Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2009; 15(17): 2125-2131
Published online May 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2125
Published online May 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2125
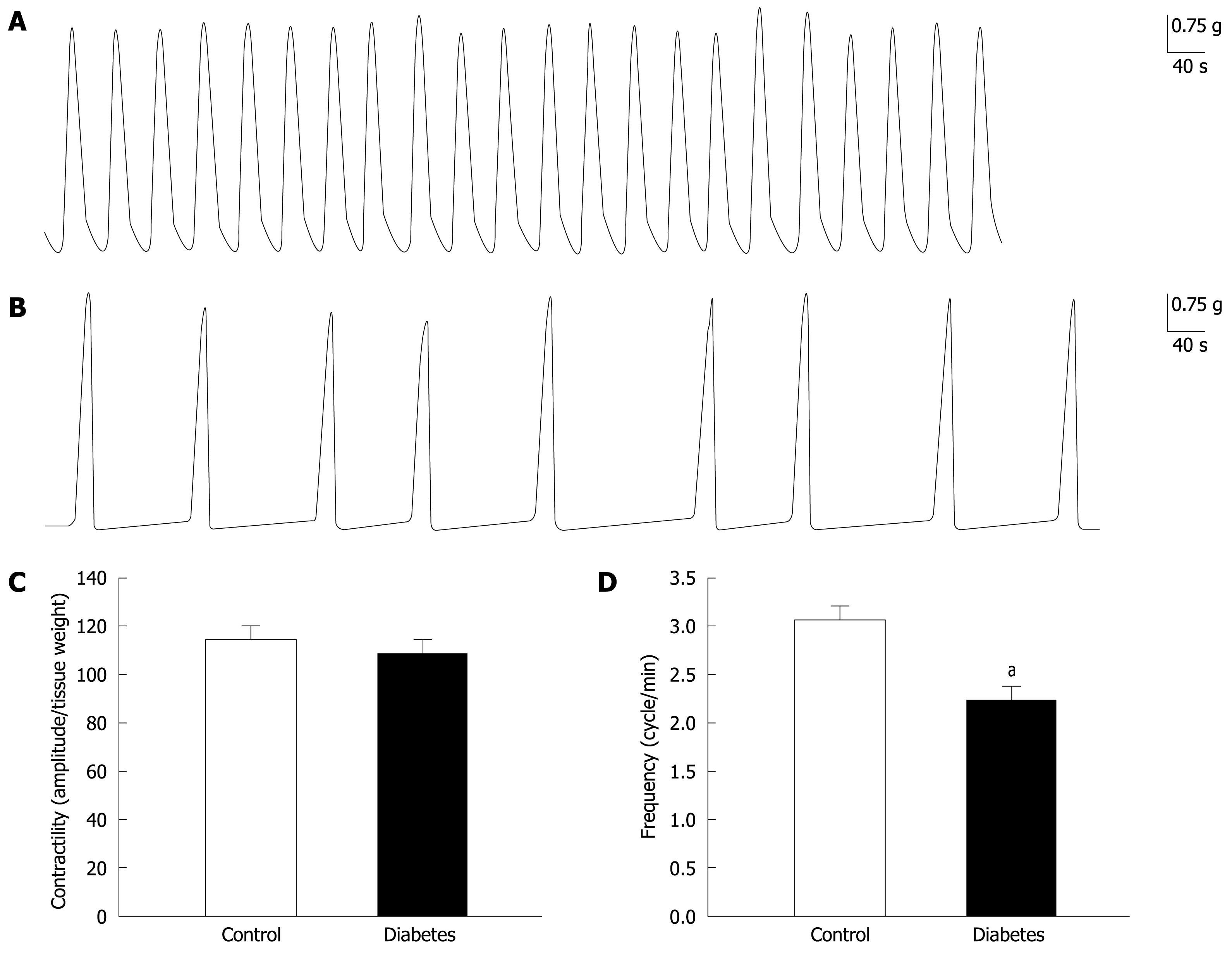
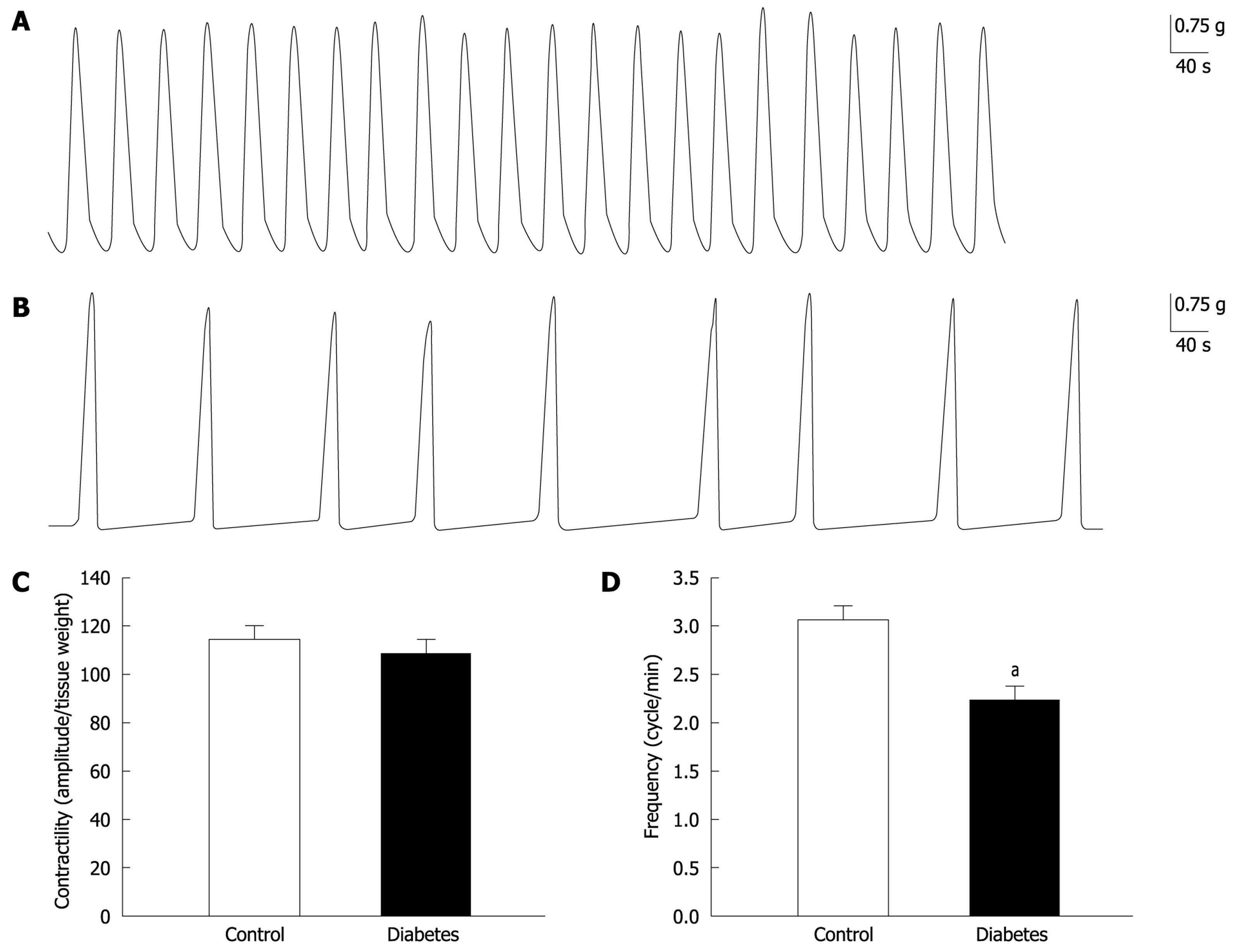
Figure 1 Comparison of gastric smooth muscle contractilities between normal and diabetic rats.
A, B: The row traces gastric smooth muscle spontaneous contractions in normal and diabetic rats; C, D: Summary of the contractility in normal and diabetic rats. The contractility per weight of gastric smooth muscle strip was not significantly different between normal and diabetic rats (A-C, n = 8, P > 0.05). However, the frequency of spontaneous contraction was significantly depressed in diabetic rats (A, B and D, n = 8, aP < 0.01).
Figure 2 The sensitivity of gastric smooth muscle to CNP.
A, B: The row traces gastric smooth muscle spontaneous contractions in response to CNP in normal and diabetic rats; C-E: Summary of the contractility in response to CNP in normal and diabetic rats. CNP induced relaxation of gastric antral smooth muscle in control and diabetic rats (A, B). However, CNP-induced inhibition of spontaneous contraction was potentiated in diabetic rats, and the amplitude (C, n = 8, bP < 0.01) and frequency (D, n = 8, dP < 0.01) of spontaneous contraction were more potentially suppressed by CNP in diabetic rats. The inhibition time of CNP of spontaneous contraction was significantly prolonged in diabetic rats (E, n = 8, fP < 0.01).
