Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2008; 14(42): 6584-6588
Published online Nov 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6584
Published online Nov 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6584
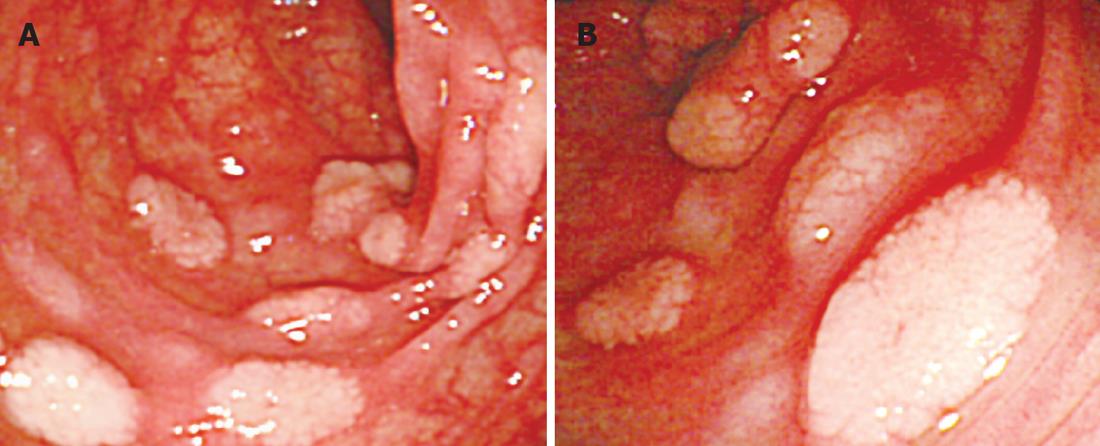
Figure 1 Colonoscopic images of the transverse colon.
A: Multiple small polypoid lesions were presented; B: Closer observation revealed tiny submucosal tumors as well as whitish polypoid lesions.
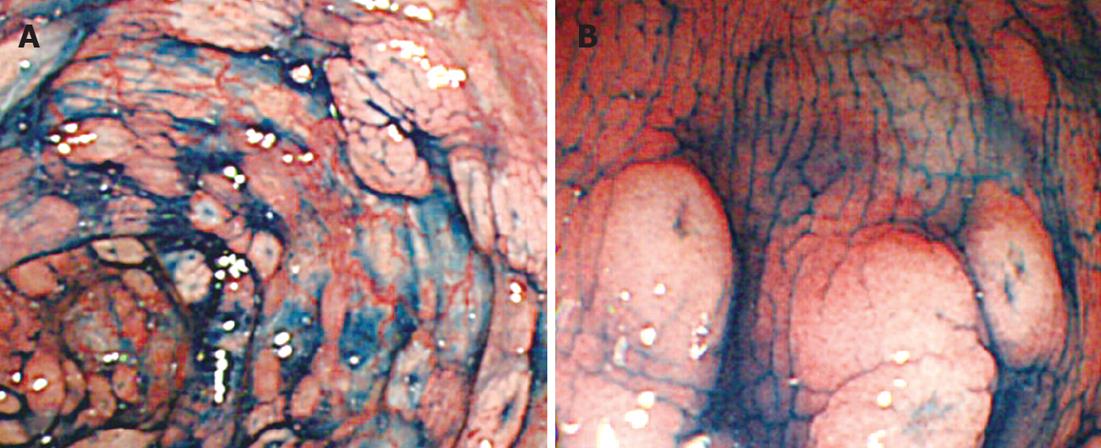
Figure 2 Colonoscopic images with indigo carmine dye.
A: Multiple lymphomatous polyposis was clearly depicted; B: Closer observation revealed polypoid and aphthoid lesions had tiny central depression.
