Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2009; 15(32): 4077-4082
Published online Aug 28, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.4077
Published online Aug 28, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.4077
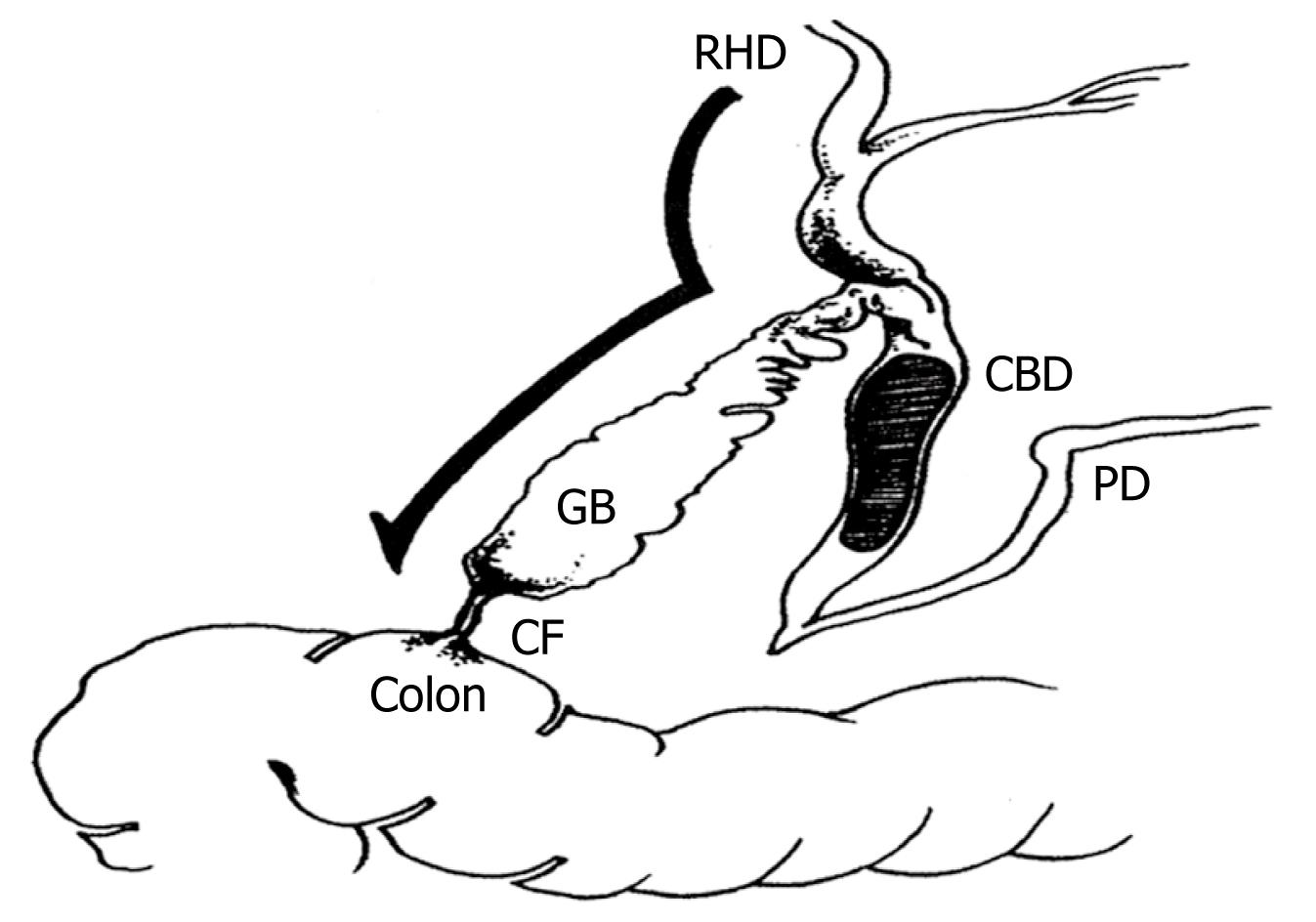
Figure 1 Schematic demonstration of a cholecystocolic fistula (modified from Benage et al[7]).
GB: Gallbladder; CBD: Common bile duct; RHD: Right hepatic duct; PD: Pancreatic duct; CF: Cholecystocolic fistula.