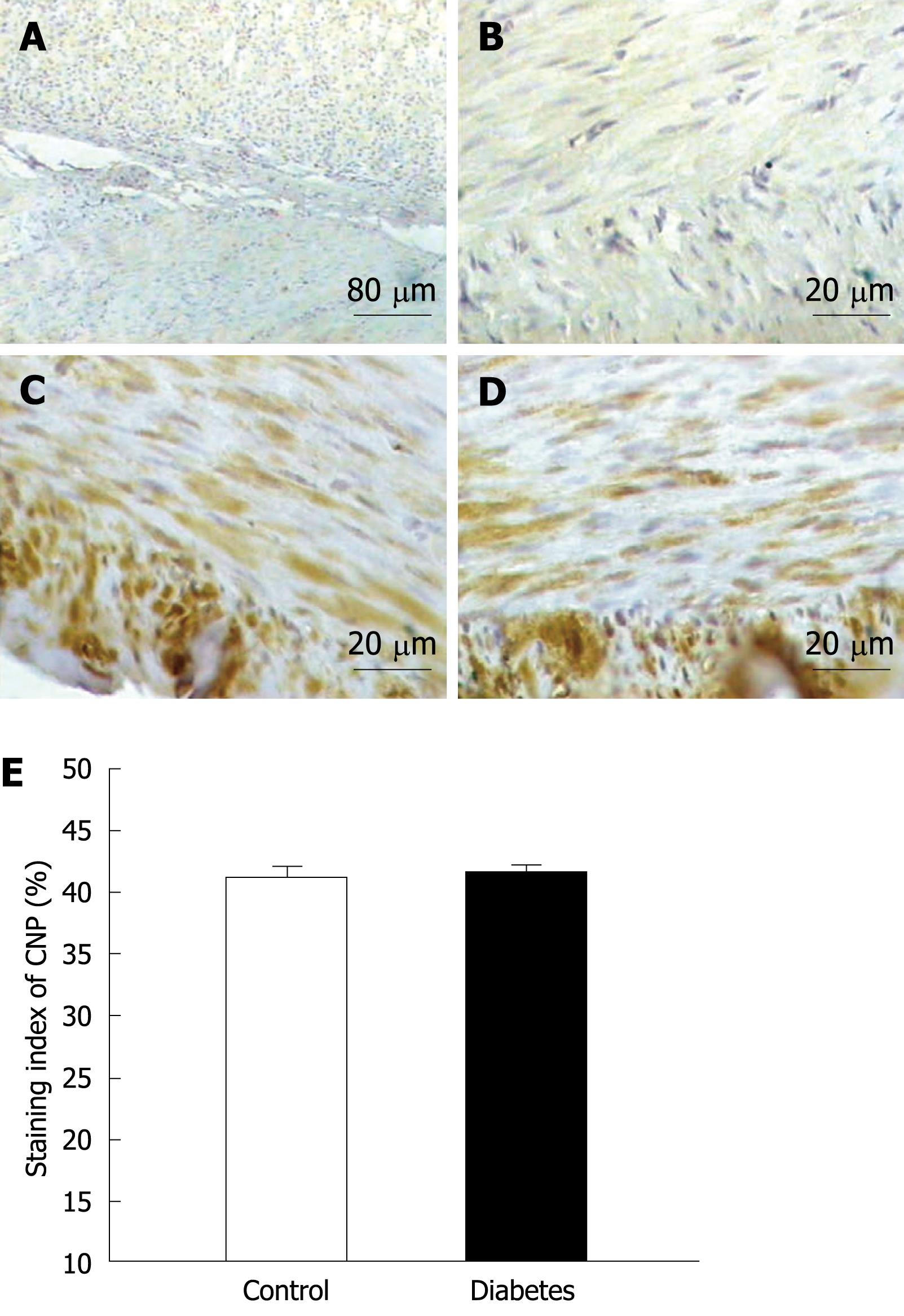
Figure 3 CNP expression in gastric tissues in normal and diabetic rats.
A-D: CNP expression in gastric smooth muscle in normal and diabetic rats. In negative controls CNP was not expressed in normal and diabetic rats (A, B) and the CNP immunopositive brown granules were mainly expressed in gastric muscle layers of normal and diabetic rats (C, D); E: Summary of CNP expression in normal and diabetic rats. The staining indexes were not significantly different between normal and diabetic rats (E, n = 8, P > 0.05). Scale bars = 80 &mgr;m (A), 20 &mgr;m (B-D).
