Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2009; 15(40): 5035-5043
Published online Oct 28, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5035
Published online Oct 28, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5035
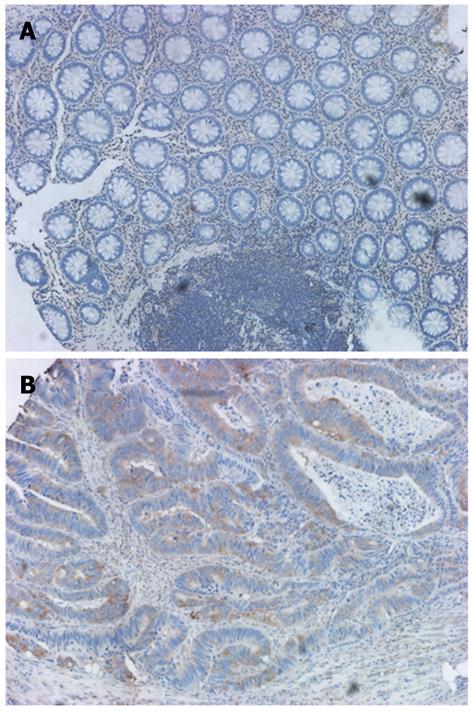
Figure 1 γ-synuclein protein expression detected by IHC.
A: Negative γ-synuclein immunostaining in NNAT; B: Positive γ-synuclein immunostaining in the cytoplasm of CRC cells (original magnification × 200). IHC: Immunohistochemistry; NNAT: Nonneoplastic adjacent tissues; CRC: Colorectal cancer.
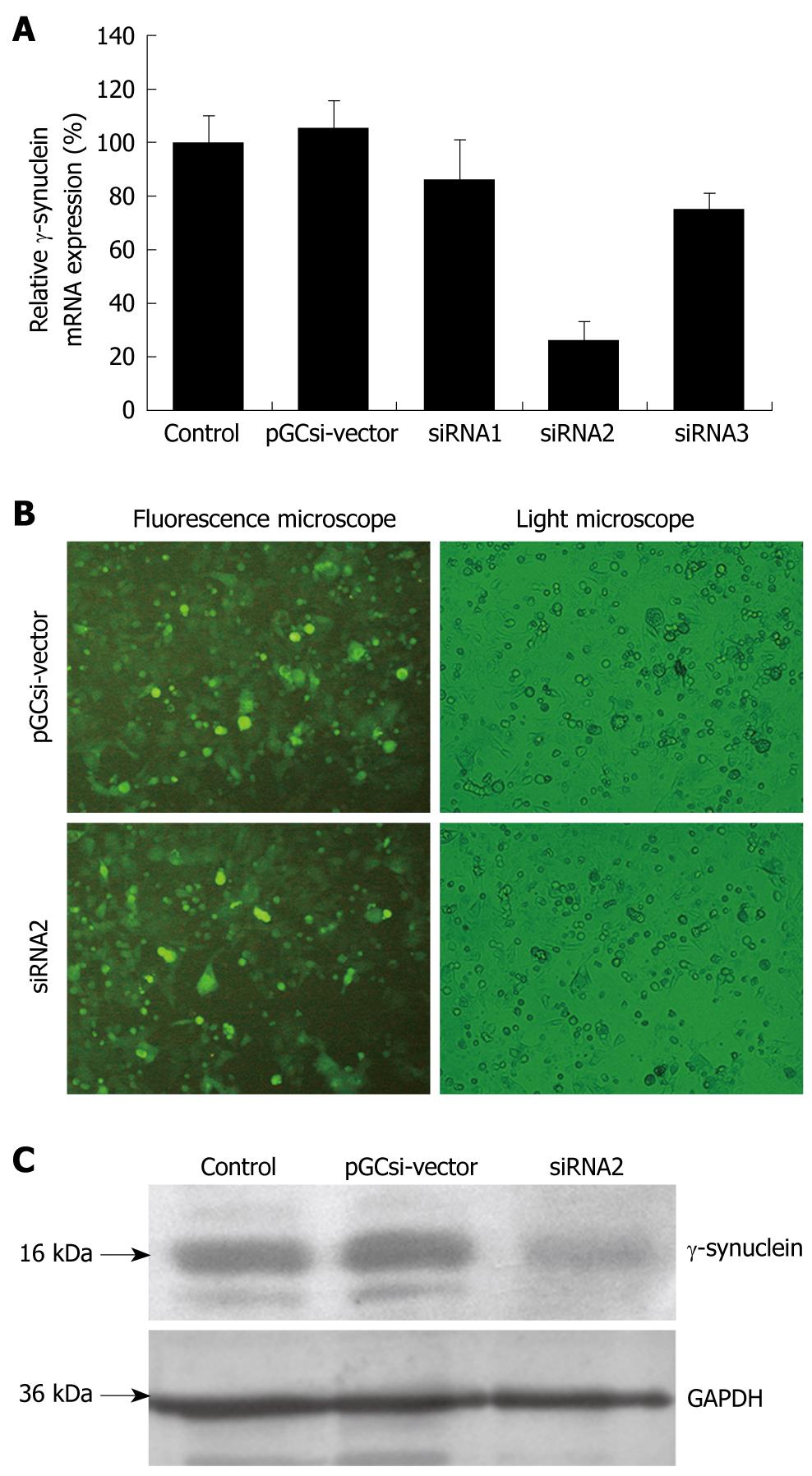
Figure 2 The siRNA plasmid can specifically knock down γ-synuclein expression in the HCT116 cells.
