Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2009; 15(19): 2418-2422
Published online May 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2418
Published online May 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2418
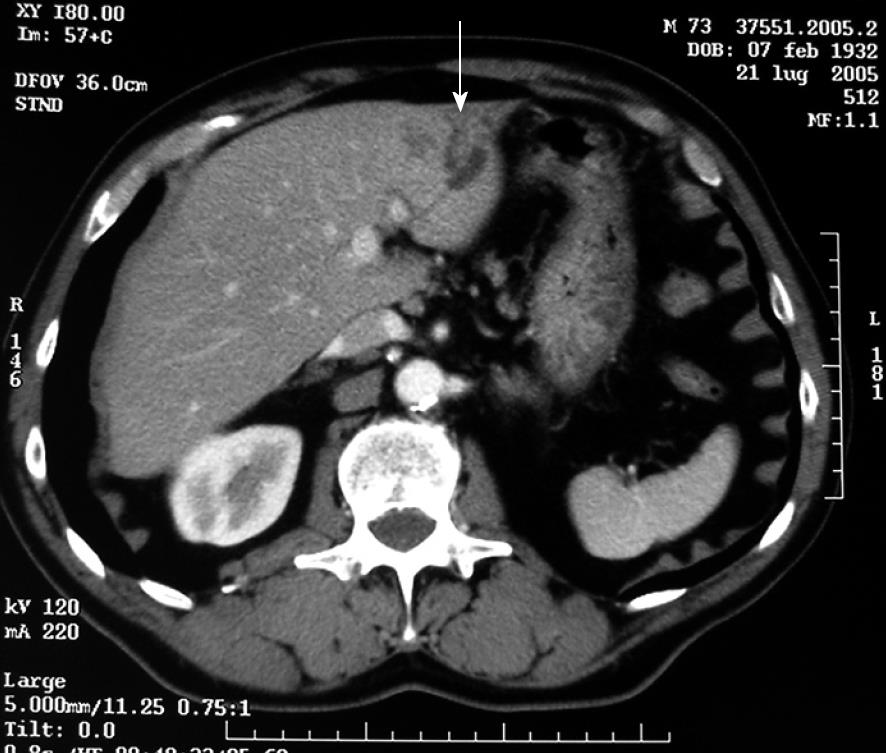
Figure 1 Abdominal CT scan (July 2005) showing a low-density pseudonodular area (arrow) of 2 cm with biliary dilatation.
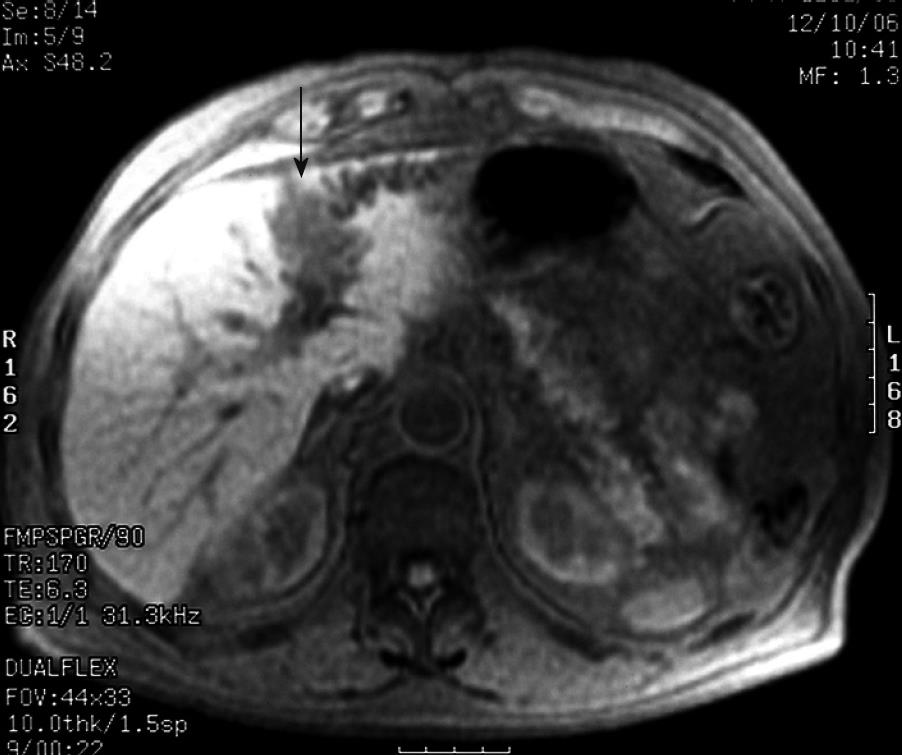
Figure 2 Abdominal MRI (August 2005) showing a pseudonodular mass (arrow) measuring about 5 cm × 3 cm of the hepatic segments II-III.
