Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2009; 15(27): 3382-3393
Published online Jul 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3382
Published online Jul 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3382
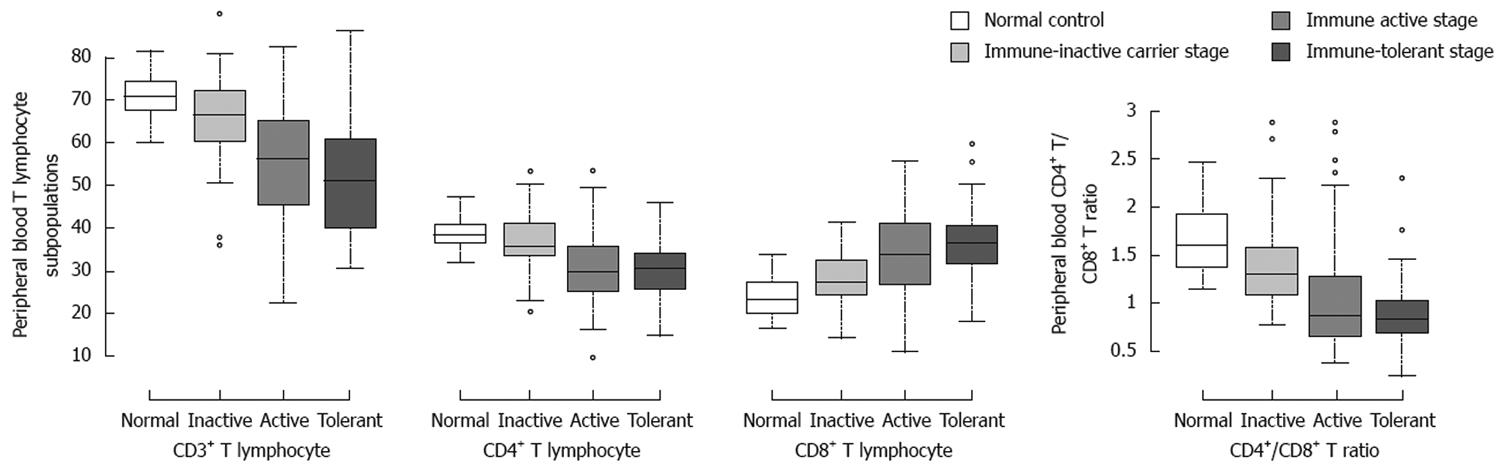
Figure 1 Peripheral blood T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients at different clinical stages of chronic HBV infection.
The mean percentages of CD3+, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and CD4+/CD8+ ratio were shown in patients at the different stages and control. Top of the box represents the 75%, the bottom of the box represents the 25%, the solid line in the middle of the box represents the median. Whiskers above and below the box indicate the 90% and 10%, while filled circles represent outliers. A statistically significant difference in T cells but not in CD4+ cells was observed between chronic HBV infection patients and normal control (P < 0.01). In the peripheral blood of patients at the immune-tolerant and immune-active stages, CD8+ T-cells were the dominant lymphocytes compared to CD4+ T-cells, whereas in the peripheral blood of patients at the immune-inactive carrier stage and normal controls, CD4+ T-cells were the dominant lymphocytes compared to CD8+ T-cells.