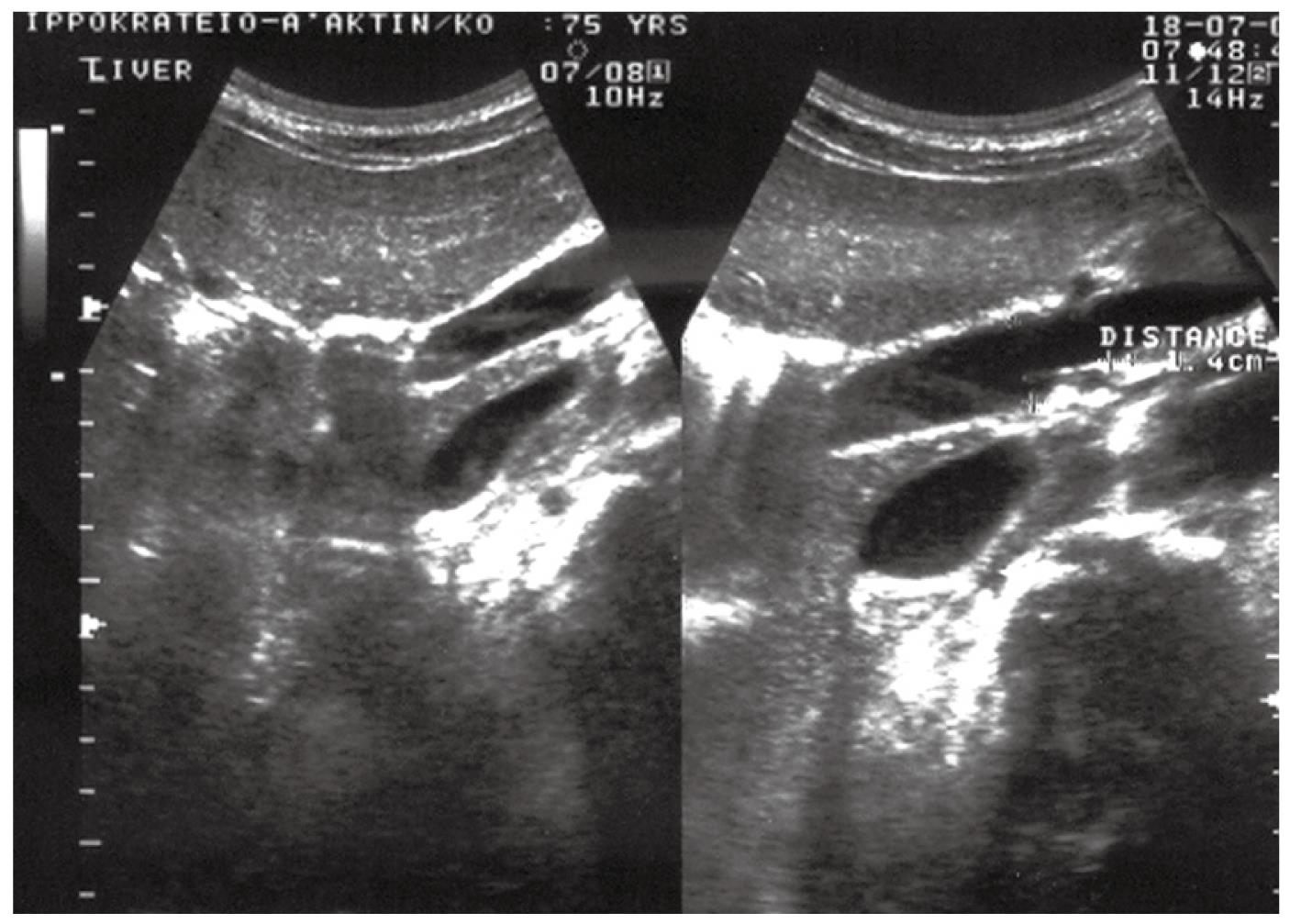
Figure 2 Ultrasonographic examination revealing pneumobilia and moderate dilatation of the intrahepatic bile ducts, with a normal common bile duct and a thick-walled gallbladder.
