Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2008; 14(32): 5059-5065
Published online Aug 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5059
Published online Aug 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5059
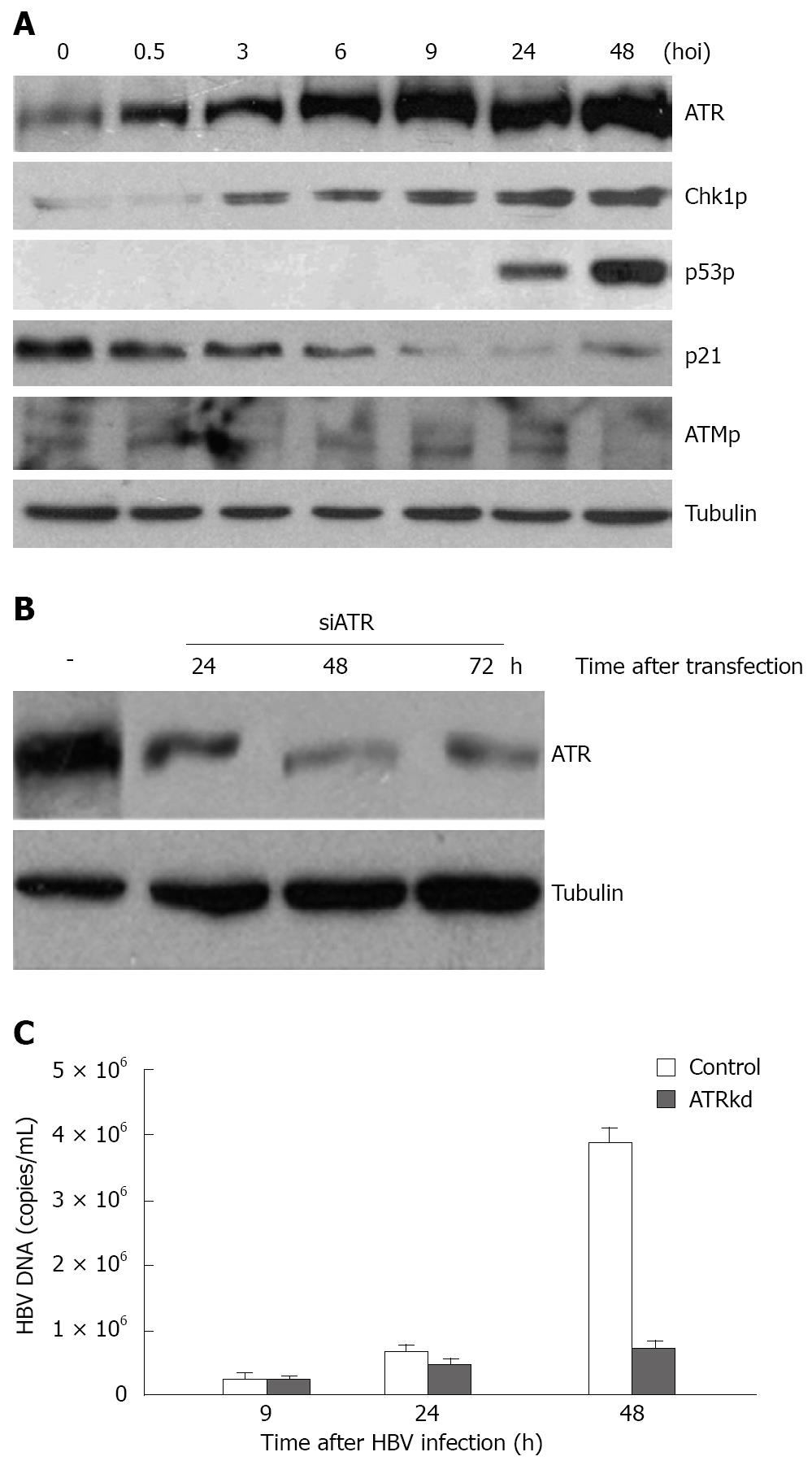
Figure 1 An ATR-dependent cellular checkpoint response activated by HBV infection.