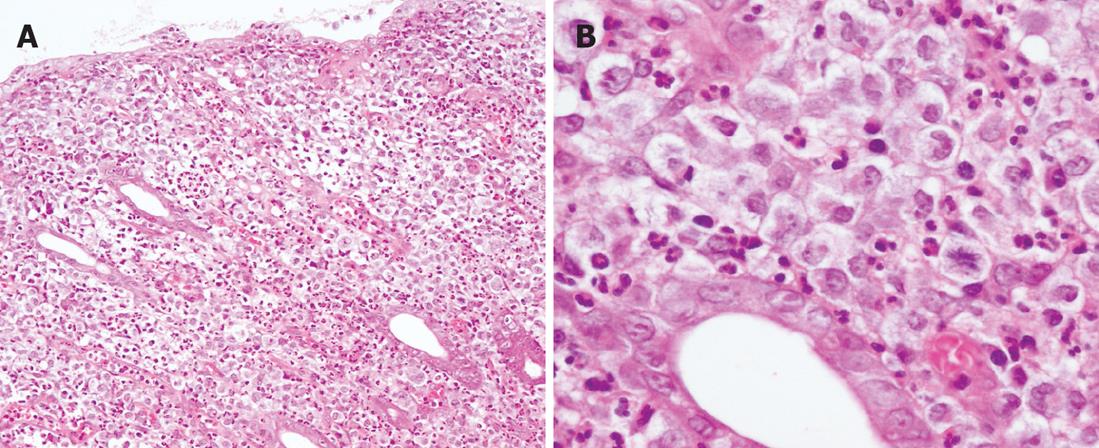
Figure 3 Pedunculated colonic mucosal tissue.
Biopsy specimens of the polypoid lesion showing diffuse proliferation of atypical lymphoid cells in the mucosal layer (A, HE, × 100). The lymphoma cells display pleomorphic nuclei and pale cytoplasm. (B, HE, × 400).
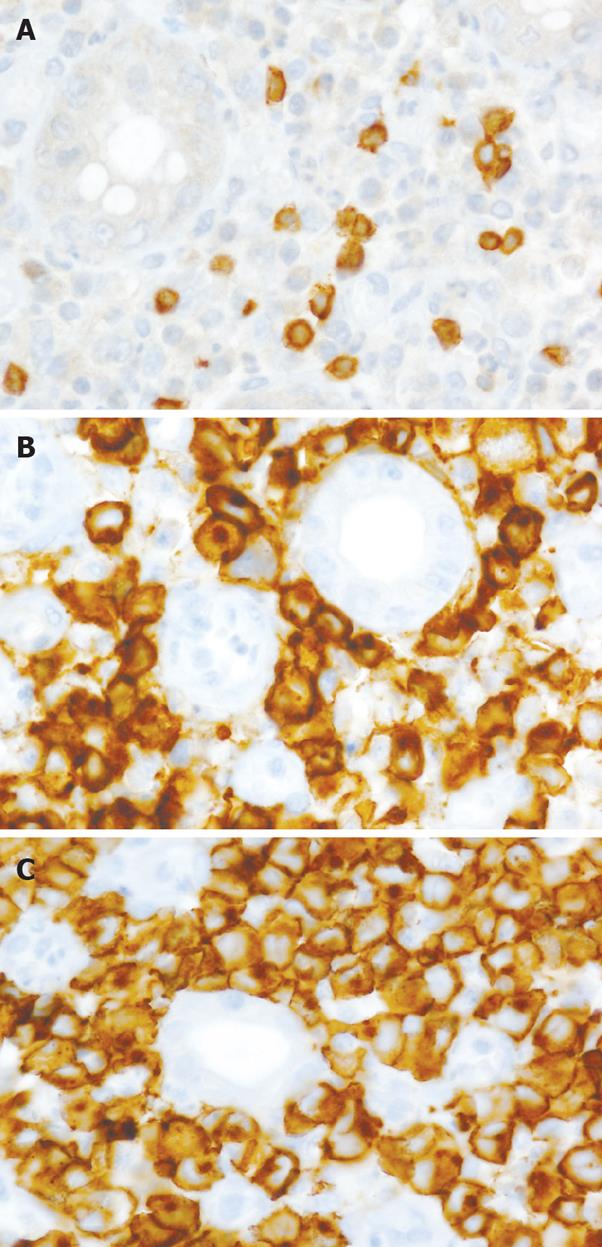
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical studies.
The lymphoma cells were positive for CD3 (A, × 400), CD25 (B, × 400) and CD30 (C, × 400), consistent with ATLL, anaplastic large cell variant.
- Citation: Hokama A, Tomoyose T, Yamamoto YI, Watanabe T, Hirata T, Kinjo F, Kato S, Ohshima K, Uezato H, Takasu N, Fujita J. Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma presenting multiple lymphomatous polyposis. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(42): 6584-6588
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i42/6584.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.6584