Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2008; 14(41): 6401-6407
Published online Nov 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6401
Published online Nov 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6401
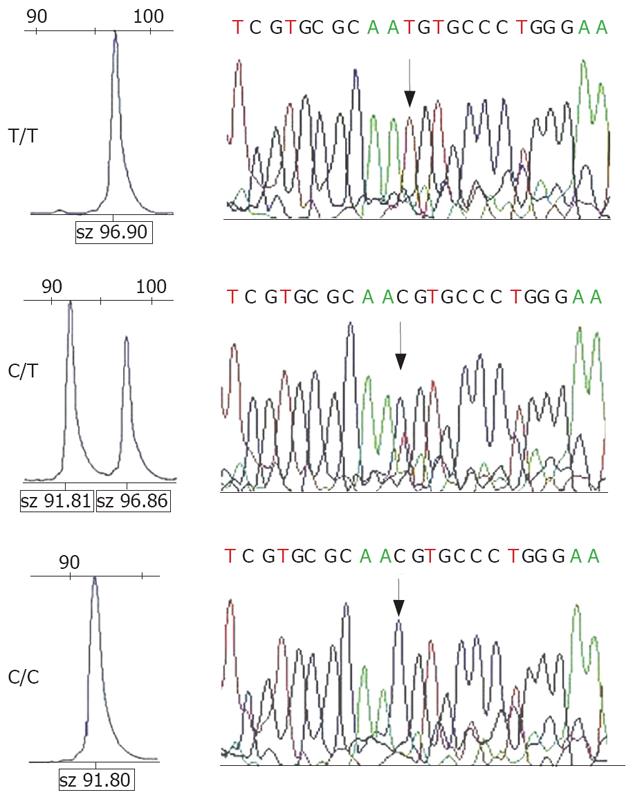
Figure 1 Genotyping results of ERCC1 codon 118 polymorphism electrophoresis results of PCR-LDR products with different genotypes and its sequencing results.
LDR products of ERCC1 118 C/C and T/T were 92 and 97 base pairs. The SNP sites are indicated by the arrowhead. The results were completely matched to the corresponding results derived from PCR-LDR.
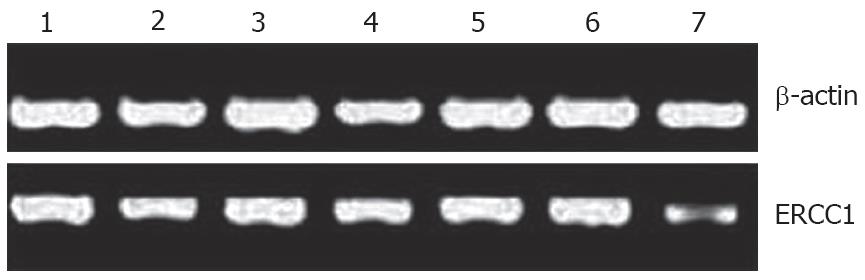
Figure 2 RT-PCR results of ERCC1 mRNA in gastric cancer tissues.
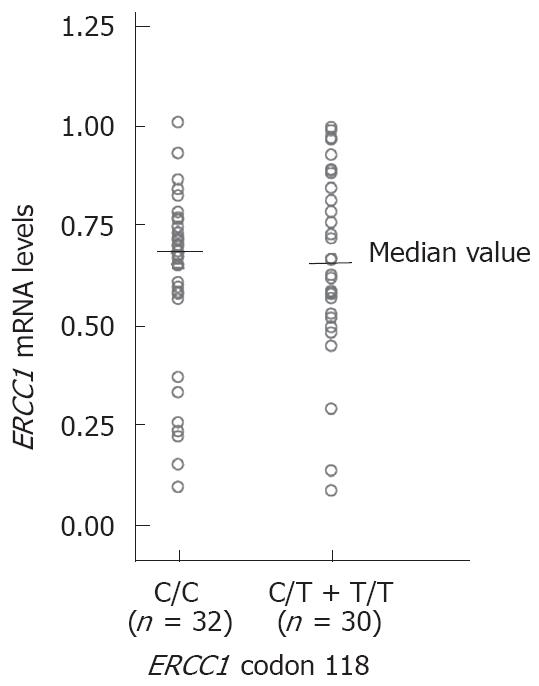
Figure 3 Relationship between ERCC1 mRNA levels and codon 118 poly-morphism.