A: γ-synuclein mRNA expression detected by Q-RT-PCR after transient transfection. Values were γ-synuclein/GAPDH expression of one group cells relative to that of parental HCT116 cells; B: The vision of HCT116 stable transfectants in fluorescence microscopy and light microscopy; C: γ-synuclein protein expression detected by western blotting after selection of stable transfectants. Control: Parental HCT116 cells; pGCsi-vector: HCT116/vector cells; siRNA1 (2,3): HCT116/siRNA1 (2,3) cells.
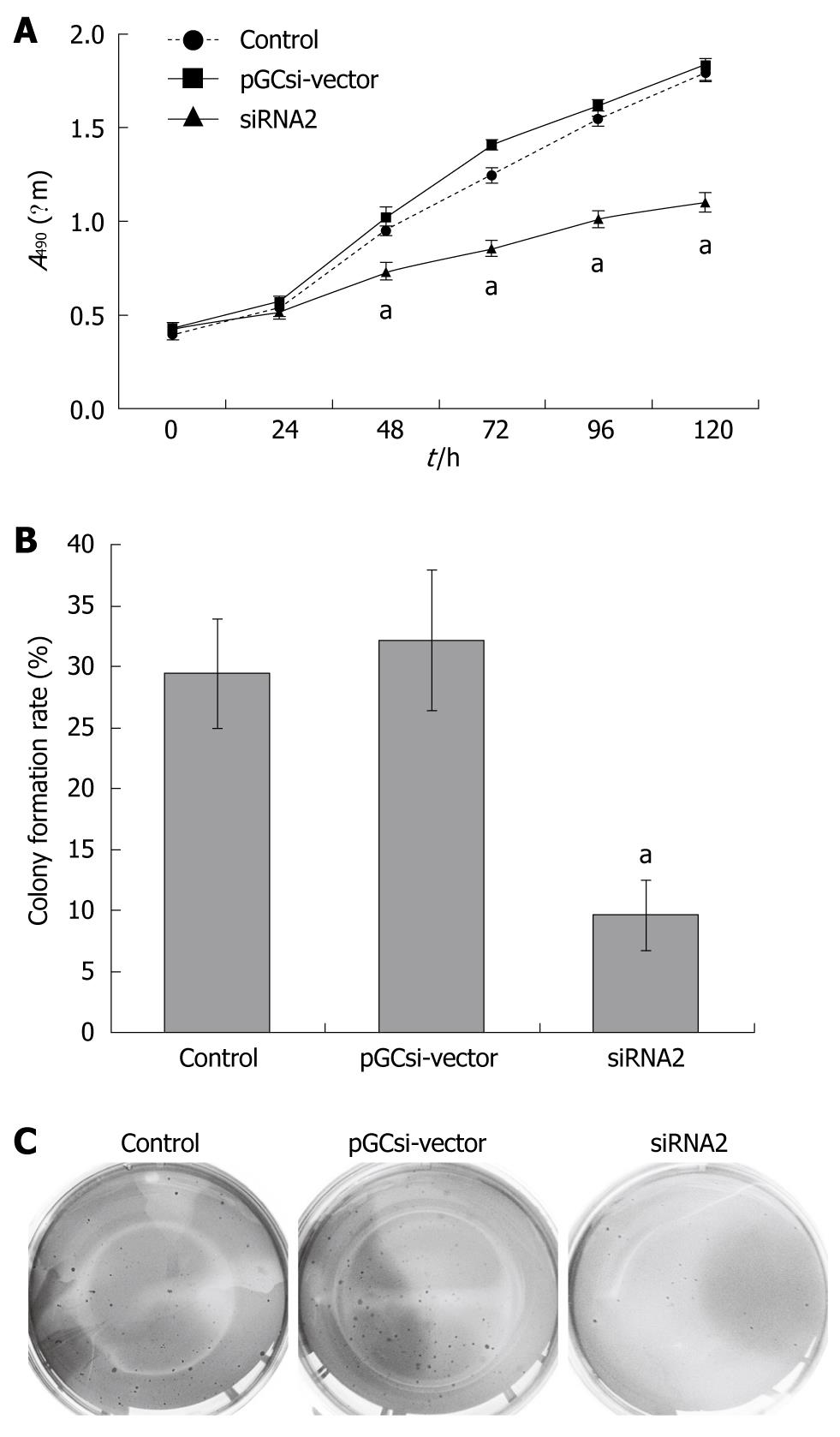
Figure 3 Inhibition of cell proliferation and colony formation by γ-synuclein knockdown.
