Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2008; 14(33): 5197-5203
Published online Sep 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5197
Published online Sep 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5197
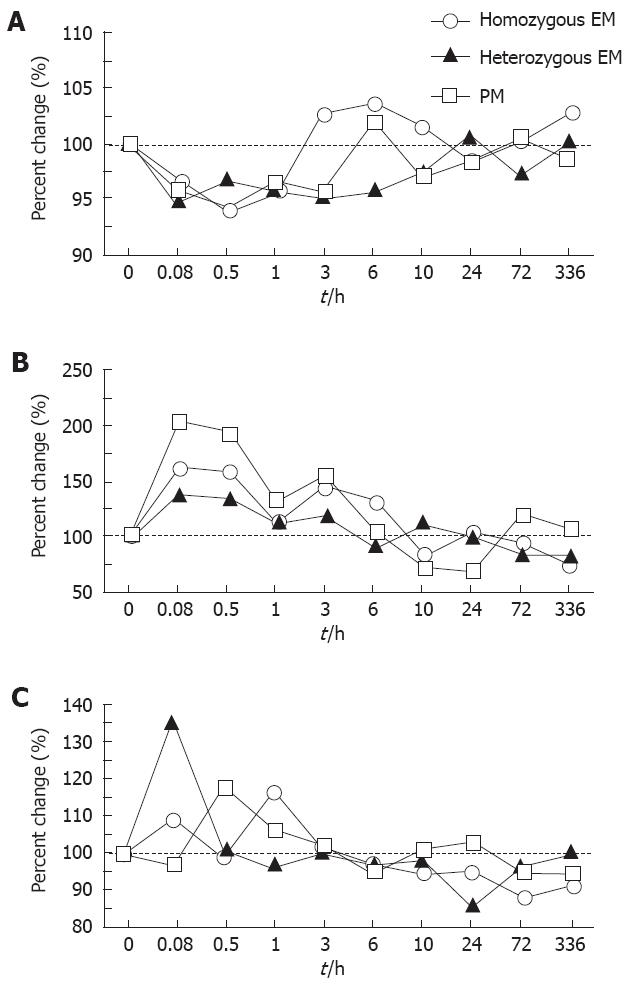
Figure 1 Median percent changes from the baseline value (before a diazepam 5 mg infusion) by a critical flicker fusion test (A), a postural sway test (B), and an eye movement test (C) in the 3 different CYP2C19 genotype groups.
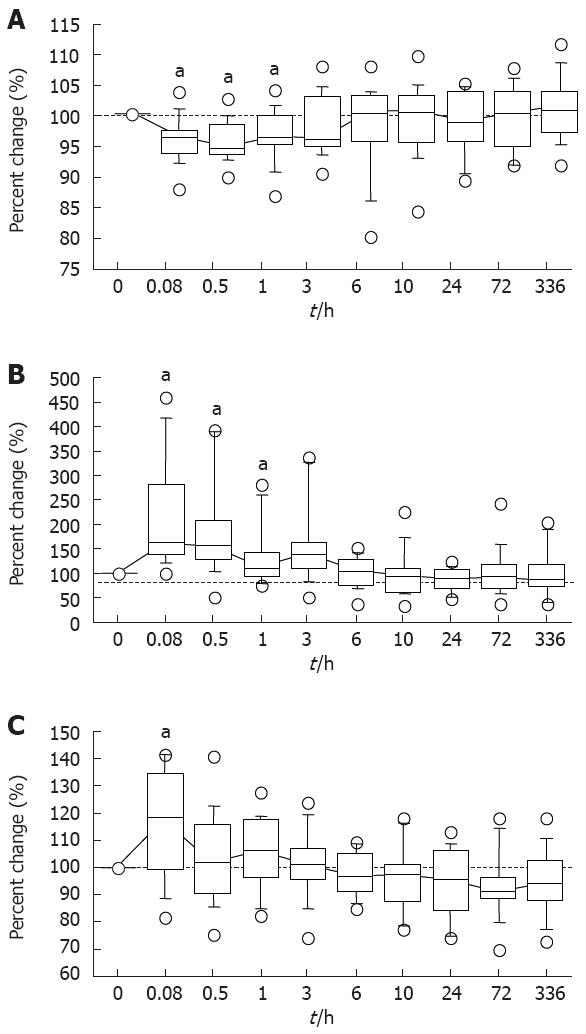
Figure 2 Median percent changes from the baseline value [before a diazepam (5-mg) infusion] by a critical flicker fusion test (A), a postural sway test (B), and an eye movement test (C) in all of the enrolled subjects.
aP < 0.05 by using the Wilcoxon’s signed rank test, when significant differences were obtained by the Friedmann’s test.