At the bottom of the lesion, the biliary tree appears dilated.
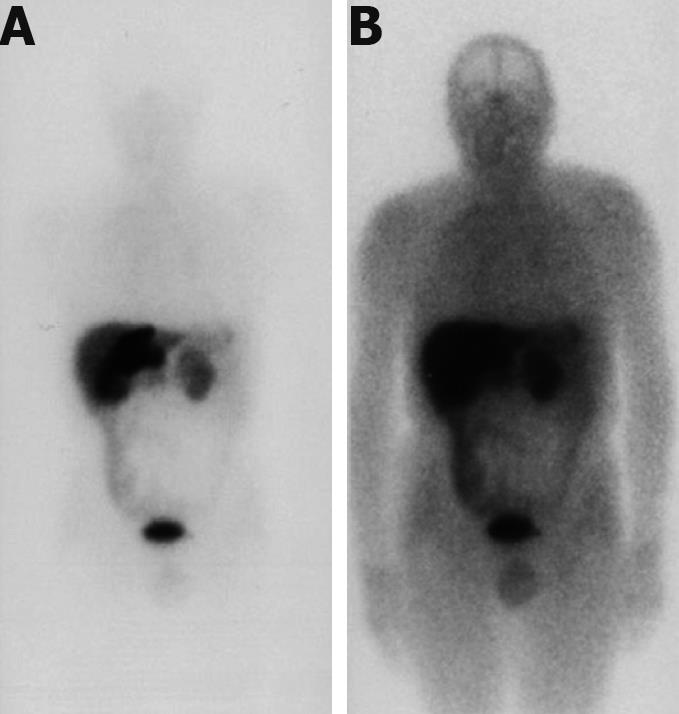
Figure 3 111 In-pentetreotide (octreotide) scintigraphy.
A: Before hepatectomy: marked hyperactivity of the lesion is observed in the left hepatic lobe and interaortal adenopathy is observed; B: After hepatectomy; abnormal fluid accumulation of ligand in the epigastric region and dishomogeneous hepatic distribution.