A: 105 human HL7702 monolayer liver cells in a 6 cm plate were infected with 106 virus particles from HBV-positive patients at 37°C in an atmosphere containing 50 mL/L CO2. Normal serum from healthy individuals was used as non-infected control. Prior to cell harvesting, the cells were washed 8 times thoroughly to remove the excessive viral input. Whole cell lysates were prepared at various time points of infection (hours of infection, hoi) and subjected to immunoblotting assay using antibodies to the indicated proteins. Alpha-tubulin was used as the equal loading control; B: Specialized siRNA for ATR was transfected in HL7702 cells using lipofectamine 2000. At the indicated time points, cells were collected for Western blotting testing the ATR level; C: HBV-positive serum was added to ATR knockdown cells 24 h after transfection, cells were then harvested for FQ-PCR to test HBV DNA titers at the indicated time points post-infection.
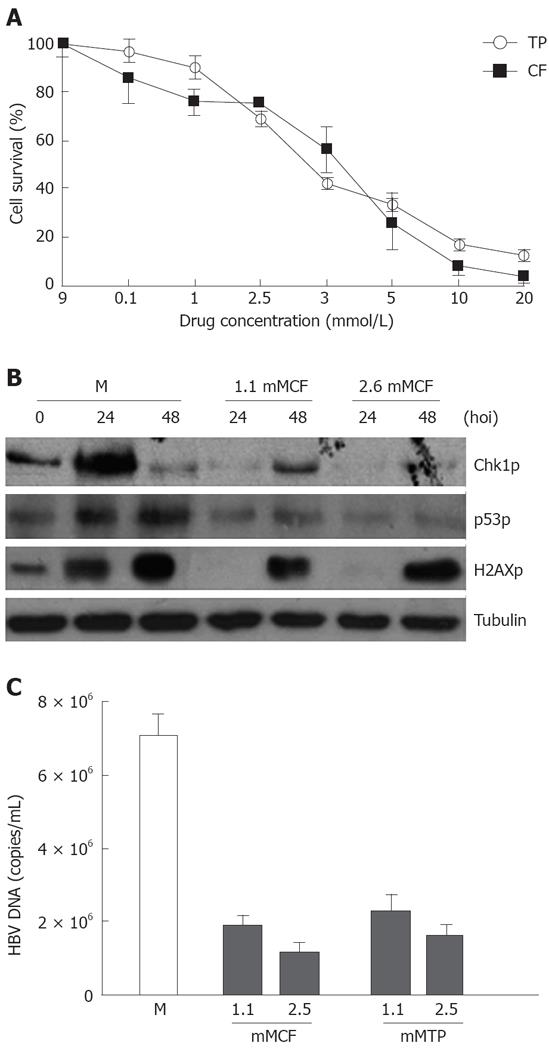
Figure 2 HBV infection and replication suppressed by CF and TP.
A: Cells were treated with CF or TP at different concentrations for 48 h, and survived cells were counted with trypan blue staining; B: Results of whole cell lysis, Western blotting of infected cells (M) or addition of CF-treated cells (1.1 mol/L CF, 2.5 mmol/L CF) and antibodies at the indicated time points; C: FQ-PCR analysis of HBV DNA from the infected cells (M) or addition of both HBV and CF (mMCF) or TP (mMTP).
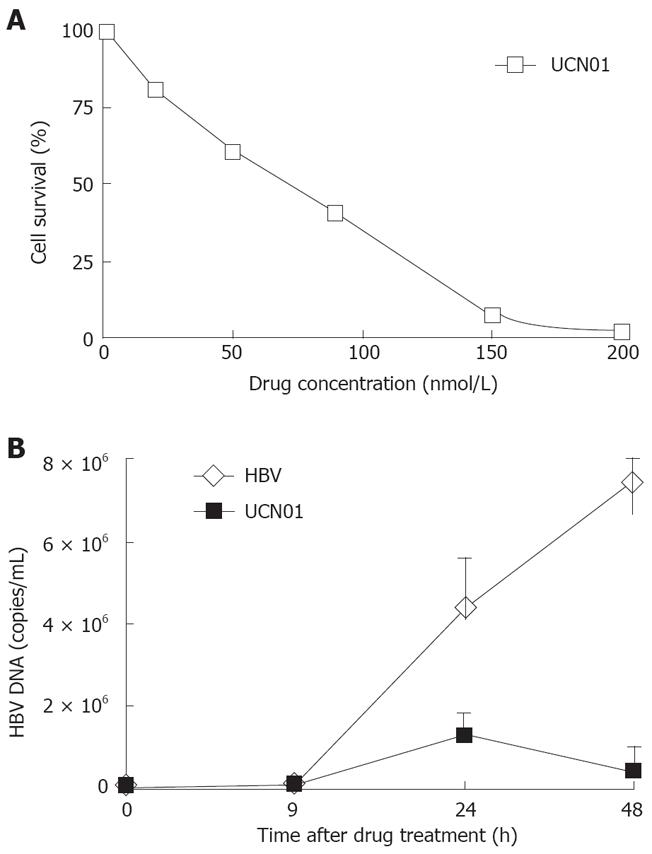
Figure 3 HBV infection and replication suppressed by CF and TP.