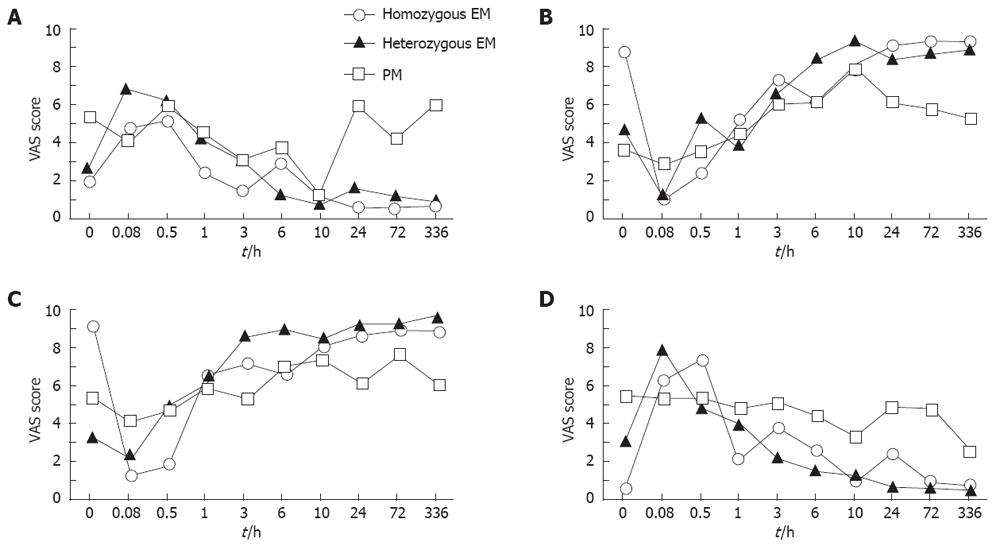
Figure 3 Median percent values for mental sedation, “alert to drowsy” (A), “fuzzy to clear-headed” (B), physical sedation, “lethargic to energetic” (C) and “well-coordinated to clumsy” (D) parameters by a VAS symptom assessment test in the 3 different CYP2C19 genotype groups.
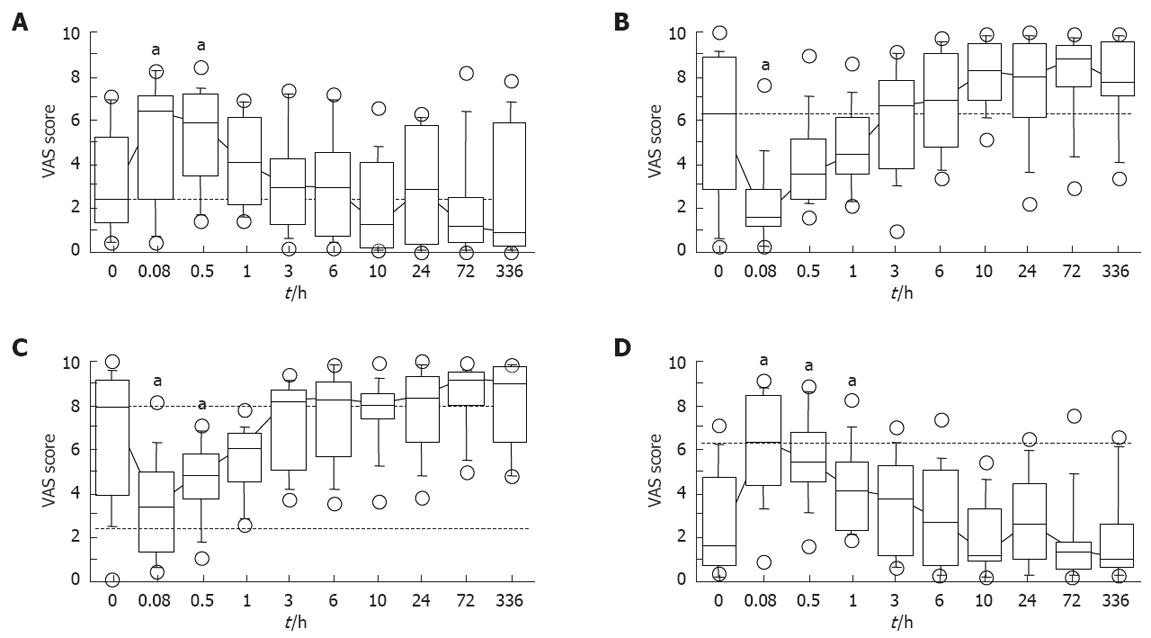
Figure 4 Median percent values for mental sedation “alert to drowsy” (A), “muzzy to clear-headed” (B), physical sedation “lethargic to energetic” (C) and “well-coordinated to clumsy” (D) parameters by a VAS symptom assessment test in all of the enrolled subjects.
aP < 0.05 by using the Wilcoxon’s signed rank test, when significant differences were obtained by the Friedmann’s test.
- Citation: Sugimoto M, Furuta T, Nakamura A, Shirai N, Ikuma M, Misaka S, Uchida S, Watanabe H, Ohashi K, Ishizaki T, Hishida A. Maintenance time of sedative effects after an intravenous infusion of diazepam: A guide for endoscopy using diazepam. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(33): 5197-5203
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i33/5197.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.5197