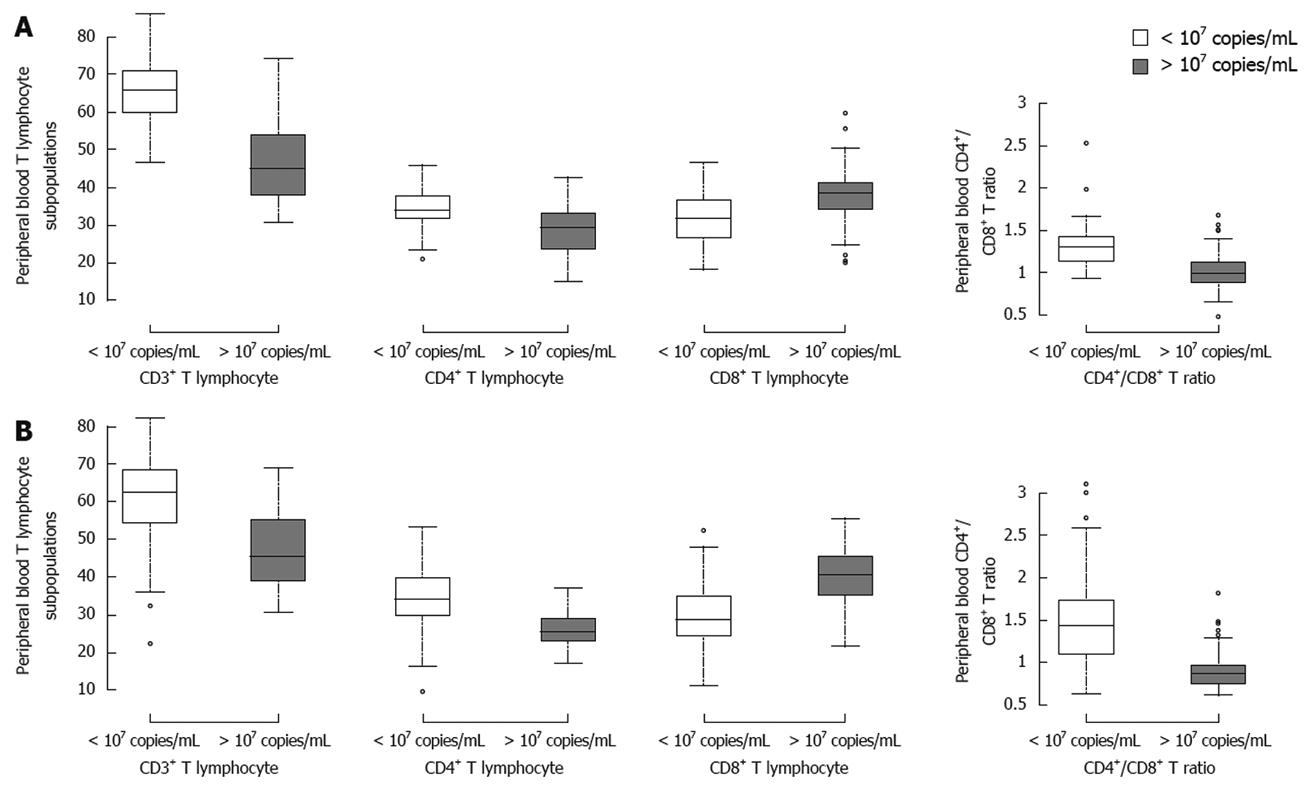
Figure 2 Mean percentages of CD3+, CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells in patients at immune-tolerant stage (A) and immune active stage (B) of chronic HBV infection.
Patients were divided into two groups based upon HBV DNA load. The proportion of CD8+ T-cells was significantly higher in patients with a high HBV load than in patients with a low HBV load at the immune-tolerant stage (38.66 ± 7.11 vs 31.50 ± 6.40, P < 0.001) and at the immune active stage (40.07 ± 7.55 vs 30.11 ± 7.69, P < 0.001). The percentage of CD4+ T-cells was significantly higher in patients with a low HBV load than in patients with a high HBV load at the immune-tolerant stage (33.77 ± 5.81 vs 29.05 ± 6.11, P < 0.001) and at the immune active stage (34.41 ± 7.23 vs 26.25 ± 4.52, P < 0.001). Significant differences were found in CD3+ T-cells and CD4+/CD8+ ratio between patients with a high HBV load and a low HBV load at the immune-tolerant stage (45.90 ± 10.69 vs 65.40 ± 8.70, 0.78 ± 0.21 vs 1.11 ± 0.32, P < 0.001) and at the immune active stage (46.82 ± 9.25 vs 62.01 ± 10.52, 0.69 ± 0.23 vs 1.24 ± 0.47, P < 0.001). CD8+ T-cells were predominant compared with CD4+ T-cells in patients with a high HBV load, whereas CD4+ T-cells were predominant compared with CD8+ T-cells in patients with a low HBV load.
