Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2008; 14(4): 647-650
Published online Jan 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.647
Published online Jan 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.647
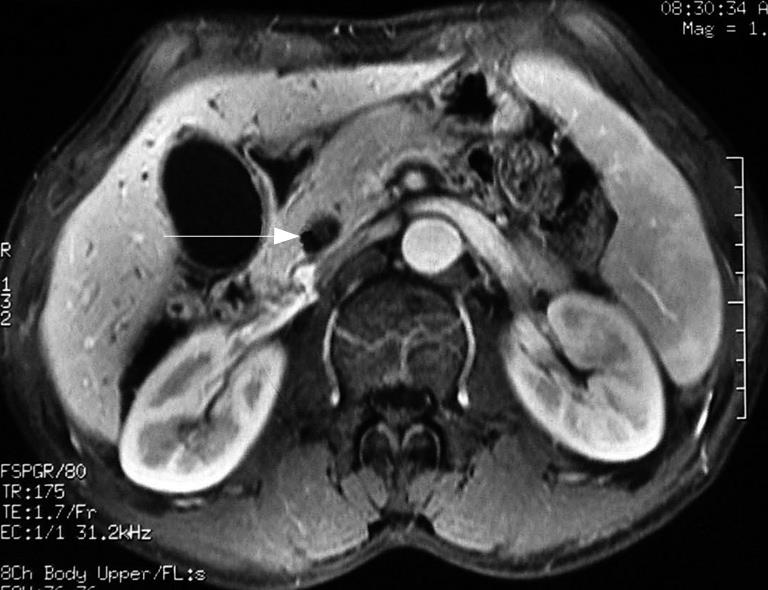
Figure 1 Contrast-enhanced MRI showing distension of gallbladder, dilatation of the intra and extrahepatic bile duct and eccentric stricture of the distal bile duct, and a mass (arrow) at the lumen of the duct.
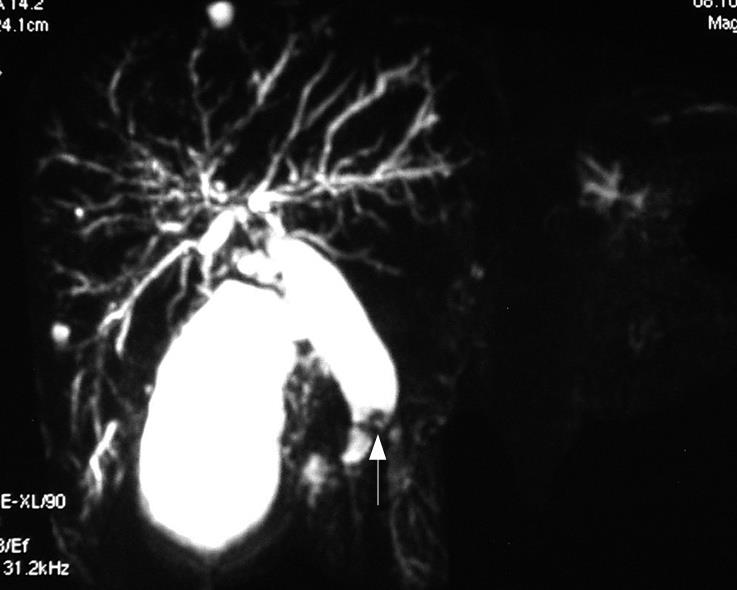
Figure 2 MRCP showing irregular stricture of the distal bile duct and a mass (arrow) at the lumen of the common bile duct.