A: The role of γ-synuclein in regulating HCT116 cell proliferation was determined by CCK8 assay. Values were the mean ± SD of absorbance at 490 nm for five independent experiments; aP < 0.05; B: The colony formation rates were analyzed by soft agar assay. Values were the mean ± SD for three independent experiments; aP < 0.05; C: The colonies were stained with 0.2% crystal violet and photographed. Control: Parental HCT116 cells; pGCsi-vector: HCT116/vector cells; siRNA2: HCT116/siRNA2 cells.
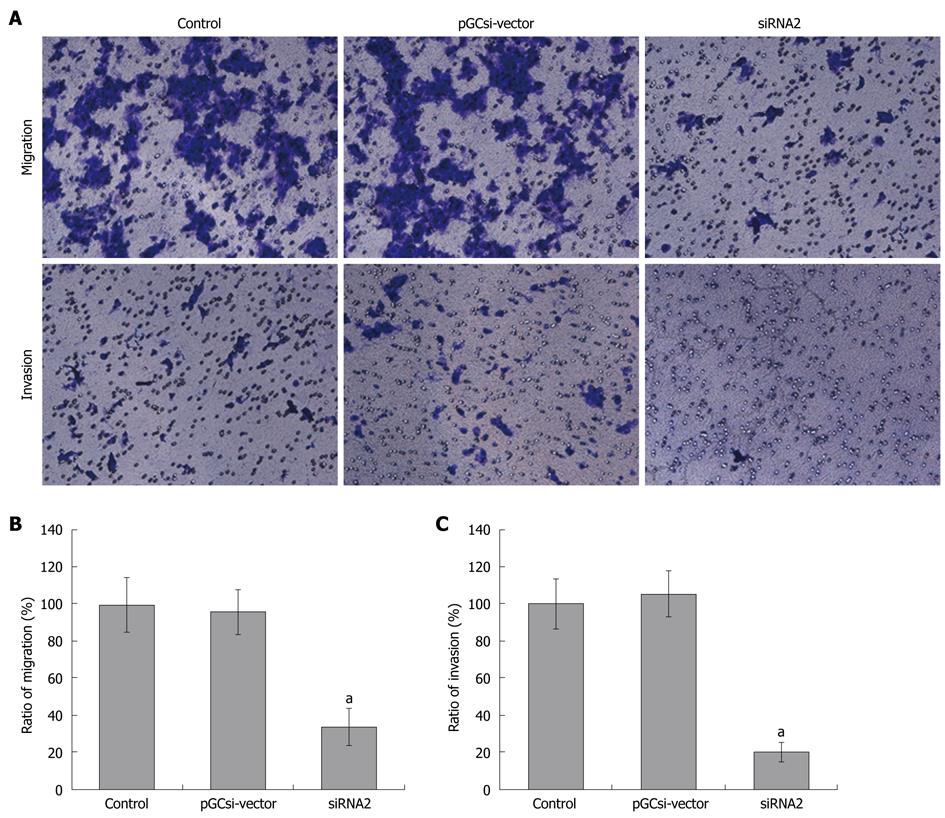
Figure 4 Inhibition of cell migration and invasion by γ-synuclein knockdown.
A: Boyden chambers with 8 μm polycarbonate membranes coated with or without 4 mg/mL growth factor-reduced Matrigel were used for migration or invasion assay. The chambers were stained with 0.2% crystal violet and analysed by photography, and the stained cells were migration or invasion cells in the lower chamber; B, C: The migration or invasion cells were counted in ten random fields of vision. Values were the number of cells relative to that of parental HCT116 cells, and expressed as mean ± SD for three independent experiments; aP < 0.05. Control: Parental HCT116 cells; pGCsi-vector: HCT116/vector cells; siRNA2: HCT116/siRNA2 cells.
- Citation: Ye Q, Feng B, Peng YF, Chen XH, Cai Q, Yu BQ, Li LH, Qiu MY, Liu BY, Zheng MH. Expression of γ-synuclein in colorectal cancer tissues and its role on colorectal cancer cell line HCT116. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(40): 5035-5043
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i40/5035.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.5035