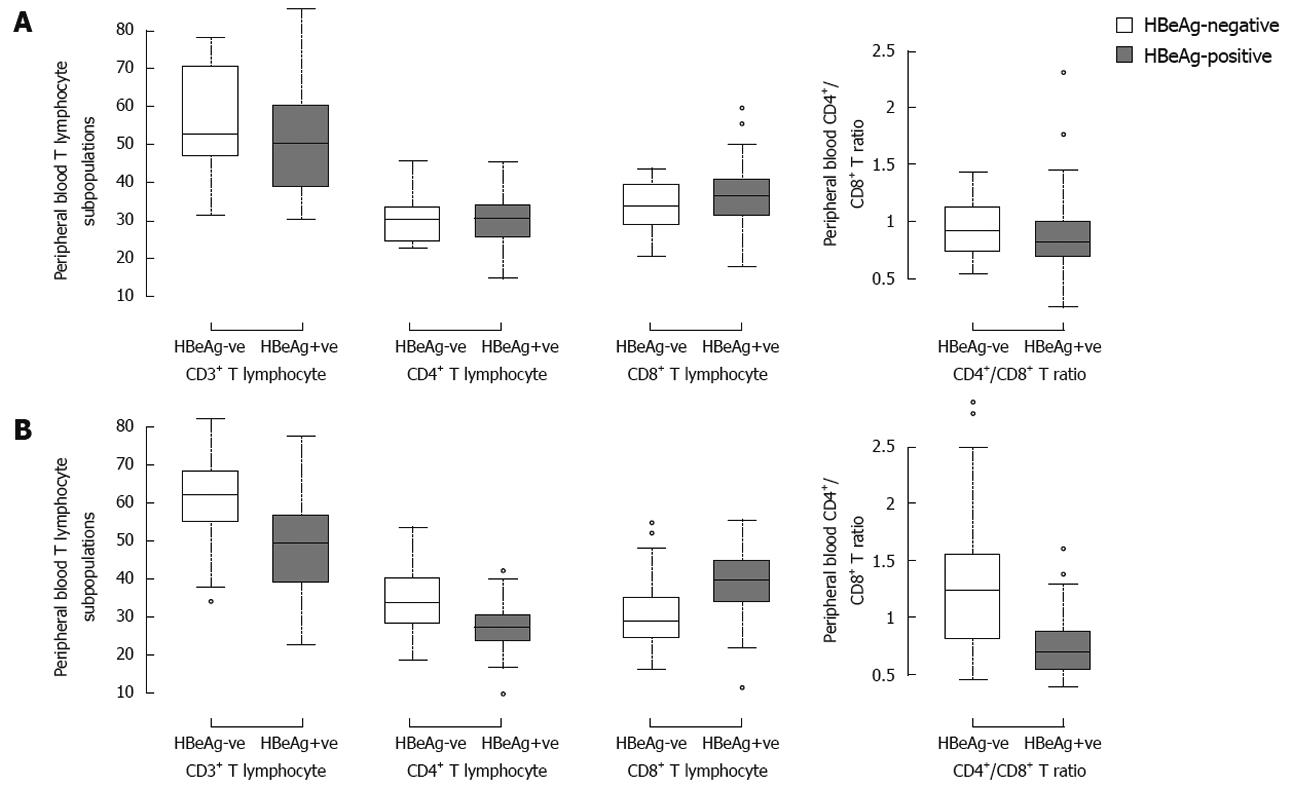
Figure 3 Mean percentages of CD3+, CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells in peripheral blood of patients at the immune-tolerant stage (A) and immune active stage (B).
Patients were divided into two groups based upon the HBeAg status. The proportion of CD8+ T-cells was significantly higher in HBeAg positive patients than in HBeAg negative patients at the immune active stage (39.24 ± 8.05 vs 30.66 ± 8.01, P < 0.001). The percentage of CD4+ T-cells was significantly higher in HBeAg negative patients than in HBeAg positive patients at the immune active stage (33.60 ± 7.41 vs 27.39 ± 5.75, P < 0.001). Significant differences were found in CD3+ T-cells and CD4+/CD8+ ratio between HBeAg positive and negative patients (48.99 ± 11.06 vs 60.48 ± 11.22, 0.74 ± 0.25 vs 1.21 ± 0.50, P < 0.001). CD8+ T-cells were predominant compared with CD4+ T-cells in patients with a high HBeAg expression level, whereas CD4+ T-cells were predominant compared with CD8+ T-cells in patients with a low HBeAg expression level. In immune-tolerant-patients, no significant difference was observed in parameters of T-cell profile between HBeAg negative and positive patients (P > 0.05).