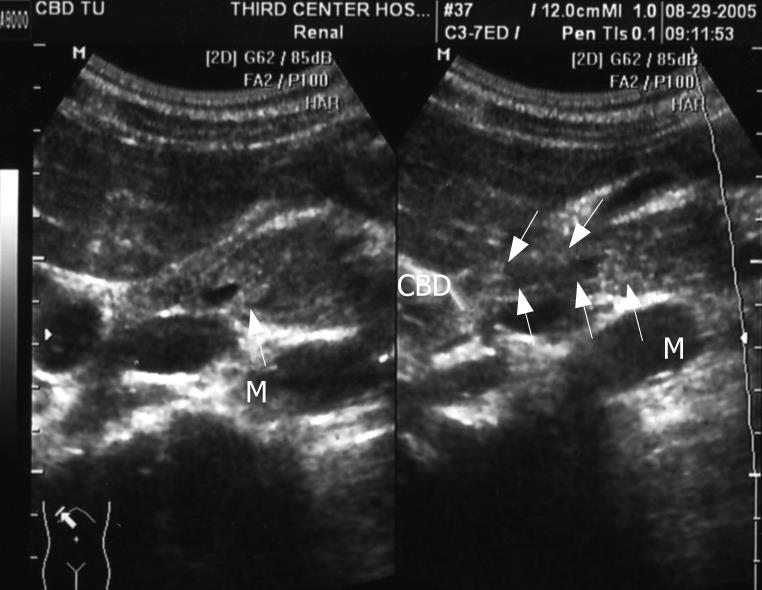
Figure 3 Ultrasonography showing a mass at the lumen of the common bile duct.
M: Mass; CBD: Common bile duct.
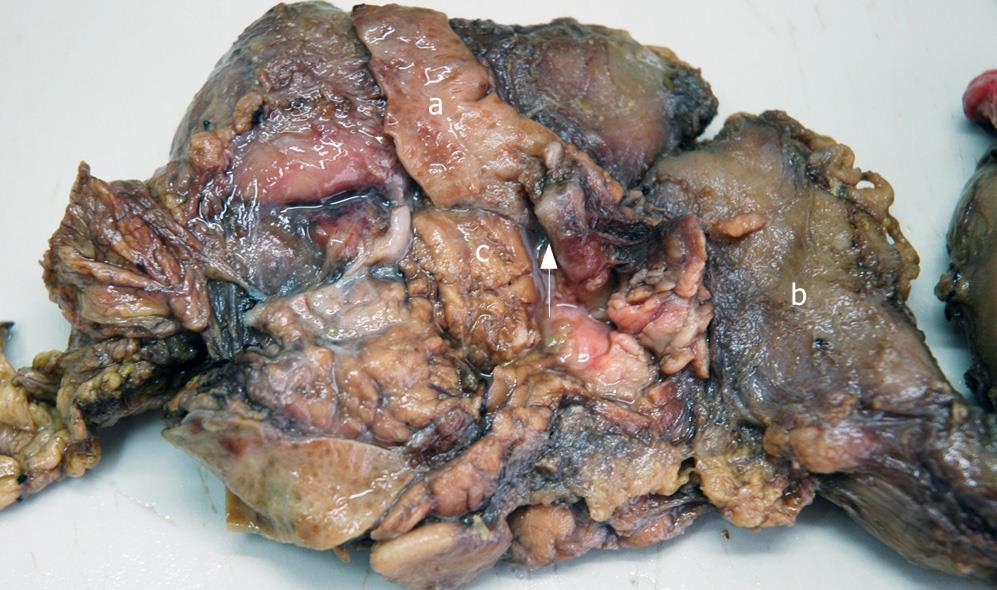
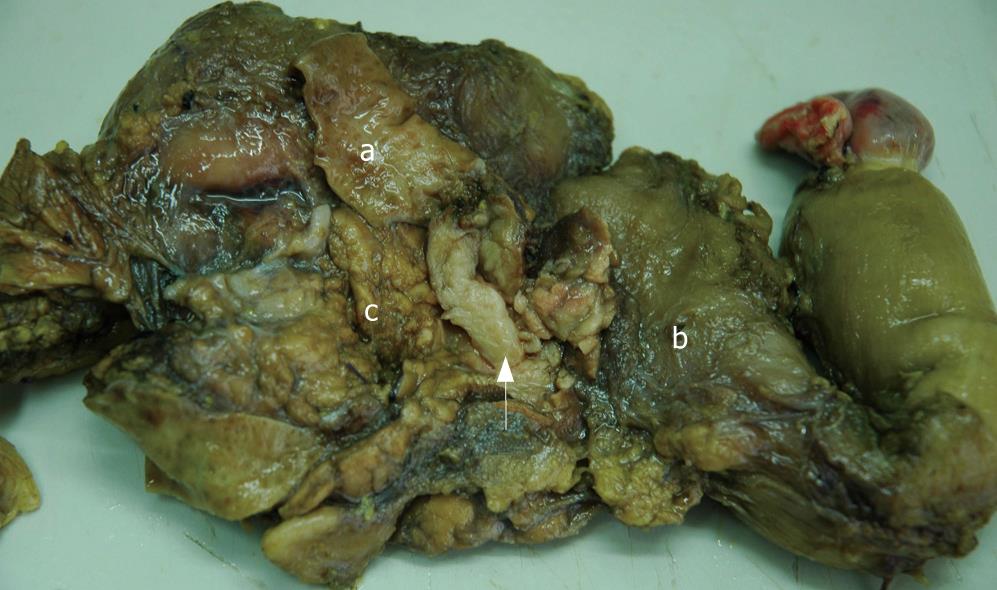
Figure 4 Gross examination showing a cord-like mass with smooth surface (arrow) and dilatation of proximal part of the common bile duct (a), duodenum (b) and pancreas (c).
