Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2008; 14(37): 5674-5682
Published online Oct 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5674
Published online Oct 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5674
Figure 1 Phylogenetic tree constructed on the complete genome (A) and S gene (B) [Mother: 602 (1 d), 6022 (6 mo); Son: 602 (S)].
Bootstrap values are shown at the beginning of each main node. The length of the horizontal bar indicates the number of nucleotide substitutions per site. The origin of each strain has also been shown.
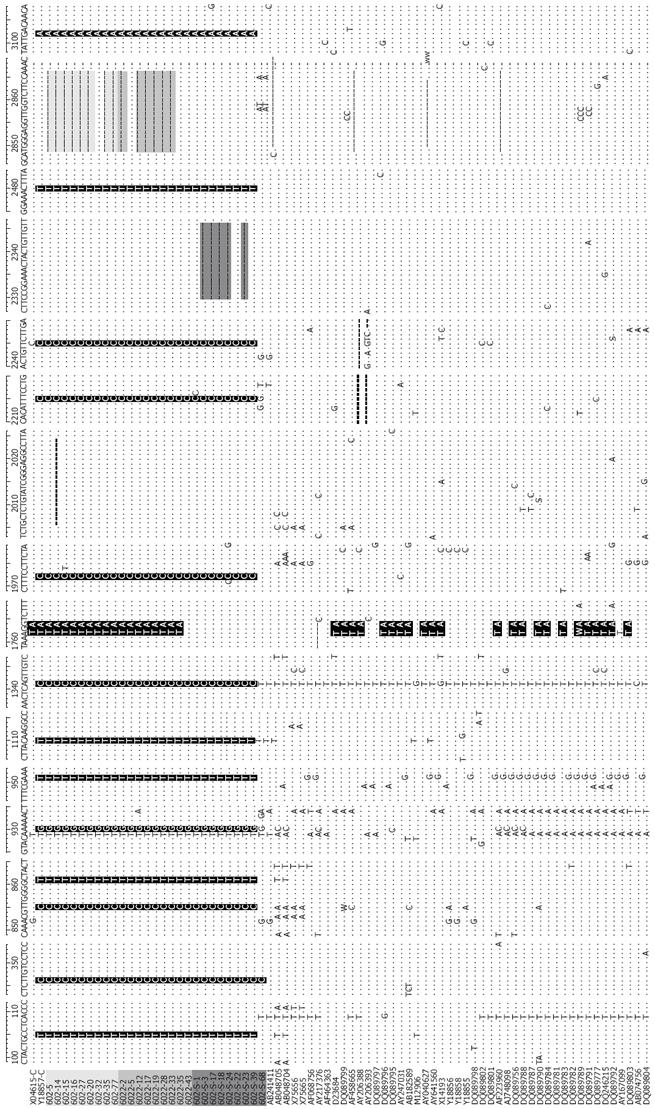
Figure 2 Nucleotide sequences of the 27 HBV/C isolates and 50 other complete genome sequences of genotype C [light gray, Mother: 602 (1 d); Gray, 6022 (6 mo); Dark gray, Son: 602-S; Sequences: Gray (deletion), black (substitution of nucleotides)].
Compared with the 50 complete genome sequences of genotype C, nucleotide positions at 105T, 346C, 855C,861T, 930G, 951T, 1110T, 1341C, 1972C, 2215C, 2246C,2480T and 3102A were specific for the 27 samples. 14 clones of the mother had an 18bp deletion from start codon; 5 clones of the son had a 17nt deletion from nt2330; 1762T/1764A double mutations were found in all clones of the mother, but none in the sequenced clones of the son. Nucleotides A1762A and G1764A double mutation comprised 54.5% of the total genotype C (42/77).
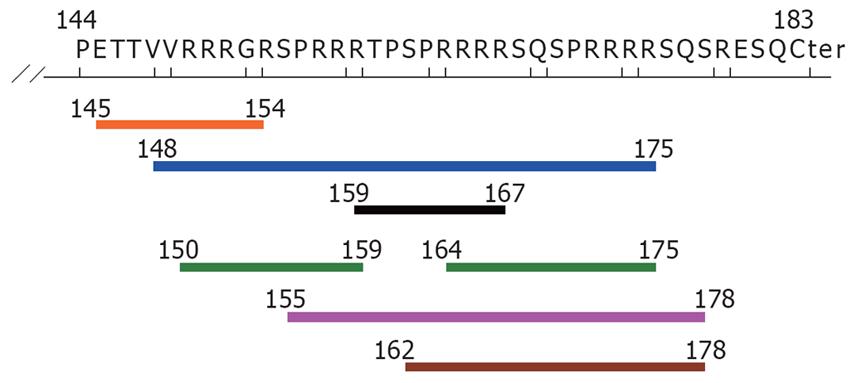
Figure 3 Potential HLA class I epitopes of the deletion fragment in HBcAg (aa residue144-183), determined by the SMM method [only IC50 (nM) < 50].
Blue line: HLA A*3101 (aa 148-175); Black line: HLA A*3201(aa 159-167); Orange line: HLA A*6801 (aa 145-154); Pink line: HLA B*0702 (aa 155-178); Brown line: HLA B*0801 (aa 162-178); Green line: HLA B*2705 (aa 150-159, 164-175).
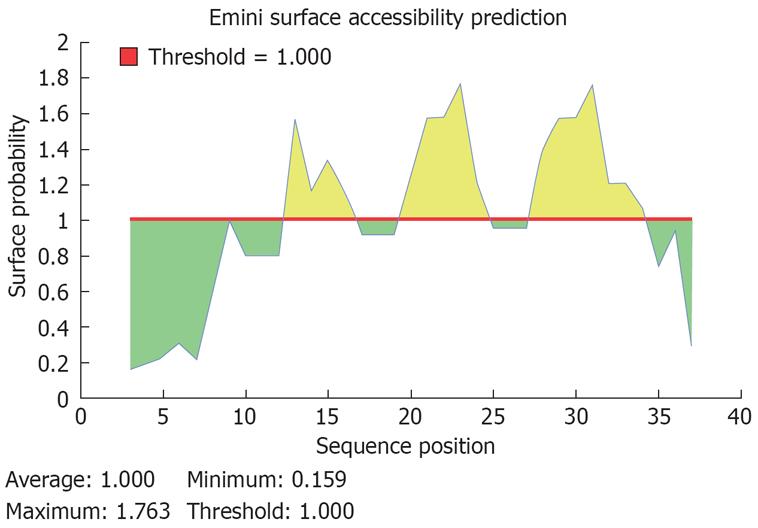
Figure 4 Predicted peptides of the potential B cell epitope of the deleted fragment in HBcAg (aa residue 144-183).
A potential sequence of B cell epotide in aa residue 144-183 of HBcAg was PRRRRSQ, start position at aa 171, end position at aa 177.
-
Citation: Shen T, Yan XM, Zou YL, Gao JM, Dong H. Virologic characteristics of hepatitis B virus in patients infected
via maternal-fetal transmission. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(37): 5674-5682 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i37/5674.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.5674