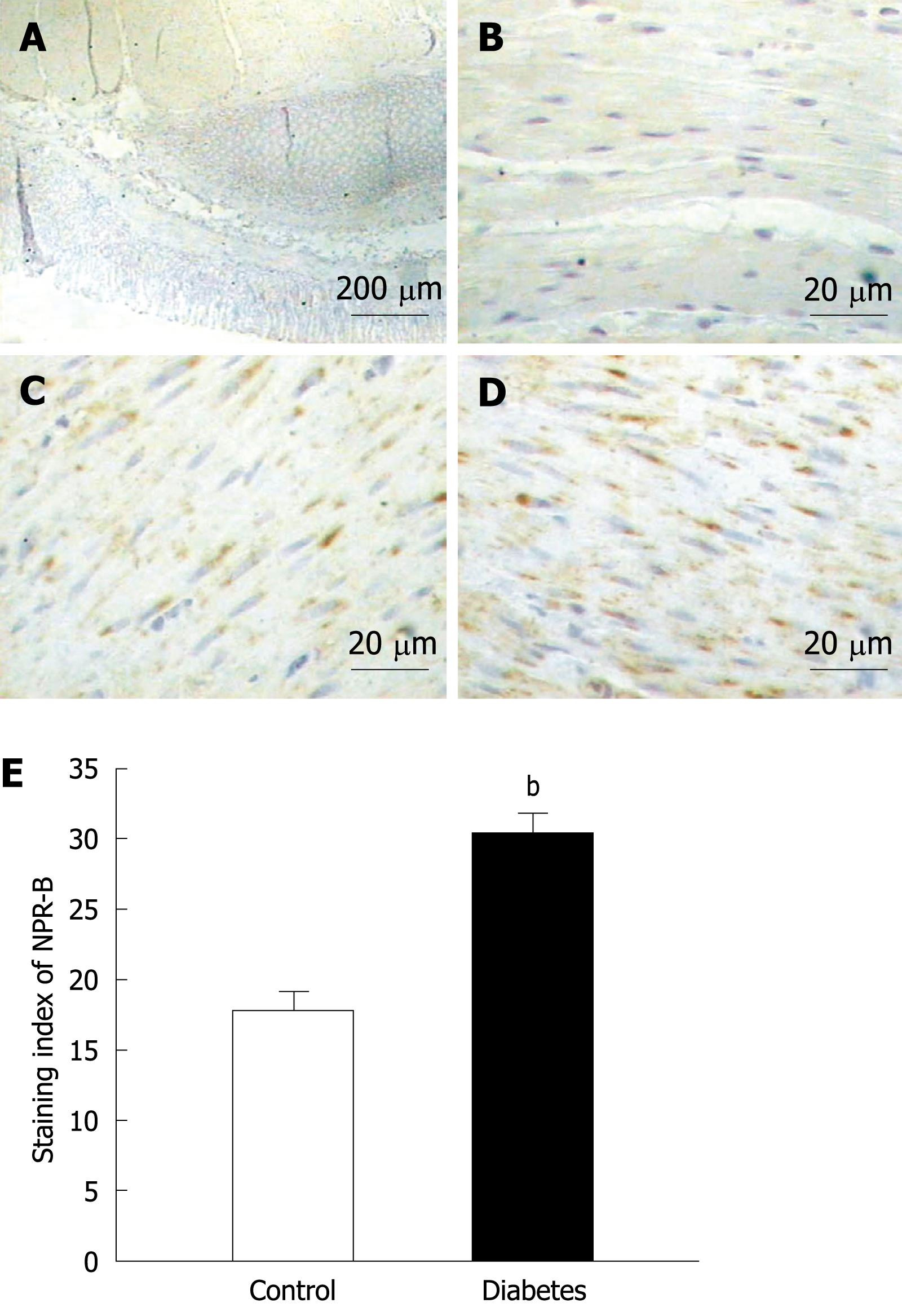
Figure 4 NPR-B expression in gastric tissues in normal and diabetic rats.
A-D: NPR-B expression in gastric smooth muscle in normal and diabetic rats. There was no NPR-B immunopositive expression in negative controls of normal and diabetic rats (A, B). The NPR-B immunopositive brown granules were expressed in gastric antral smooth muscle in normal and diabetic rats. The staining was deeper in diabetic rats (C, D); E: Summary of NPR-B expression in normal and diabetic rats. The staining indexes were increased significantly in diabetic rats (E, n = 8, bP < 0.01). Scale bars = 200 &mgr;m (A), 20 &mgr;m (B-D).
- Citation: Cai YL, Xu DY, Li XL, Qiu ZX, Jin Z, Xu WX. C-type natriuretic-peptide-potentiated relaxation response of gastric smooth muscle in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(17): 2125-2131
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i17/2125.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.2125