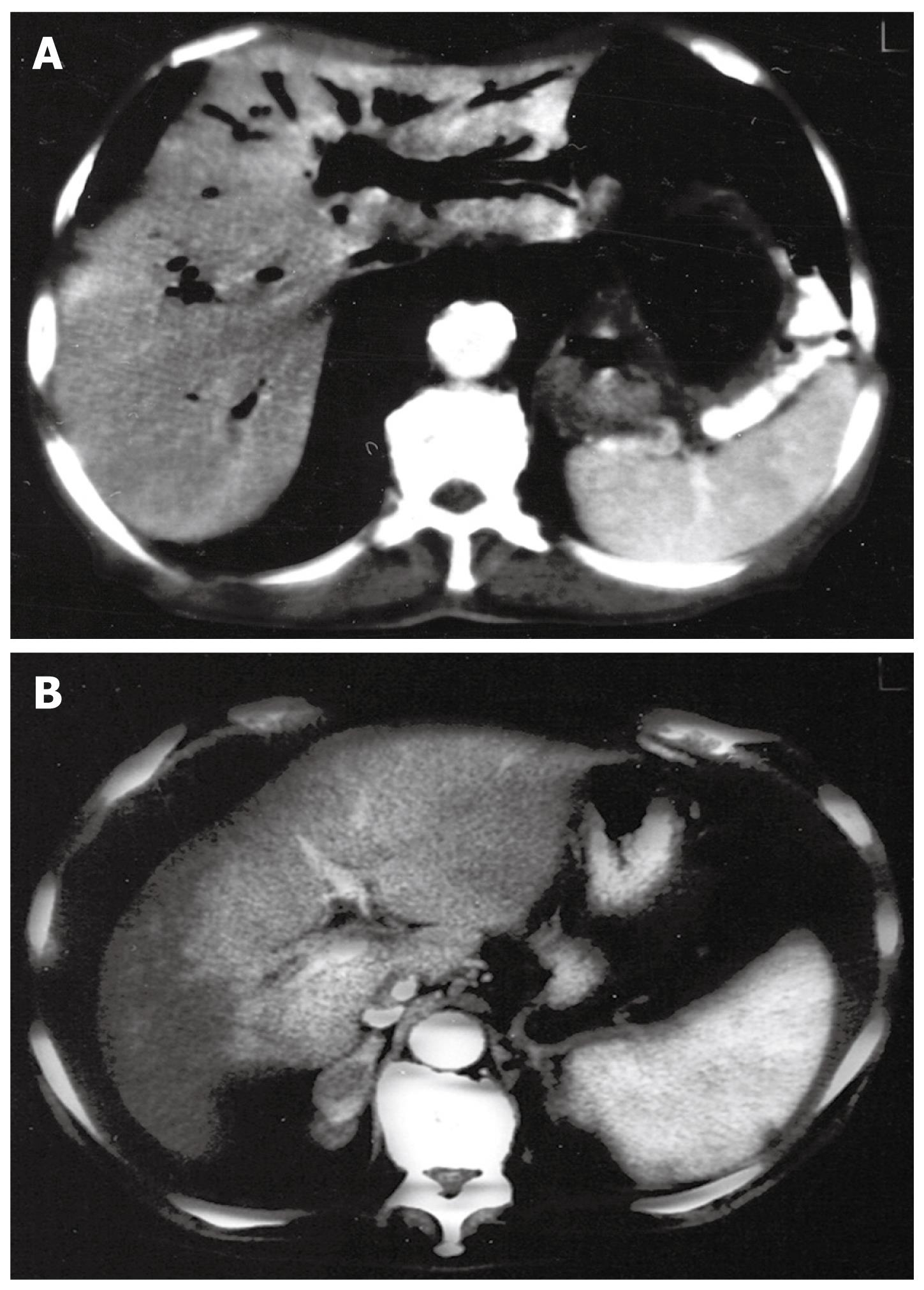
Figure 3 Computed tomography scan.
A: Massive pneumobilia (“air cholangiogram”); B: Presence of air detected in the gallbladder.
- Citation: Savvidou S, Goulis J, Gantzarou A, Ilonidis G. Pneumobilia, chronic diarrhea, vitamin K malabsorption: A pathognomonic triad for cholecystocolonic fistulas. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(32): 4077-4082
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i32/4077.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.4077