A: HL7702 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of UCN01, and survived cells were counted 48 h post-treatment with trypan blue staining; B: FQ-PCR analysis of HBV DNA from the infected cells (HBV) or addition of both HBV and UCN01 (UCN01) at the indicated time points.
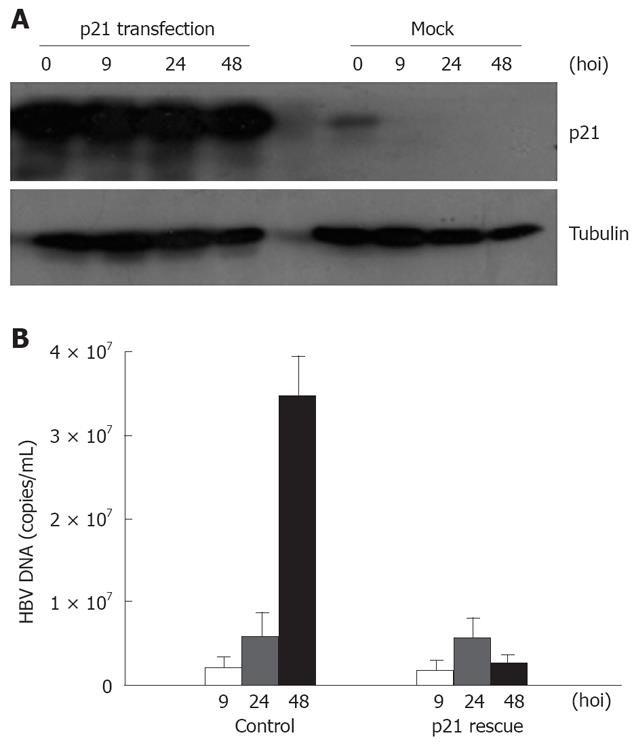
Figure 4 HBV infection and replication suppressed by introduction of p21.
A: Result of whole cell lysis, Western blotting of p21- transfected cells and control cells (Mock) at the indicated time points; B: FQ-PCR analysis of HBV DNA from the infected cells (control) or both HBV and p21- transfected cells (p21 rescue) at the indicated time points.
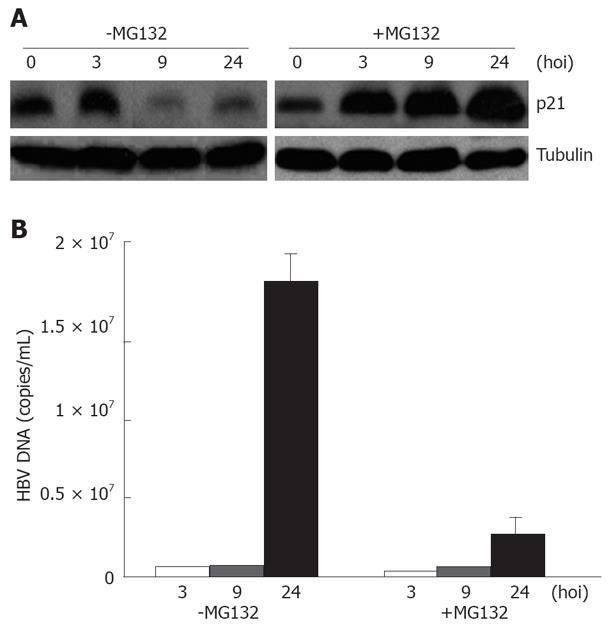
Figure 5 HBV replication inhibited by MG132.
A: Result of whole cell lysis, Western blotting of MG132- treated cells (+MG132) and control cells (-MG132) at the indicated time points; B: FQ-PCR analysis of HBV DNA from the infected cells (-MG132) or both HBV and MG132-treated cells (+MG132) at the indicated time points.
- Citation: Zhao F, Hou NB, Song T, He X, Zheng ZR, Ma QJ, Li L, Zhang YH, Zhong H. Cellular DNA repair cofactors affecting hepatitis B virus infection and replication. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(32): 5059-5065
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i32/5059.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.5059