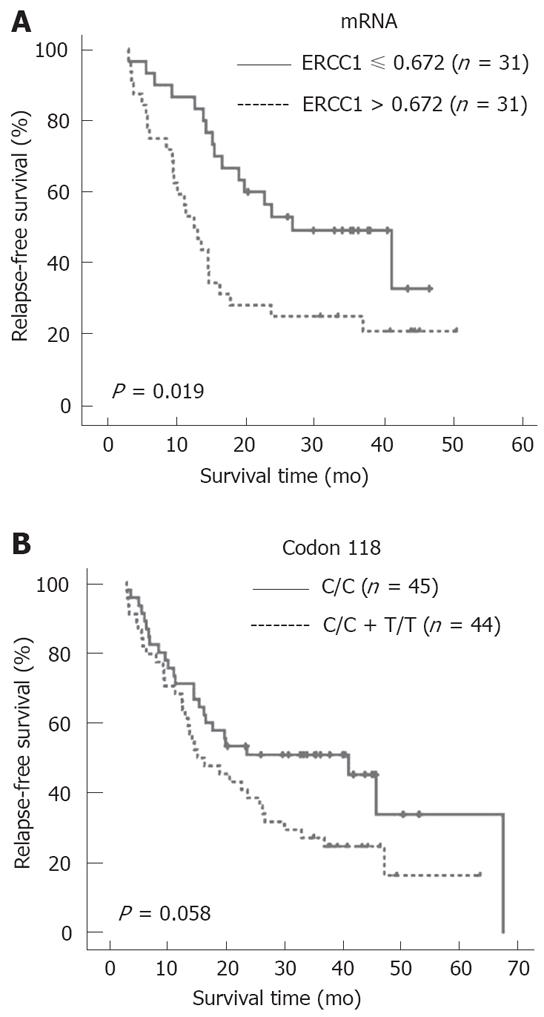
Figure 4 Relapse-free survival curves of gastric cancer patients according to ERCC1 mRNA expression and ERCC1 118 C/T polymorphism relapse-free survival curves according to ERCC1 mRNA expression (A) or ERCC1 118 polymorphism (B).
The relapse-free survival in patients with high levels of ERCC1 mRNA (> 0.672) was significantly poorer than that in patients with low levels (≤ 0.672) (P < 0.05), while there was no significant difference between patients with ERCC1 118 C/C and variant genotypes (T/T or C/T).
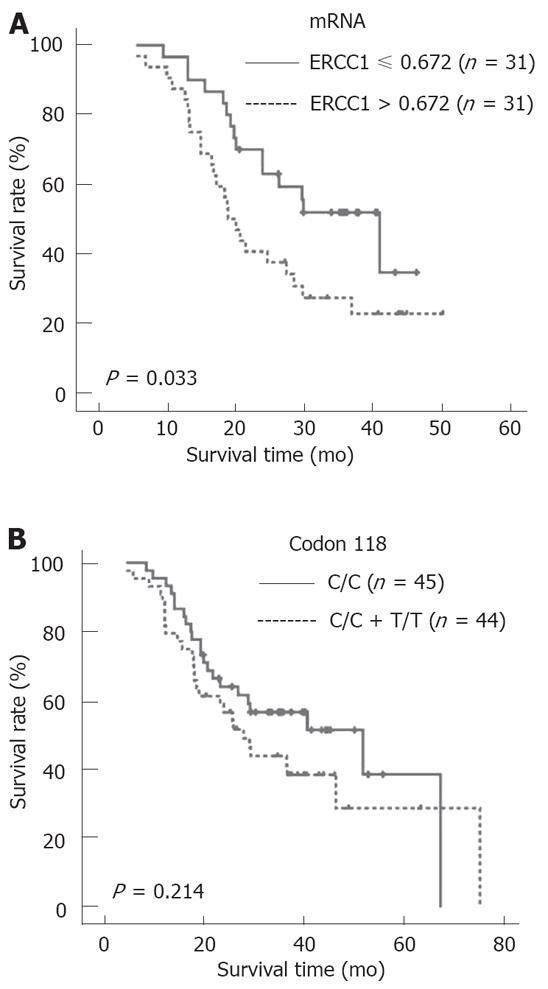
Figure 5 Overall survival curves of gastric cancer patients according to ERCC1 mRNA expression and ERCC1 118 C/T polymorphism survival curves according to ERCC1 mRNA levels (A) or ERCC1 118 polymorphism (B).
The overall survival in patients with low level of ERCC1 mRNA was significantly longer than that in patients with high levels (P < 0.05), while there was no significant difference found between patients with ERCC1 118 C/C and variant genotypes (T/T or C/T).
-
Citation: Huang ZH, Hua D, Du X, Li LH, Mao Y, Liu ZH, Song MX, Zhou XK.
ERCC1 polymorphism, expression and clinical outcome of oxaliplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(41): 6401-6407 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i41/6401.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.6401