Figure 5 Gross examination of the mass: white color in resecting surface, wide and immovable base (arrow).
a: Dilatation of proximal part of the common bile duct; b: Duodenum; c: Pancreas.
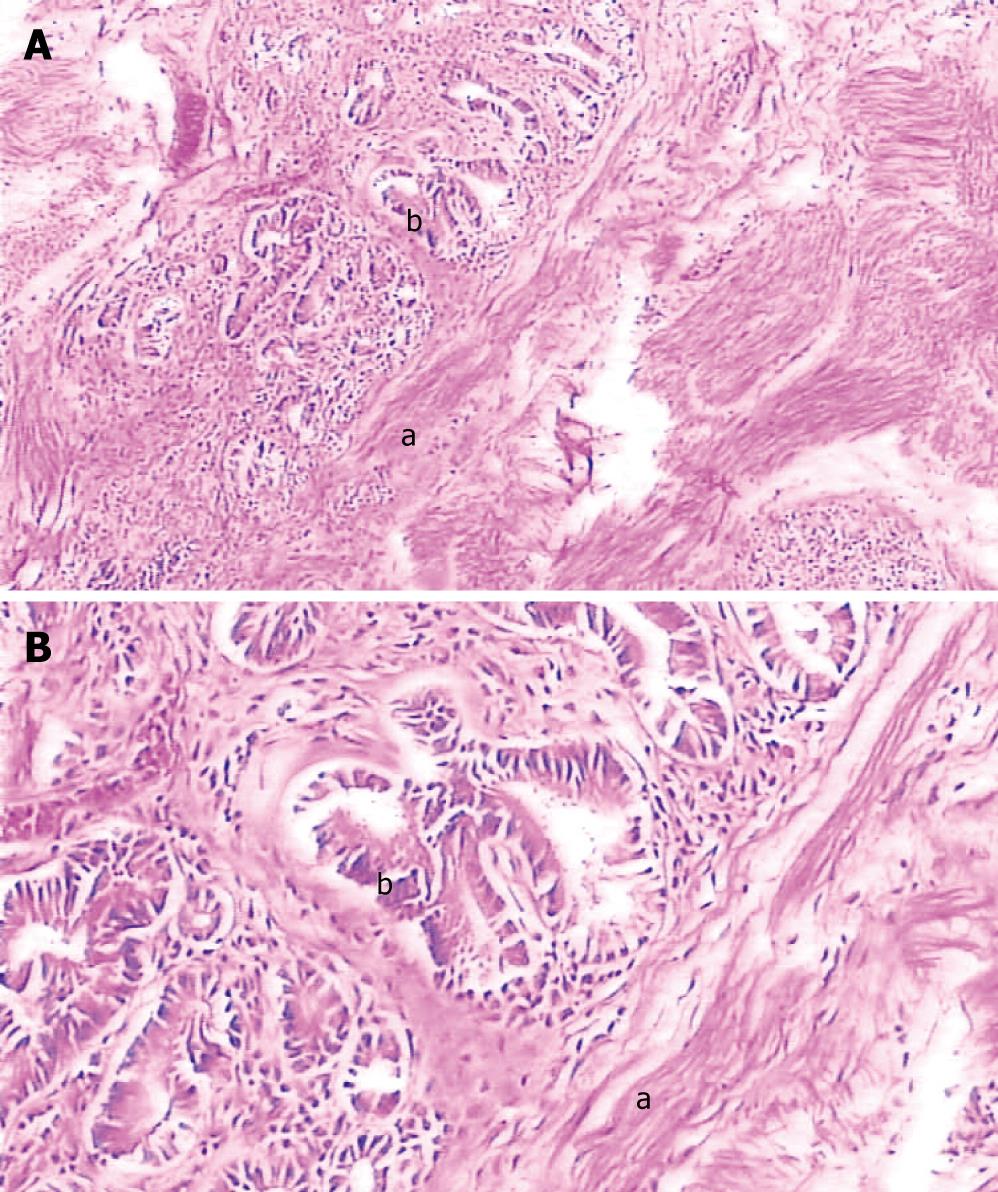
Figure 6 Pathological examination demonstrating the tumor epithelium is adenomyomatosis with adenoid (b) and myofibrous tissues (a) and moderate atypia (b).
A: HE, × 100; B: HE, × 400.
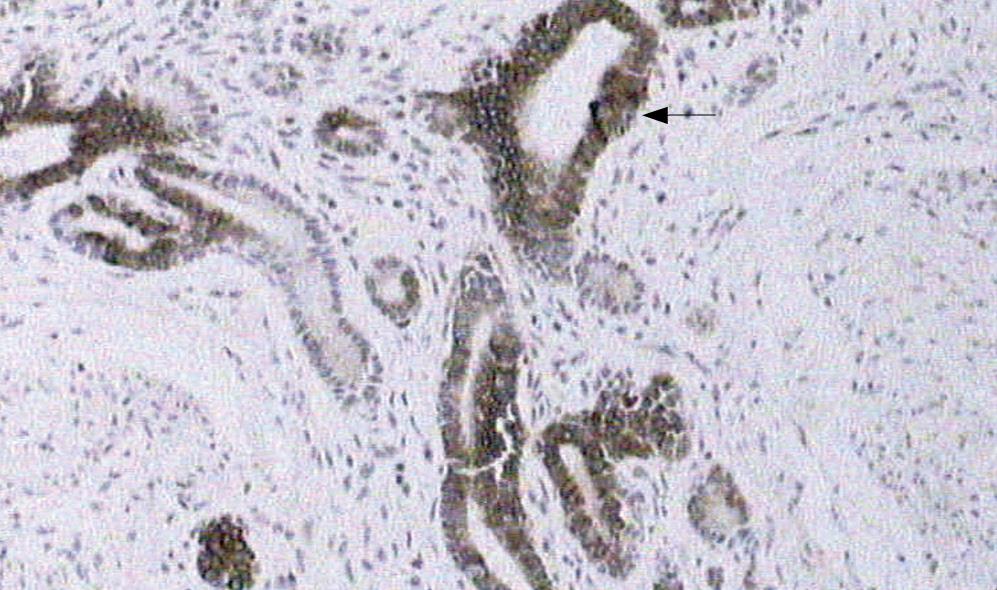
Figure 7 Immunohistochemical features demonstrated that cytokeratin 7 was strongly expressed in the epithelial cells of glandular structures (arrow).
- Citation: Shu GM, Wang YJ, Du Z, Li DY, Liu CL. Bile tract adenomyoma: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(4): 647-650
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i4/647.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.647