Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2008; 14(40): 6115-6121
Published online Oct 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6115
Published online Oct 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6115
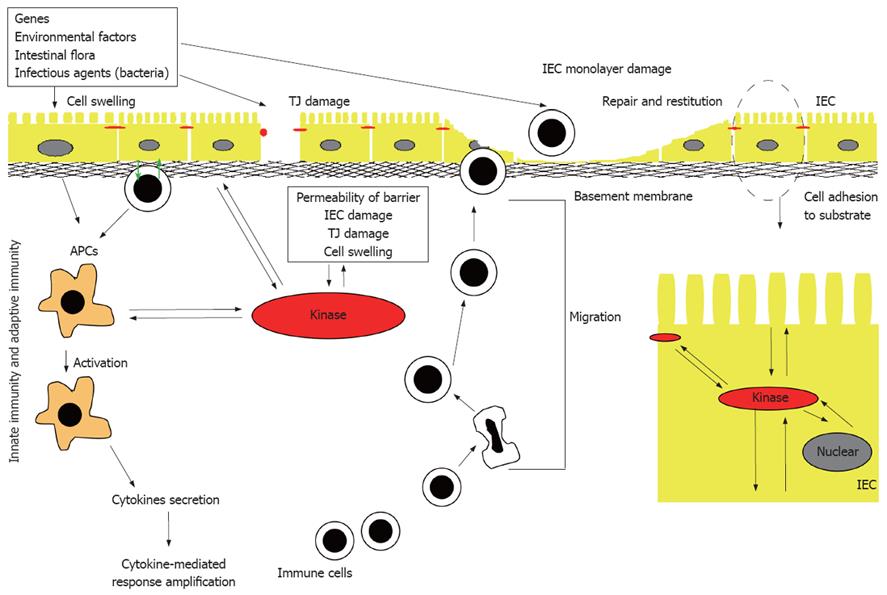
Figure 1 Pathogenesis of IBD.
Many different factors, such as genetic factors, environmental factors, and intestinal non-pathogenic or pathogenic bacteria can damage the mucus, epithelium, or the tight junction, to initiate the inappropriate regulation or deregulation of the immune response, leading to the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, decrease in epithelial barrier function and initiation of the inflammation-related signaling pathways. IEC: Intestinal epithelial cell; APC: Antigen presenting cell; TJ: Tight junction.
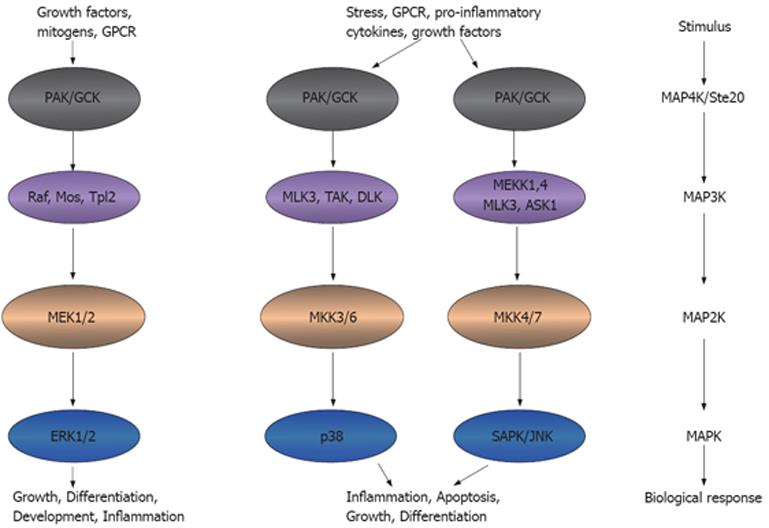
Figure 2 Ste20 kinases participate in inflammation.
Ste20 kinases that function as an MAP4K can activate MAP3K, MAP2K and MAPK, leading to the inflammatory functions. This model adapted from the model presented in http://www.cellsignal.com/pathways/map-kinase.jsp. MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase. GPCR: G-protein coupled receptor; PAK: p21 activated kinase; GCK: Germinal central kinase; MLK: Multiple lineage kinase; TAK: Tat-associated kinase; DLK: Dual leucine zipper-bearing kinase; MEK: MAPK/Erk kinase; MEKK: MEK kinase; ASK: Aspartate kinase; MKK: MAPK kinase; Erk: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; SAPK: Stress-activated protein kinase; JNK: Jun-amino-terminal kinase.
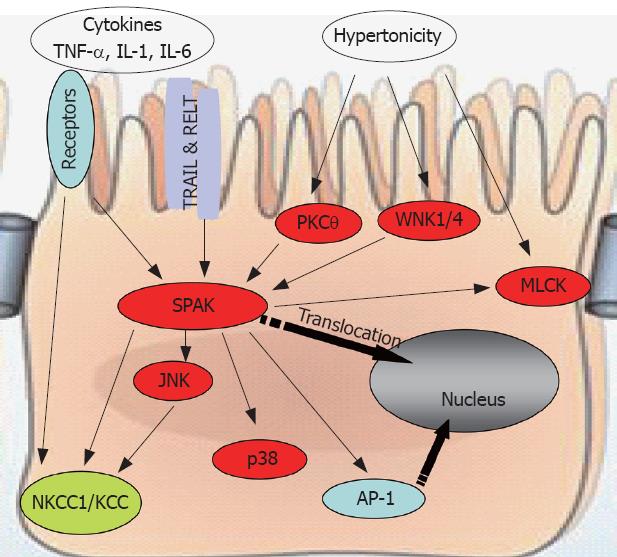
Figure 3 SPAK interacts with other molecules to maintain cellular homeostasis.
SPAK can be a substrate, indirectly or directly, for pro-inflammatory cytokines, environmental stress including hypertonicity, some other kinases such as PKCtheta;, WNK1/4, or other receptors, for example TRAIL & RELT. Also SPAK can function as upstream kinase to JNK, p38, or ion transport NKCC1/KCC, transcription factor AP-1, as well as MLCK. WNK: With no lysine kinase 1/4; TRIL: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; RELT: Receptor expressed in lymphoid tissues; MLCK: Myosin II regulatory light chain kinase; NKCC1: Sodium potassium chloride chloride transporter 1; KCC: Potassium chloride chloride transporter; AP-1: Activating protein 1.
- Citation: Yan Y, Merlin D. Ste20-related proline/alanine-rich kinase: A novel regulator of intestinal inflammation. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(40): 6115-6121
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i40/6115.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.6115