Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2008; 14(38): 5893-5899
Published online Oct 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5893
Published online Oct 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5893
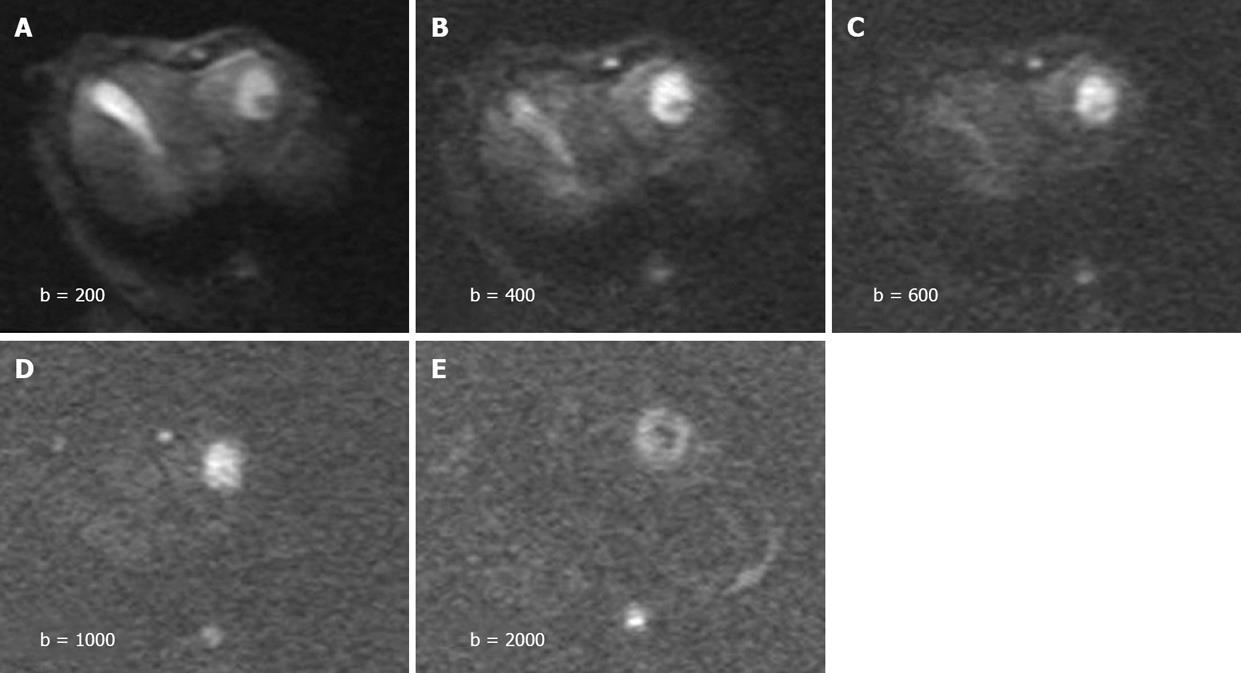
Figure 1 Diffusion-weighted images obtained with different b-values.
A and B: High signal intensity in tumors and hyperintense gallbladder on b200 and b400 DWI; C-E: Hyperintensive tumors and invisible gallbladder on b600, b1000 and b2000 DWI. The image qualities degrade with increasing b values.
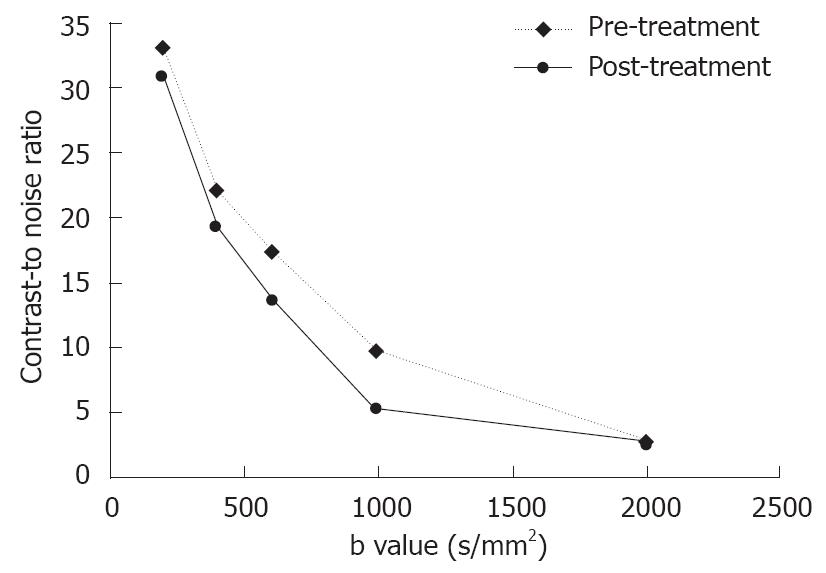
Figure 2 Contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) of the diffusion-weighted images vs different sets of b-values of hepatic tumors pre- and post-treatment.
CNR decreases with increasing b values after TACE, especially at b1000 on DWI.