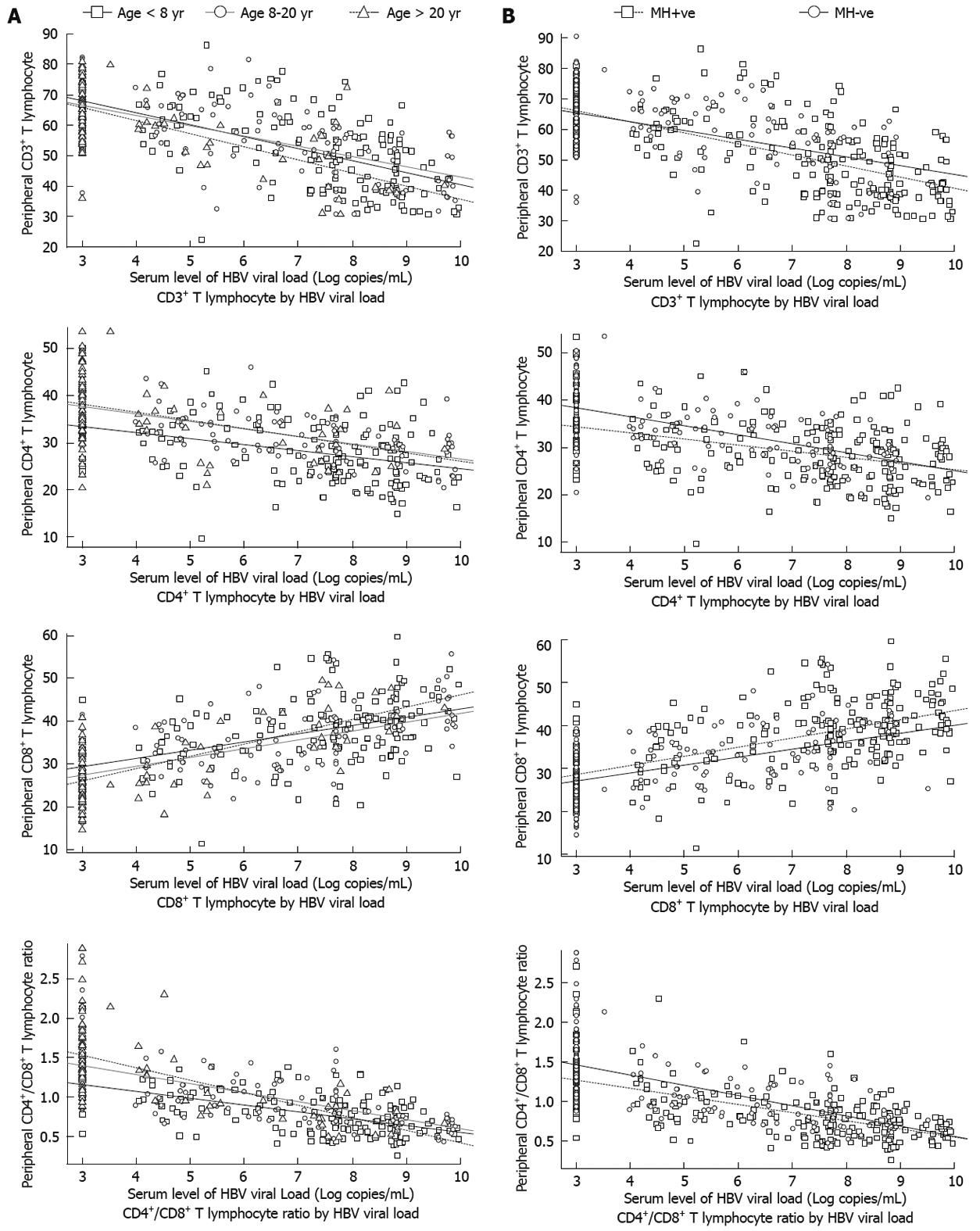
Figure 4 Correlation between T-cell subsets and HBV load stratified by age at HBV infection (A) and maternal HBV infection status (B).
Three regression lines (with different slopes) were drawn for patients at different ages of HBV infection. The coefficient of the interaction term “HBVDNA: age-at-HBV-infection” was not statistically significant for each parameter of T lymphocyte subpopulations (P > 0.05). A similar pattern was seen when stratified by maternal HBV infection status.
- Citation: You J, Zhuang L, Zhang YF, Chen HY, Sriplung H, Geater A, Chongsuvivatwong V, Piratvisuth T, McNeil E, Yu L, Tang BZ, Huang JH. Peripheral T-lymphocyte subpopulations in different clinical stages of chronic HBV infection correlate with HBV load. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(27): 3382-3393
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i27/3382.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.3382