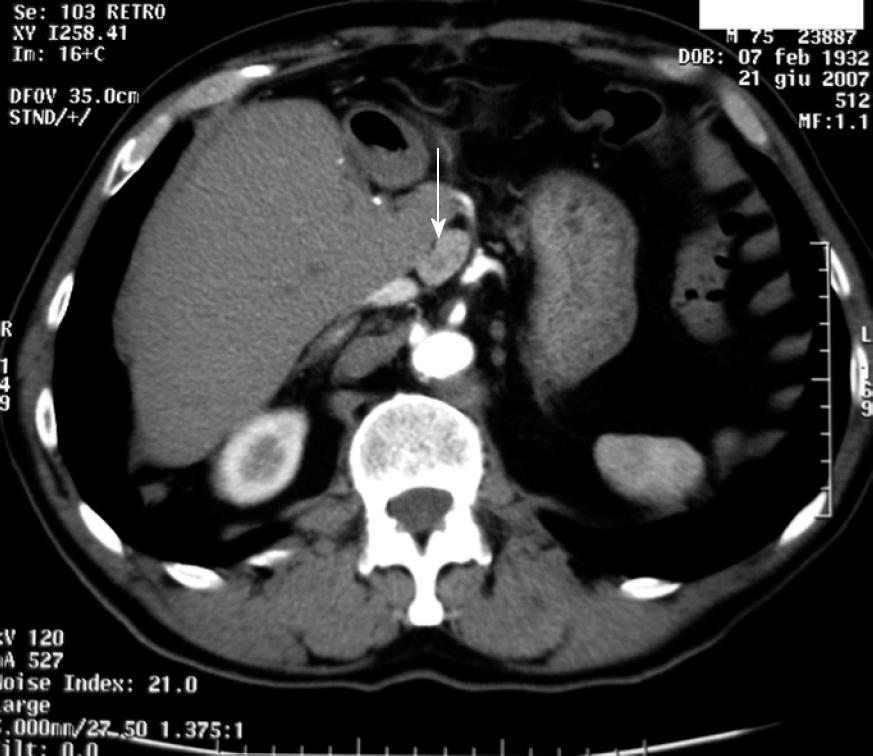
Figure 4 Abdominal CT scan.
Results of left hepatectomy show an extended nodular mass measuring about 2.5 cm × 1.5 cm arranged on the back part of the caudate lobe, indicating a lymph node localization of disease.
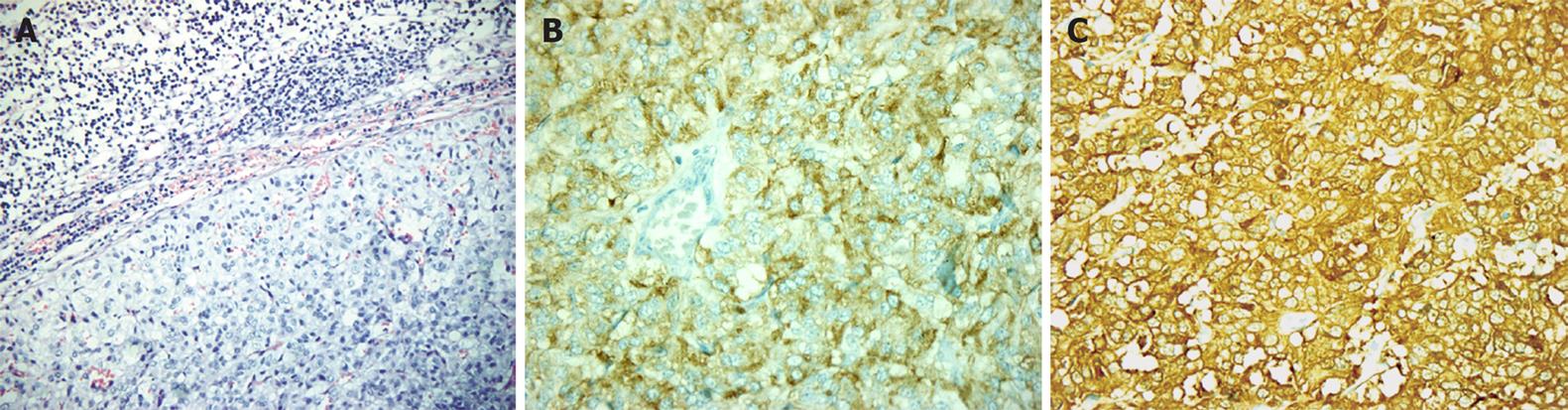
Figure 5 Histological and immunohistochemistry.
Proliferation of average sized monomorphic epithelial cells collected in strings and glandular structures (A). Positive immunohistochemistry staining for CgA (B) and NSE (C).
- Citation: Fenoglio LM, Severini S, Ferrigno D, Gollè G, Serraino C, Bracco C, Castagna E, Brignone C, Pomero F, Migliore E, David E, Salizzoni M. Primary hepatic carcinoid: A case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(19): 2418-2422
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i19/2418.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.2418