Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2008; 14(32): 5051-5058
Published online Aug 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5051
Published online Aug 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5051
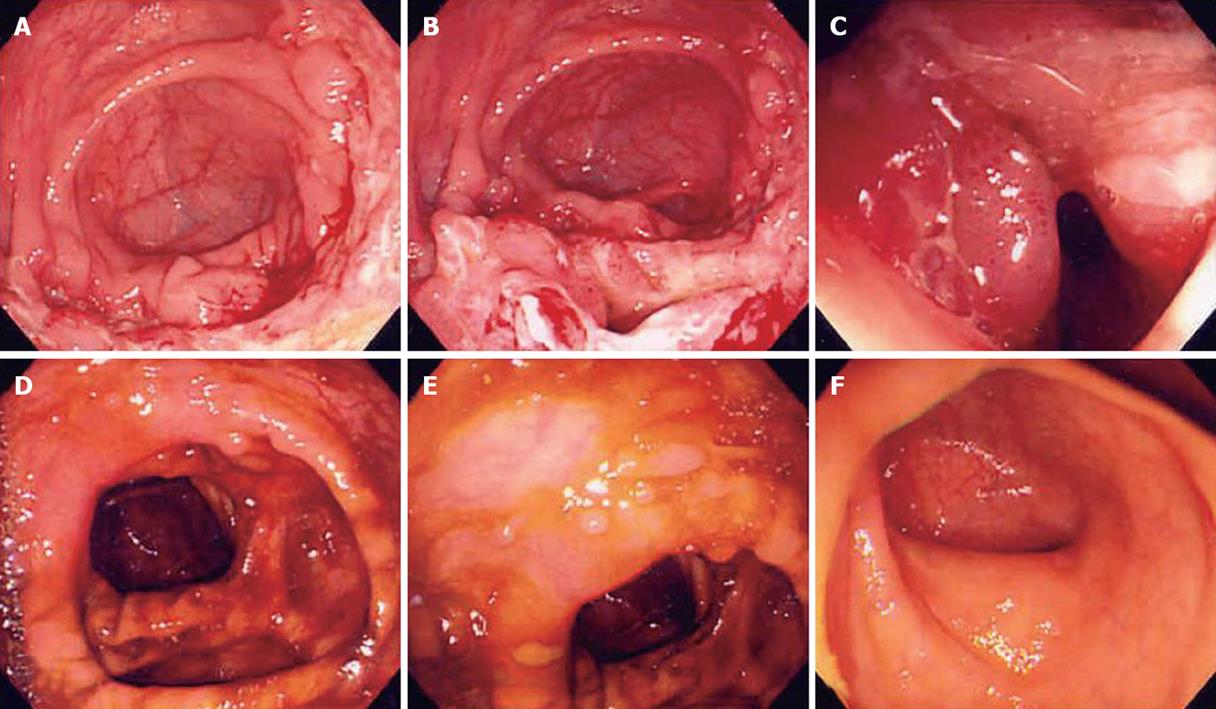
Figure 1 Colonoscopy findings before (A-C) and after (D-F) anti-tuberculosis medication in a 30-year-old male patient with tuberculous colitis on the ileocecal valve which shows acid-fast bacilli on biopsy.
After medication, scar and inflammatory polyps were noted.
