Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2008; 14(25): 3948-3955
Published online Jul 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3948
Published online Jul 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3948
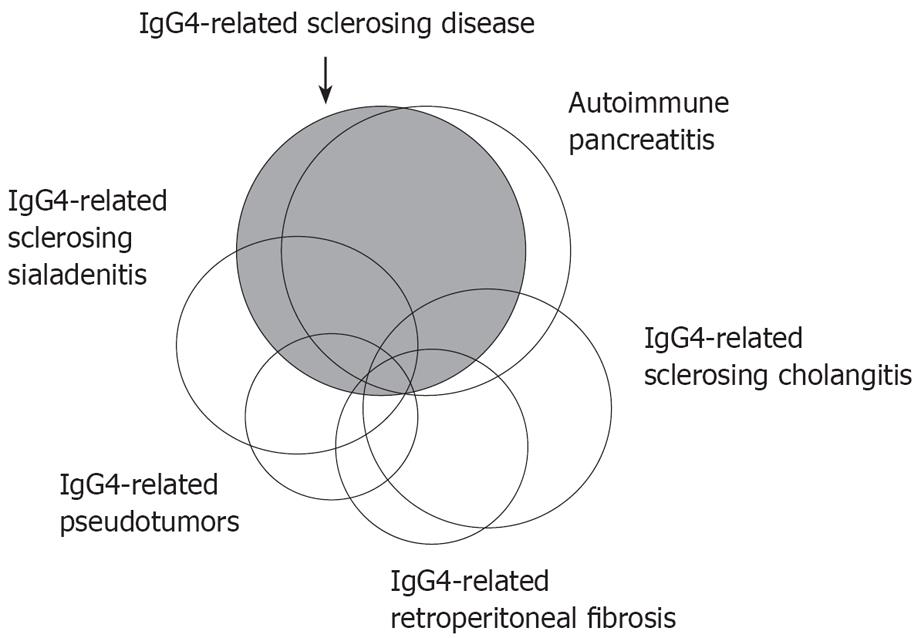
Figure 1 Schematic illustration showing the relationship between IgG4-related sclerosing disease, AIP, IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis, IgG4-related sclerosing sialadenitis, IgG4-related retroperitoneal fibrosis, and IgG4-related pseudotumors.
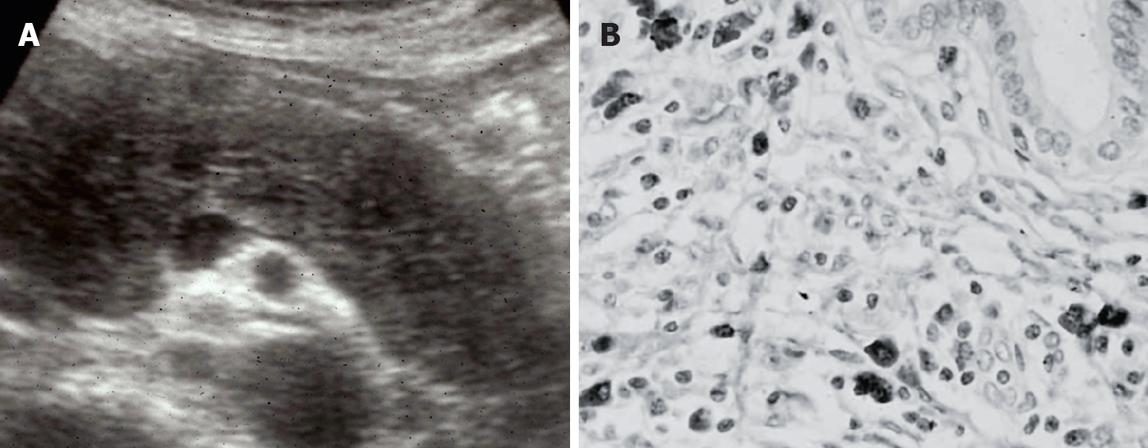
Figure 2 AIP.
(A) Diffuse hypoechoic enlargement of the pancreas on ultrasonography; (B) Dense infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells in the pancreas.
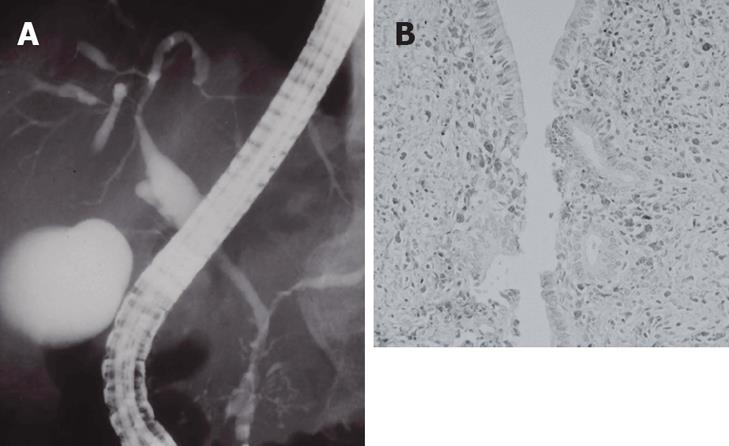
Figure 3 IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis.
(A) Stenosis of the intrahepatic bile duct, similar to that in PSC; (B) Dense infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells in the bile duct wall.
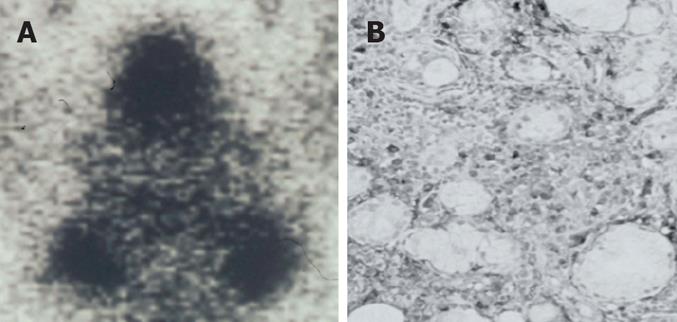
Figure 4 IgG4-related sclerosing sialadenitis.
(A) Bilateral swelling of submandibular glands (Gallium scintigraphy); (B) Dense infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells in the salivary gland.
- Citation: Kamisawa T, Okamoto A. IgG4-related sclerosing disease. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(25): 3948-3955
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i25/3948.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.3948