Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2009; 15(12): 1518-1523
Published online Mar 28, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1518
Published online Mar 28, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1518
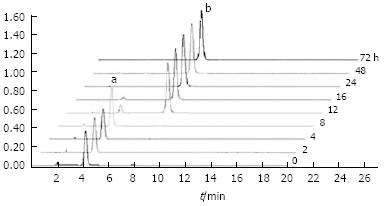
Figure 1 Biotransformation of aseculin by anaerobic human gut bacteria.
The gut bacteria comprised 20 pooled fecal samples from healthy volunteers. Incubation was performed under anaerobic conditions (80% N2, 10% CO2, 10% H2) at 37°C for defined time periods. Ten millilitre of samples was collected at 0, 2, 4, 8, 12, 16, 24, 48 and 72 h, respectively post-incubation. Aesculin and metabolites were then extracted with methanol and analyzed by HPLC. The vertical axis shows the relative values for the concentration of aesculin and/or its metabolite. The horizontal axis indicates the HPLC overflow time.
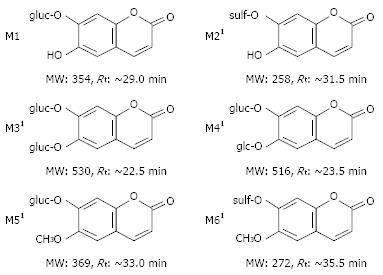
Figure 2 Summary of aesculetin metabolites identified in rat urine.
1The position(s) of methylation and/or conjugation(s) may be exchangeable on the two phenols.
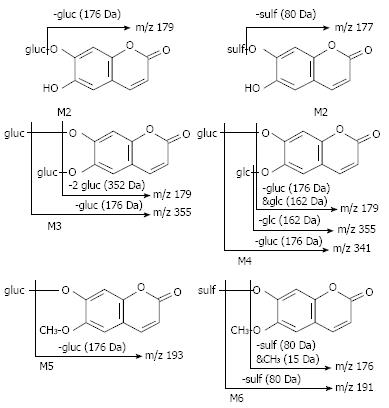
Figure 3 Proposed characteristic (-) CAD-MS/MS fragmentations for aesculetin metabolites.
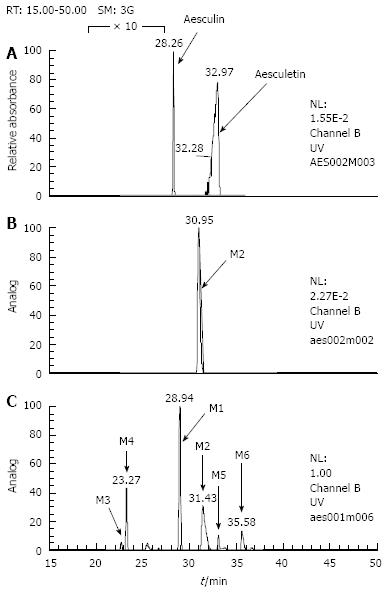
Figure 4 HPLC UV-chromatograms of reference standards for aesculetin and aesculin (A), M2 isolated from rat urine (B), and a rat urine sample dosed with aesculetin with assignments of aesculetin urinary metabolites (C).
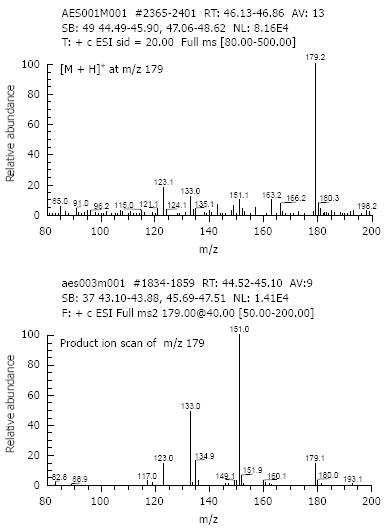
Figure 5 Aesculetin LC/(+)ESI-MS and MS/MS spectral data.
- Citation: Ding WJ, Deng Y, Feng H, Liu WW, Hu R, Li X, Gu ZM, Dong XP. Biotransformation of aesculin by human gut bacteria and identification of its metabolites in rat urine. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(12): 1518-1523
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i12/1518.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.1518