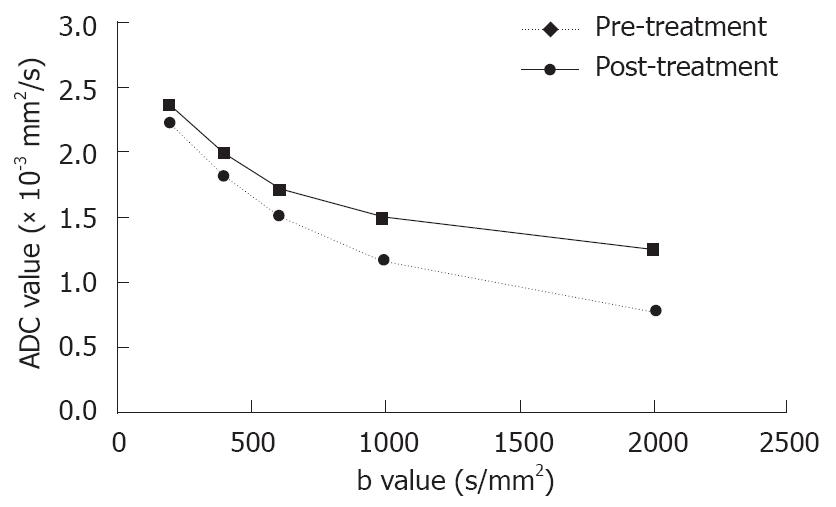
Figure 3 Plots of averaged ADC values for all 12 tumors vs different sets of b-values of hepatic tumors pre- and post-treatment.
ADC values present as a function of b factors. The early effect of therapy on diffusion is shown by a substantial increase in ADCs, especially at a large b factor (≥ 600 s/mm2).
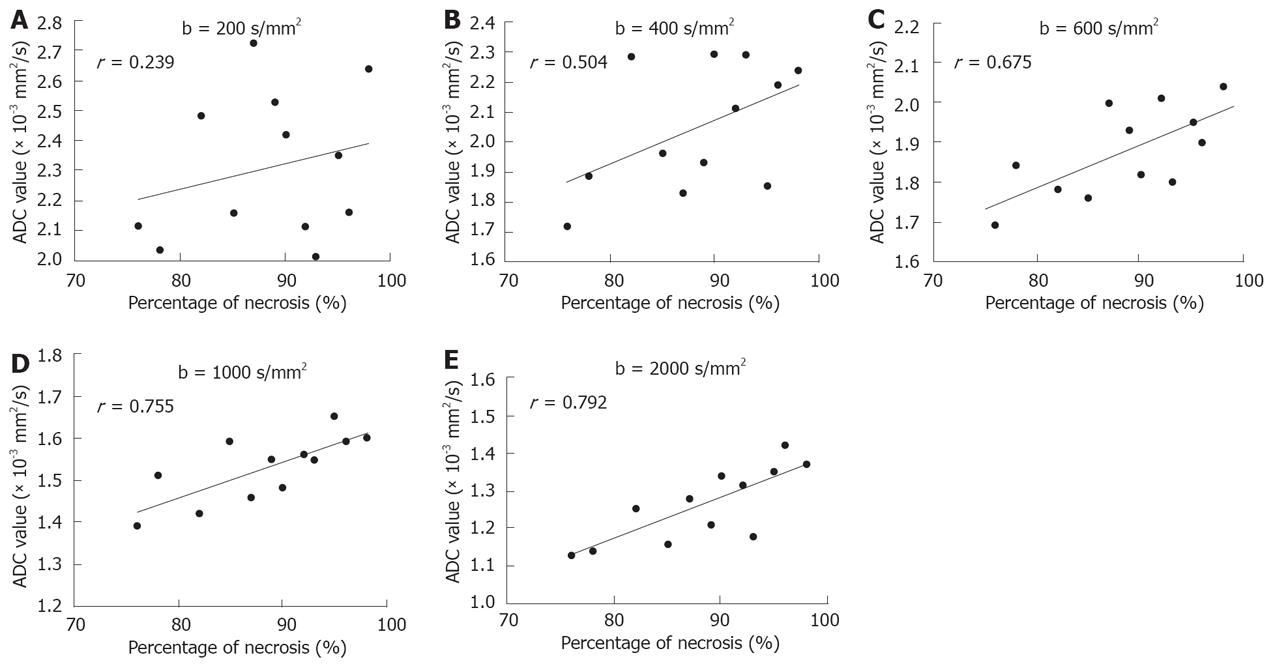
Figure 4 Plots of post-treatment ADC values as a percentage of necrosis measured on the sections of tumors.
The r values of 0.239, 0.504, and 0.675 found at b200, b400 and b600 (A-C), and a higher r value at b1000 and b2000 are found on DWI (D and E).
- Citation: Jiang ZX, Peng WJ, Li WT, Tang F, Liu SY, Qu XD, Wang JH, Lu HF. Effect of b value on monitoring therapeutic response by diffusion-weighted imaging. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(38): 5893-5899
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i38/5893.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.5893