoxylin. Immunoreactivity for CA19-9 was not detected in sarcomatoid (L), papillary epithelioid (M) and microcystic (N) components. The apical surface of the entrapped bile duct showed immunoreactivity for CA19-9 (L, upper right corner). Immunostaining for CA19-9 and hematoxylin. Sarcomatoid (O) and microcystic (P) components showed strong nuclear immunoreactivity for p53. A few papillary epithelioid cells showed nuclear immunoreactivity for p53 (Q). (Immunostaining for p53 and hematoxylin, × 400).
- Citation: Sasaki M, Araki I, Yasui T, Kinoshita M, Itatsu K, Nojima T, Nakanuma Y. Primary localized malignant biphasic mesothelioma of the liver in a patient with asbestosis. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(5): 615-621
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i5/615.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.615