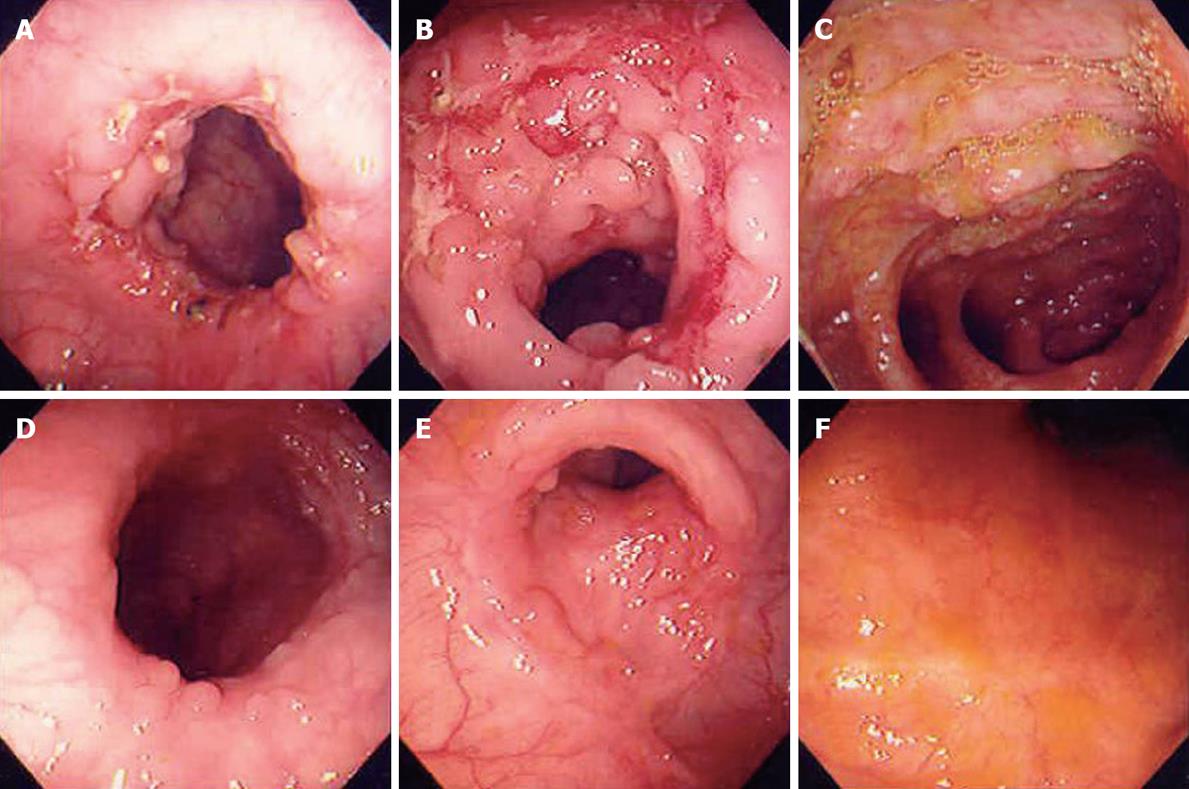
Figure 2 Colonoscopy findings before (A-C) and after (D-F) anti-tuberculosis treatment in a 37-year-old female patient.
It showed transverse arrayed geographic ulcers on ileocecal valve with granuloma on biopsy and presented nodularity on terminal ileum. After medication, only healing stage ulcers were left. We classified this case as “suspicious tuberculous colitis group”.
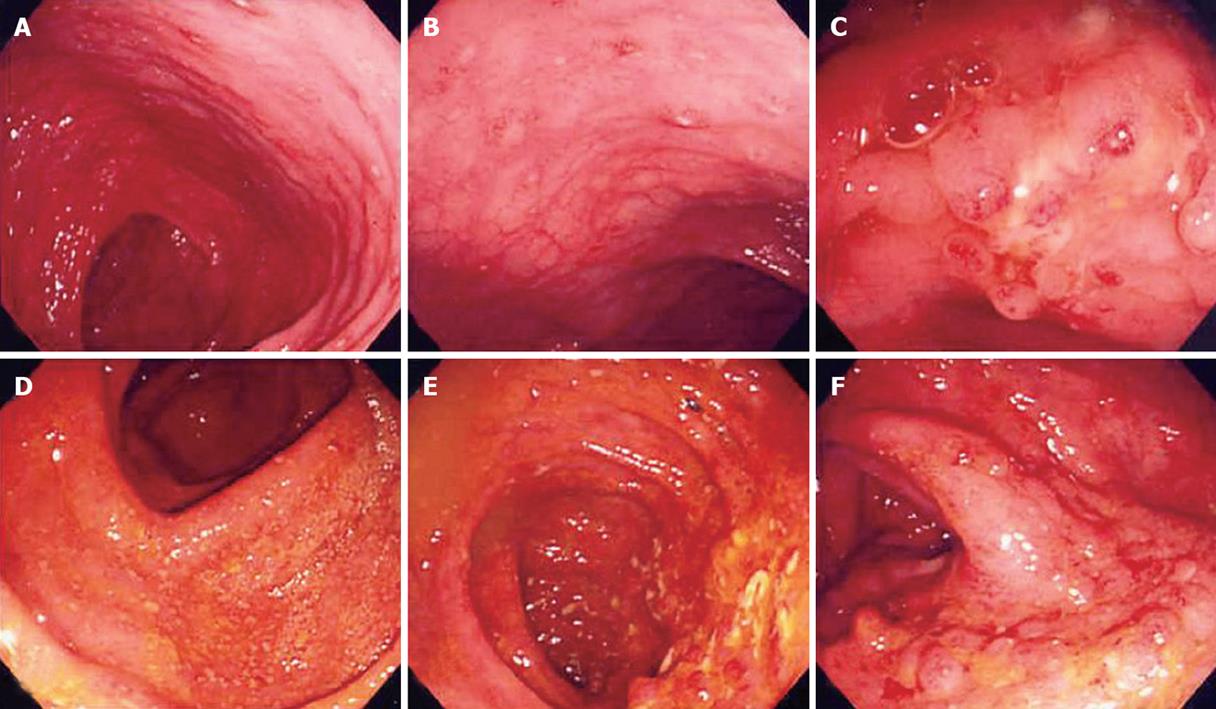
Figure 3 Colonoscopy findings before (A-C) and after (D-F) anti-tuberculosis treatment in a 23-year-old male patient with aphthous ulcers on the proximal ascending colon.
