Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2009; 15(2): 240-244
Published online Jan 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.240
Published online Jan 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.240
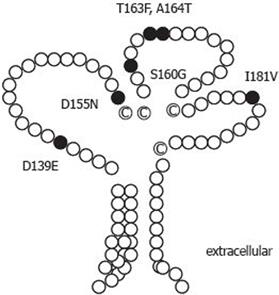
Figure 1 Putative structure of tupaia CD81.
Tupaia CD81 LEL cDNA was cloned and sequenced as described in Materials and Methods. Deduced amino acid sequence was compared with that of human. The tupaia CD81 secondary structure was drawn according to the three-dimensional structure of human CD81 LEL, and changes in six amino acids of tupaia CD81 LEL were illustrated by black color.
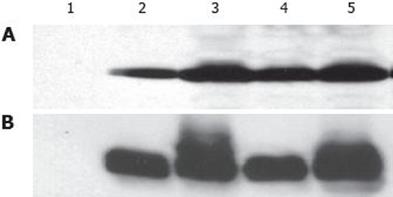
Figure 2 Expression and purification of soluble tupaia CD81 LEL using mouse monoclonal anti-human CD81 5A6 (A), and 1D6 (B) antibodies.
Tupaia CD81 LEL was expressed and purified in E. coli as a GST fusion protein as described in Materials and Methods. Purified proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE, and immunoblot using mouse monoclonal anti-human CD81 5A6 and 1D6 antibodies. Tup: tupaia; h: human; AGM: African green monkey; hCD81 LEL T163A: human CD81 containing a mutation of T to A at amino acid residue 163; 1: GST; 2: TupCD81 LEL-GST; 3: hCD81 LELT163A-GST; 4: AGMCD8 LEL-GST; 5: hCD81 LEL-GST.
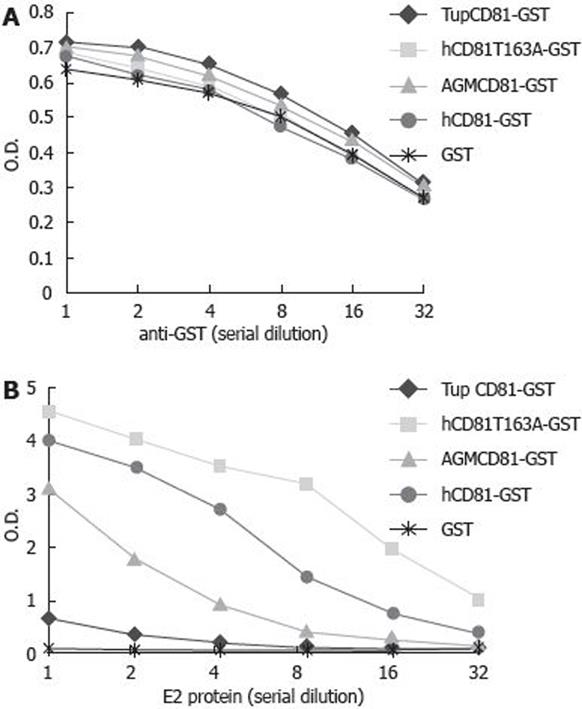
Figure 3 Interaction between tupaia CD81 LEL and HCV E2 protein.
Plates were coated with 100 &mgr;L of recombinant GST or GST-CD81 LEL fusion proteins (5 mg/L), reciprocally diluted anti-GST antibody (A) (starting dilution at 1:1000) or HCV E2 protein (B) (starting concentration 2 mg/L) was added to the plates. Binding of anti-GST or HCV E2 protein was assessed as described in Materials and Methods. OD: optical density; Tup: tupaia; h: human; AGM: African green monkey; hCD81T163A: human CD81 containing a mutation of T to A at amino acid 165.
-
Citation: Tian ZF, Shen H, Fu XH, Chen YC, Blum HE, Baumert TF, Zhao XP. Interaction of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2 with the large extracellular loop of
tupaia CD81. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(2): 240-244 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i2/240.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.240