After medication it shows aggravating active ulcers and extension of the lesion. We classified this case as the “suspicious IBD group”.
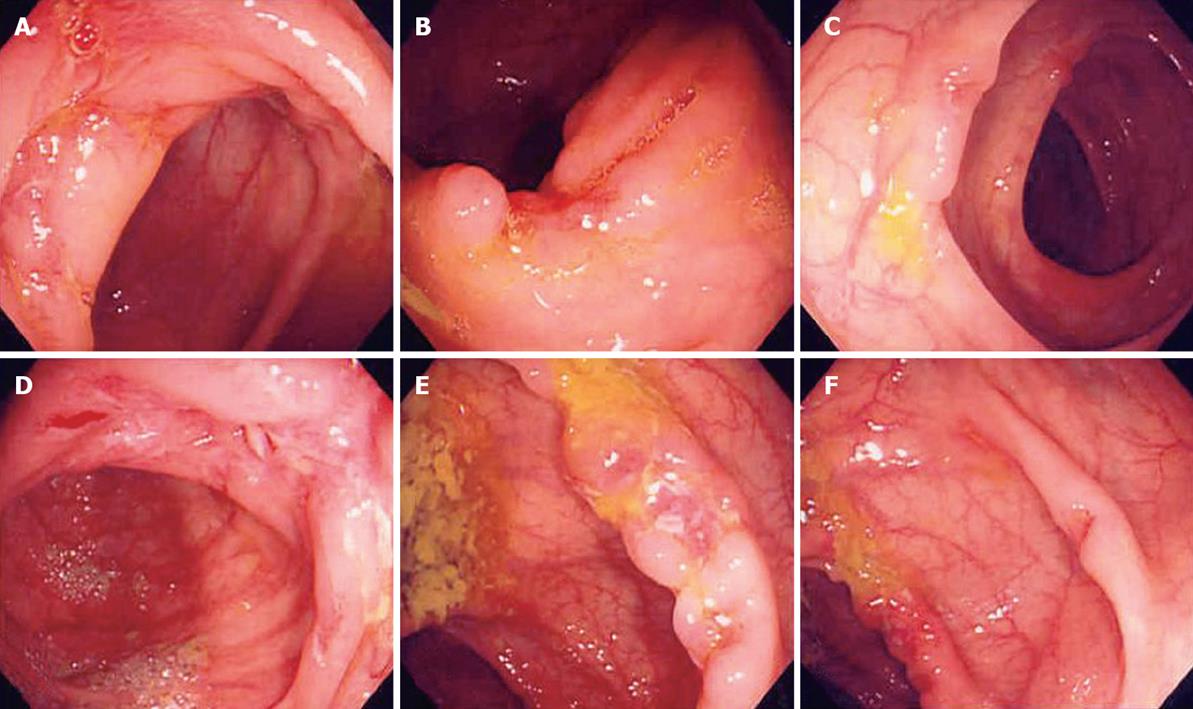
Figure 4 Colonoscopy findings before (A-C) and after (D-F) anti-tuberculosis medication in a 39-year-old female patient with irregular ulcers on the Ileocecal valve and proximal AC.
After medication, it showed active ulcers and extension. We classified this case as “suspicious IBD group” and performed mesalazine trial. The patient showed no response to all the medical trials, so we confirmed this case as the “nonspecific colonic ulcers” by surgery.
- Citation: Park YS, Jun DW, Kim SH, Lee HH, Jo YJ, Song MH, Kim NI, Lee JS. Colonoscopy evaluation after short-term anti-tuberculosis treatment in nonspecific ulcers on the ileocecal area. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(32): 5051-5058
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i32/5051.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.5051